92nd United States Congress
| 92nd United States Congress | |
|---|---|
91st ← → 93rd | |
 United States Capitol (2002) | |
| January 3, 1971 – January 3, 1973 | |
| Senate President | Spiro Agnew (R) |
| Senate Pres. pro tem | Richard Russell (D) to January 21, 1971 Allen J. Ellender (D) January 22, 1971 – July 27, 1972 James Eastland (D) from July 28, 1972 |
| House Speaker | Carl Albert (D) |
| Members | 100 senators 435 representatives |
| Senate Majority | Democratic |
| House Majority | Democratic |
| Sessions | |
1st: January 21, 1971 – December 17, 1971 2nd: January 18, 1972 – October 18, 1972 | |
The Ninety-second United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, DC from January 3, 1971, to January 3, 1973, during the third and fourth years of Richard Nixon's presidency.
The apportionment of seats in this House of Representatives was based on the 1960 Census. Both chambers had a Democratic majority.
Contents
1 Major events
2 Major legislation
3 Constitutional amendments
4 Party summary
4.1 Senate
4.2 House of Representatives
5 Leadership
5.1 Senate
5.1.1 Majority (Democratic) leadership
5.1.2 Minority (Republican) leadership
5.2 House of Representatives
5.2.1 Majority (Democratic) leadership
5.2.2 Minority (Republican) leadership
6 Caucuses
7 Members
7.1 Senate
7.1.1 Alabama
7.1.2 Alaska
7.1.3 Arizona
7.1.4 Arkansas
7.1.5 California
7.1.6 Colorado
7.1.7 Connecticut
7.1.8 Delaware
7.1.9 Florida
7.1.10 Georgia
7.1.11 Hawaii
7.1.12 Idaho
7.1.13 Illinois
7.1.14 Indiana
7.1.15 Iowa
7.1.16 Kansas
7.1.17 Kentucky
7.1.18 Louisiana
7.1.19 Maine
7.1.20 Maryland
7.1.21 Massachusetts
7.1.22 Michigan
7.1.23 Minnesota
7.1.24 Mississippi
7.1.25 Missouri
7.1.26 Montana
7.1.27 Nebraska
7.1.28 Nevada
7.1.29 New Hampshire
7.1.30 New Jersey
7.1.31 New Mexico
7.1.32 New York
7.1.33 North Carolina
7.1.34 North Dakota
7.1.35 Ohio
7.1.36 Oklahoma
7.1.37 Oregon
7.1.38 Pennsylvania
7.1.39 Rhode Island
7.1.40 South Carolina
7.1.41 South Dakota
7.1.42 Tennessee
7.1.43 Texas
7.1.44 Utah
7.1.45 Vermont
7.1.46 Virginia
7.1.47 Washington
7.1.48 West Virginia
7.1.49 Wisconsin
7.1.50 Wyoming
7.2 House of Representatives
7.2.1 Alabama
7.2.2 Alaska
7.2.3 Arizona
7.2.4 Arkansas
7.2.5 California
7.2.6 Colorado
7.2.7 Connecticut
7.2.8 Delaware
7.2.9 Florida
7.2.10 Georgia
7.2.11 Hawaii
7.2.12 Idaho
7.2.13 Illinois
7.2.14 Indiana
7.2.15 Iowa
7.2.16 Kansas
7.2.17 Kentucky
7.2.18 Louisiana
7.2.19 Maine
7.2.20 Maryland
7.2.21 Massachusetts
7.2.22 Michigan
7.2.23 Minnesota
7.2.24 Mississippi
7.2.25 Missouri
7.2.26 Montana
7.2.27 Nebraska
7.2.28 Nevada
7.2.29 New Hampshire
7.2.30 New Jersey
7.2.31 New Mexico
7.2.32 New York
7.2.33 North Carolina
7.2.34 North Dakota
7.2.35 Ohio
7.2.36 Oklahoma
7.2.37 Oregon
7.2.38 Pennsylvania
7.2.39 Rhode Island
7.2.40 South Carolina
7.2.41 South Dakota
7.2.42 Tennessee
7.2.43 Texas
7.2.44 Utah
7.2.45 Vermont
7.2.46 Virginia
7.2.47 Washington
7.2.48 West Virginia
7.2.49 Wisconsin
7.2.50 Wyoming
7.2.51 Non-voting members
8 Changes in membership
8.1 Senate
8.2 House of Representatives
9 Committees
9.1 Senate
9.2 House of Representatives
9.3 Joint committees
10 Employees and legislative agency directors
10.1 Legislative branch agency directors
10.2 Senate
10.3 House of Representatives
11 Footnotes
12 See also
13 References
14 External links
Major events
Passing legislation on revenue-sharing was a key event of the congress. President Richard Nixon had it listed on his list of top policies to cover for the year. Nixon signed the bill into law at Independence Hall in Philadelphia. The law gained support from many state and local officials including: San Francisco Mayor Joseph Alioto whose city received $27 million in revenue-sharing money in the first year. Alito said that many projects that would not have been possible could now be done, "That will effectively enable us to meet those programs which up to now because of very tough budgeting we've had to trench."[1]
Major legislation
