48th United States Congress
| 48th United States Congress | |
|---|---|
47th ← → 49th | |
 United States Capitol (1906) | |
| March 4, 1883 – March 4, 1885 | |
| Senate President | Vacant |
| Senate Pres. pro tem | George F. Edmunds (R) |
| House Speaker | John G. Carlisle (D) |
| Members | 76 senators 325 representatives 8 non-voting delegates |
| Senate Majority | Republican |
| House Majority | Democratic |
| Sessions | |
1st: December 3, 1883 – July 7, 1884 2nd: December 1, 1884 – March 3, 1885 | |
The Forty-Eighth United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1883, to March 4, 1885, during the last two years of the administration of U.S. President Chester A. Arthur. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Tenth Census of the United States in 1880. The Senate had a Republican majority, and the House had a Democratic majority.
Contents
1 Major events
2 Major legislation
3 Territories organized
4 Party summary
4.1 Senate
4.2 House of Representatives
5 Leadership
5.1 Senate
5.2 House of Representatives
6 Members
6.1 Senate
6.1.1 Alabama
6.1.2 Arkansas
6.1.3 California
6.1.4 Colorado
6.1.5 Connecticut
6.1.6 Delaware
6.1.7 Florida
6.1.8 Georgia
6.1.9 Illinois
6.1.10 Indiana
6.1.11 Iowa
6.1.12 Kansas
6.1.13 Kentucky
6.1.14 Louisiana
6.1.15 Maine
6.1.16 Maryland
6.1.17 Massachusetts
6.1.18 Michigan
6.1.19 Minnesota
6.1.20 Mississippi
6.1.21 Missouri
6.1.22 Nebraska
6.1.23 Nevada
6.1.24 New Hampshire
6.1.25 New Jersey
6.1.26 New York
6.1.27 North Carolina
6.1.28 Ohio
6.1.29 Oregon
6.1.30 Pennsylvania
6.1.31 Rhode Island
6.1.32 South Carolina
6.1.33 Tennessee
6.1.34 Texas
6.1.35 Vermont
6.1.36 Virginia
6.1.37 West Virginia
6.1.38 Wisconsin
6.2 House of Representatives
6.2.1 Alabama
6.2.2 Arkansas
6.2.3 California
6.2.4 Colorado
6.2.5 Connecticut
6.2.6 Delaware
6.2.7 Florida
6.2.8 Georgia
6.2.9 Illinois
6.2.10 Indiana
6.2.11 Iowa
6.2.12 Kansas
6.2.13 Kentucky
6.2.14 Louisiana
6.2.15 Maine
6.2.16 Maryland
6.2.17 Massachusetts
6.2.18 Michigan
6.2.19 Minnesota
6.2.20 Mississippi
6.2.21 Missouri
6.2.22 Nebraska
6.2.23 Nevada
6.2.24 New Hampshire
6.2.25 New Jersey
6.2.26 New York
6.2.27 North Carolina
6.2.28 Ohio
6.2.29 Oregon
6.2.30 Pennsylvania
6.2.31 Rhode Island
6.2.32 South Carolina
6.2.33 Tennessee
6.2.34 Texas
6.2.35 Vermont
6.2.36 Virginia
6.2.37 West Virginia
6.2.38 Wisconsin
6.2.39 Non-voting members
7 Changes in membership
7.1 Senate
7.2 House of Representatives
8 Committees
8.1 Senate
8.2 House of Representatives
8.3 Joint committees
9 Caucuses
10 Employees
10.1 Senate
10.2 House of Representatives
11 See also
12 References
13 External links
Major events

Washington Monument (seen here in 2006) was completed December 6, 1884.
- September 5, 1883: Mary F. Hoyt became the first woman appointed to the U.S. federal civil service (and the second person appointed by examination (in which she came top) instituted under the Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act) when she became a clerk in the Bank Redemption Agency of the Department of the Treasury.
- October 15, 1883: The Supreme Court of the United States declared part of the Civil Rights Act of 1875 unconstitutional, as the Court allowed private individuals and corporations to discriminate based on race.