- December 18, 1971: Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act, Pub.L. 92–203, 85 Stat. 688
- December 23, 1971: National Cancer Act, Pub.L. 92–218, 85 Stat. 778
- February 7, 1972: Federal Election Campaign Act, Pub.L. 92–225, 86 Stat. 3
- March 24, 1972: Equal Employment Opportunity Act, Pub.L. 92–261, 86 Stat. 103
- June 23, 1972: Title IX Amendment of the Higher Education Act, Pub.L. 92–318, 86 Stat. 235
- October 6, 1972: Federal Advisory Committee Act, Pub.L. 92–463, 86 Stat. 770
- October 18, 1972: Federal Water Pollution Control Amendments of 1972, Pub.L. 92–500, 86 Stat. 816
- October 21, 1972: Marine Mammal Protection Act, Pub.L. 92–522, 86 Stat. 1027
- October 27, 1972: Consumer Product Safety Act, Pub.L. 92–573, 86 Stat. 1207
- October 27, 1972: Noise Control Act, Pub.L. 92–574, 86 Stat. 1234
- October 27, 1972: Coastal Zone Management Act, Pub.L. 92–583, 86 Stat. 1280
Constitutional amendments
- March 23, 1971: Approved an amendment to the United States Constitution prohibiting the states and the federal government from using age as a reason for denying the right to vote to citizens of the United States who are at least eighteen years old, and submitted it to the state legislatures for ratification
- July 1, 1971: The Twenty-sixth Amendment to the United States Constitution was ratified by the requisite number of states (38) to become part of the Constitution
- March 22, 1972: Approved an amendment to the Constitution designed to guarantee equal rights for women, and submitted it to the state legislatures for ratification
- This amendment, commonly known as the Equal Rights Amendment, was later rendered inoperative, as it was not ratified within the seven–year time frame set by Congress (nor the later time extension granted)
Party summary
The count below identifies party affiliations at the beginning of the first session of this Congress, and includes members from vacancies and newly admitted states, when they were first seated. Changes resulting from subsequent replacements are shown below in the Changes in membership section.
Senate
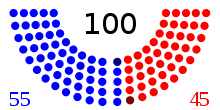
Party standings on the opening day of the 92nd Congress
54 Democratic Senators
1 Independent Senator, caucusing with Democrats
44 Republican Senators
1 Conservative Senator, caucusing with Republicans
Democratic: 54 (majority)
Republican: 44
Conservative: 1
Independent: 1
TOTAL members: 100
House of Representatives

| House seats by party holding plurality in state | |
|---|---|
80% Democratic | 80%+ Republican |
60%+ to 80% Democratic | 60%+ to 80% Republican |
up to 60% Democratic | up to 60% Republican |
Democratic: 255 (58.6%)(majority)
Republican: 180 (41.4%)
TOTAL members: 435
Leadership
Senate
President of the Senate: Spiro Agnew (R)
President pro tempore:
Richard Russell Jr. (D), until January 21, 1971
Allen J. Ellender (D), January 22, 1971 – July 27, 1972
James Eastland (D), from July 28, 1972
Permanent Acting President pro tempore: Lee Metcalf (D)
Majority (Democratic) leadership
Majority Leader: Mike Mansfield
Majority Whip: Robert Byrd
Caucus Secretary: Frank Moss
Minority (Republican) leadership
Minority Leader: Hugh Scott
Minority Whip: Robert P. Griffin
Republican Conference Chairman: Margaret Chase Smith
Republican Conference Secretary: Norris Cotton
National Senatorial Committee Chair: Peter H. Dominick
Policy Committee Chairman: Gordon L. Allott
House of Representatives
Speaker: Carl Albert (D)
Majority (Democratic) leadership
Majority Leader: Hale Boggs
Majority Whip: Tip O'Neill
Democratic Caucus Chairman: Olin E. Teague
Caucus Secretary: Leonor Sullivan
Minority (Republican) leadership
Minority Leader: Gerald Ford
Minority Whip: Leslie C. Arends
Conference Chair: John B. Anderson
Policy Committee Chairman: John Jacob Rhodes
Caucuses
- Congressional Black Caucus
- House Democratic Caucus
- Senate Democratic Caucus
Members
This list is arranged by chamber, then by state. Senators are listed in order of seniority, and Representatives are listed by district.