- November 18, 1883: U.S. and Canadian railroads instituted 5 standard continental time zones, ending the confusion of thousands of local times.
- August 10, 1884: An earthquake measuring 5.5 Mfa (based on the felt area) affected a very large portion of the eastern United States. The shock had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII (Very strong). Chimneys were toppled in New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, and Pennsylvania. Property damage was severe in Jamaica and Amityville in New York.
- October 6, 1884: The United States Naval War College was established in Newport, Rhode Island.
- October 22, 1884: International Meridian Conference in Washington, D.C. fixed the Greenwich meridian as the world's prime meridian.
- November 4, 1884: United States presidential election, 1884: Democratic Governor of New York Grover Cleveland defeated Republican James G. Blaine in a very close contest to win the first of his non-consecutive terms.
- December 6: 1884: The Washington Monument was completed.
Major legislation
Territories organized
- May 17, 1884: District of Alaska was organized.
Party summary
The count below identifies party affiliations at the beginning of the first session of this Congress, and includes members from vacancies and newly admitted states, when they were first seated. Changes resulting from subsequent replacements are shown below in the "Changes in membership" section.
Senate
| Party (shading shows control) | Total | Vacant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Democratic (D) | Independent (I) | Readjuster (RA) | Republican (R) | |||
| End of the previous congress | 37 | 1 | 1 | 37 | 76 | 0 |
| Begin | 36 | 0 | 2 | 37 | 75 | 1 |
| End | 38 | 76 | 0 | |||
| Final voting share | 7001474000000000000♠47.4% | 5000000000000000000♠0.0% | 7000260000000000000♠2.6% | 7001500000000000000♠50.0% | ||
| Beginning of the next congress | 34 | 0 | 2 | 37 | 73 | 3 |
House of Representatives
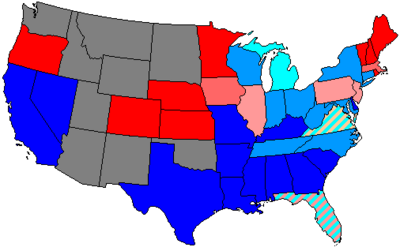
| House seats by party holding plurality in state | |
|---|---|
80+% to 100% Democratic | 80+% to 100% Republican |
60+% to 80% Democratic | 60+% to 80% Republican |
Up to 60% Democratic | Up to 60% Republican |
Democratic: 196 (majority)
Republican: 117
Readjuster: 4
National Greenback: 2- Independent: 2
- Independent Democratic: 3
- Independent Republican: 1
TOTAL members: 325
Leadership
Senate
President: Vacant. Chester Arthur (R), the most recent Senate President, had become U.S. President on the death of his predecessor September 19, 1881, leaving the office vacant through the end of this Congress.
President pro tempore: George F. Edmunds (R)
Republican Conference Chairman: John Sherman
Democratic Caucus Chairman: George H. Pendleton
House of Representatives
Speaker: John G. Carlisle (D)
Democratic Caucus Chairman: George W. Geddes
Republican Conference Chair: Joseph Gurney Cannon
Democratic Campaign Committee Chairman: William Rosecrans
Members
This list is arranged by chamber, then by state.
- Skip to House of Representatives, below
Senate
Senators are listed by their states and Senate class numbers, which indicate the cycle of their election.
|
|  President pro tempore George F. Edmunds |
House of Representatives
Members of the House of Representatives are preceded by their district numbers.
|
|  Speaker of the House John G. Carlisle |
Changes in membership
The count below reflects changes from the beginning of the first session of this Congress.