Senate
Senators are popularly elected statewide every two years, with one-third beginning new six-year terms with each Congress. Preceding the names in the list below are Senate class numbers, which indicate the cycle of their election. In this Congress, Class 1 meant their term began with this Congress, requiring reelection in 1976; Class 2 meant their term ended with this Congress, requiring reelection in 1972; and Class 3 meant their term began in the last Congress, requiring reelection in 1974.
|
|  Senate Majority Leader Mike Mansfield |
House of Representatives
The names of members of the House of Representatives are preceded by their district numbers.
|
|
Changes in membership
The count below reflects changes from the beginning of the first session of this Congress.
Senate
- replacements: 3
Democratic: no net change
Republican: no net change
- deaths: 3
- resignations:
- Total seats with changes: 3
| State (class) | Vacator | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Georgia (2) | Richard Russell Jr. (D) | Died January 21, 1971 | David H. Gambrell (D) | February 1, 1971 |
Vermont (1) | Winston L. Prouty (R) | Died September 10, 1971 | Robert Stafford (R) | September 16, 1971 |
Louisiana (2) | Allen J. Ellender (D) | Died July 27, 1972 | Elaine S. Edwards (D) | August 1, 1972 |
Georgia (2) | David H. Gambrell (D) | Successor elected November 7, 1972 | Sam Nunn (D) | November 7, 1972 |
Louisiana (2) | Elaine S. Edwards (D) | Successor elected November 13, 1972 | Bennett Johnston Jr. (D) | November 14, 1972 |
House of Representatives
- replacements: 10
Democratic: no net loss
Republican: no net gain
- deaths: 8
- resignations: 6
- Total seats with changes: 16
| District | Vacator | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
District of Columbia At-large | Vacant | District elected first delegate since the seat was re-established during previous congress | Walter E. Fauntroy (D) | March 23, 1971 |
South Carolina 1st | Vacant | Rep. L. Mendel Rivers died during previous congress | Mendel J. Davis (D) | April 27, 1971 |
Maryland 1st | Rogers Morton (R) | Resigned January 29, 1971, after being appointed United States Secretary of the Interior | William O. Mills (R) | May 25, 1971 |
Pennsylvania 18th | Robert J. Corbett (R) | Died April 25, 1971 | H. John Heinz III (R) | November 2, 1971 |
Vermont At-large | Robert Stafford (R) | Resigned after being appointed to the US Senate September 16, 1971 | Richard W. Mallary (R) | January 7, 1972 |
Kentucky 6th | John C. Watts (D) | Died September 24, 1971 | William P. Curlin Jr. (D) | December 4, 1971 |
Pennsylvania 27th | James G. Fulton (R) | Died October 6, 1971 | William S. Conover (R) | April 25, 1972 |
Illinois 15th | Charlotte T. Reid (R) | Resigned October 7, 1971, after being appointed to the Federal Communication Commission | Cliffard D. Carlson (R) | April 4, 1972 |
Alabama 3rd | George W. Andrews (D) | Died December 25, 1971 | Elizabeth B. Andrews (D) | April 4, 1972 |
Massachusetts 5th | Frank B. Morse (R) | Resigned May 1, 1972, after being appointed Undersecretary General for Political and General Assembly Affairs at the United Nations | Vacant | Not filled this congress |
Louisiana 7th | Edwin Edwards (D) | Resigned after being elected Governor of Louisiana May 9, 1972 | John Breaux (D) | September 30, 1972 |
Virginia 6th | Richard H. Poff (R) | Resigned after being appointed as a judge of the Supreme Court of Virginia | M. Caldwell Butler (R) | November 7, 1972 |
New York 20th | William Fitts Ryan (D) | Died September 17, 1972. | Vacant | Not filled this congress |
Ohio 16th | Frank T. Bow (R) | Died November 13, 1972. | Vacant | Not filled this congress |
Illinois 6th | George W. Collins (D) | Died in a plane crash December 8, 1972. | Vacant | Not filled this congress |
Alaska At-large | Nick Begich (D) | He and Hale Boggs were lost in a plane crash October 16, 1972. Presumptive death dertificate for Rep. Begich was issued December 29, 1972. | Vacant | Not filled this congress |
Committees
Lists of committees and their party leaders, for members (House and Senate) of the committees and their assignments, go into the Official Congressional Directory at the bottom of the article and click on the link (2 links), in the directory after the pages of terms of service, you will see the committees of the Senate, House (Standing with Subcommittees, Select and Special) and Joint and after the committee pages, you will see the House/Senate committee assignments in the directory, on the committees section of the House and Senate in the Official Congressional Directory, the committee's members on the first row on the left side shows the chairman of the committee and on the right side shows the ranking member of the committee.
Senate
- Aeronautical and Space Sciences
- Agriculture and Forestry
- Appropriations
- Commerce
- District of Columbia
Equal Educational Opportunity (Select)- Finance
- Foreign Relations
- Government Operations
- Interior and Insular Affairs
- Judiciary
- Labor and Public Welfare
Nutrition and Human Needs (Select)- Public Works
Secret and Confidential Government Documents (Special)
Small Business (Select)
Standards and Conduct (Select)- Subcommittee on Internal Security
- Whole
House of Representatives
- Agriculture
- Appropriations
- Banking and Currency
- District of Columbia
- Education and Labor
- Foreign Affairs
- Government Operations
- House Administration
- Interior and Insular Affairs
- Internal Security
- Merchant Marine and Fisheries
- Post Office and Civil Service
- Rules
- Science and Astronautics
Small Business (Select)- Standards of Official Conduct
- Transportation and Infrastructure
- Veterans' Affairs
- Ways and Means
- Whole
Joint committees
- Atomic Energy
- Congressional Operations
- Defense Production
- Economic
- The Library
- Navajo-Hopi Indian Administration
- Printing
- Reduction of Nonessential Federal Expenditures
- Taxation
Employees and legislative agency directors
Legislative branch agency directors
Architect of the Capitol: George M. White, appointed January 27, 1971
Attending Physician of the United States Congress: Rufus Pearson
Comptroller General of the United States: Elmer B. Staats
Librarian of Congress: Lawrence Quincy Mumford
Public Printer of the United States: Adolphus N. Spence (until 1972)
Senate
Chaplain: Edward L.R. Elson (Presbyterian), elected January 9, 1969
Secretary: Francis R. Valeo
Democratic Party Secretary: J. Stanley Kimmitt
Republican Party Secretary: J. Mark Trice
Sergeant at Arms:
Robert G. Dunphy of Rhode Island, until June 30, 1972 (resigned)
William H. Wannall of Maryland, elected July 1, 1972
House of Representatives
Clerk: W. Pat Jennings
Sergeant at Arms:
Zeake W. Johnson of Tennessee, January 21, 1971 – September 30, 1972 (resigned)
Kenneth R. Harding of New York, October 1, 1972 – September 30, 1972 (resigned)
Doorkeeper: William M. Miller
Postmaster: H. H. Morris, January 21, 1971 – June 30, 1972 (resigned)
Robert V. Rota, from July 1, 1972
Parliamentarian: Lewis Deschler
Reading Clerks:
- Joe Bartlett (until 1971) (R), Bob Berry (starting 1971) (R)
- N/A (D)
Chaplain: Edward G. Latch (Methodist), elected January 10, 1967
Footnotes
^ "1972 congress"
Martis, Kenneth C. (1989). The Historical Atlas of Political Parties in the United States Congress. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
Martis, Kenneth C. (1982). The Historical Atlas of United States Congressional Districts. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
See also
United States elections, 1970 (elections leading to this Congress)
- United States Senate elections, 1970
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1970
United States elections, 1972 (elections during this Congress, leading to the next Congress)
- United States presidential election, 1972
- United States Senate elections, 1972
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1972
References
- Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress
- U.S. House of Representatives: Congressional History
- U.S. Senate: Statistics and Lists
External links
House of Representatives Session Calendar for the 92nd Congress (PDF).
Congressional Pictorial Directory for the 92nd Congress.
Official Congressional Directory for the 92nd Congress, 1st Session.
Official Congressional Directory for the 92nd Congress, 2nd Session.