Senate
- replacements: 1
Democratic: no net change
Republican: 1 seat net gain- Liberal Republican: 1 seat net loss
- Deaths: 1
- Resignations: 0
- Interim appointment: 1
- Late election: 1
- Total seats with changes: 3
| State (class) | Vacator | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
New Hampshire (2) | Vacant | Legislature had failed to elect. Senator elected August 2, 1883. | Austin F. Pike (R) | August 2, 1883 |
Rhode Island (2) | Henry B. Anthony (R) | Incumbent died September 2, 1884. Successor appointed November 19, 1884. | William P. Sheffield (R) | November 19, 1884 |
Rhode Island (2) | William P. Sheffield (R) | Interim appointee replaced by successor elected January 20, 1885. | Jonathan Chace (R) | January 20, 1885 |
House of Representatives
- replacements: 15
Democratic: 1 seat net gain
Republican: 1 seat net loss
National Greenback: 1 seat net gain
- deaths: 9
- resignations: 9
- contested election: 8
- Total seats with changes: 25
| District | Vacator | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Mississippi 2nd | Vacant | Chalmers took seat after an election contest with Van H. Manning who challenged his election | James R. Chalmers (I) | June 25, 1884 |
West Virginia 3rd | John E. Kenna (D) | Resigned March 4, 1883, after being elected to the U.S. Senate | Charles P. Snyder (D) | May 15, 1883 |
Alabama 1st | Thomas H. Herndon (D) | Died March 28, 1883 | James T. Jones (D) | December 3, 1883 |
Iowa 6th | Marsena E. Cutts (R) | Died September 1, 1883 | John C. Cook (D) | October 9, 1883 |
Virginia 7th | John Paul (D) | Resigned September 5, 1883, after being appointed judge of the U.S. District Court of the Western District of Virginia. The House election was subsequently contested. | Charles T. O'Ferrall (D) | May 5, 1884 |
Kansas 2nd | Dudley C. Haskell (R) | Died December 16, 1883 | Edward H. Funston (R) | March 21, 1884 |
North Carolina 1st | Walter F. Pool (R) | Died August 25, 1883 | Thomas G. Skinner (D) | November 20, 1883 |
Massachusetts 12th | George D. Robinson (R) | Resigned January 7, 1884, after being elected Governor of Massachusetts | Francis W. Rockwell (R) | January 17, 1884 |
South Carolina 7th | Edmund W. M. Mackey (R) | Died January 27, 1884 | Robert Smalls (R) | March 18, 1884 |
New Mexico Territory At-large | Tranquilino Luna (R) | Lost contested election March 5, 1884 | Francisco A. Manzanares (D) | March 5, 1884 |
Virginia 1st | Robert M. Mayo (Readjuster) | Lost contested election March 20, 1884 | George T. Garrison (D) | March 20, 1884 |
Indiana 7th | Stanton J. Peelle (R) | Lost contested election May 22, 1884 | William E. English (D) | May 22, 1884 |
Ohio 18th | William McKinley (R) | Lost contested election May 27, 1884 | Jonathan H. Wallace (D) | May 27, 1884 |
Ohio 7th | Henry L. Morey (R) | Lost contested election June 20, 1884 | James E. Campbell (D) | June 20, 1884 |
Iowa 7th | John A. Kasson (R) | Resigned July 13, 1884, after being appointed Minister to Germany | Hiram Y. Smith (R) | December 2, 1884 |
Indiana 13th | William H. Calkins (R) | Resigned October 20, 1884 | Benjamin F. Shively (Anti-Monopoly) | December 1, 1884 |
South Carolina 4th | John H. Evins (D) | Died October 20, 1884 | John Bratton (D) | December 8, 1884 |
Pennsylvania 19th | William A. Duncan (D) | Died November 14, 1884 | John A. Swope (D) | December 23, 1884 |
North Carolina 5th | Alfred M. Scales (D) | Resigned December 30, 1884, after being elected Governor of North Carolina | James W. Reid (D) | January 28, 1885 |
Alabama 4th | Charles M. Shelley (D) | Lost contested election January 9, 1885 | George H. Craig (R) | January 9, 1885 |
Ohio 9th | James S. Robinson (R) | Resigned January 12, 1885, after becoming Ohio Secretary of State | Vacant | Not filled this term |
Rhode Island 2nd | Jonathan Chace (R) | Resigned January 26, 1885, after being elected to the U.S. Senate | Nathan F. Dixon III (R) | February 12, 1885 |
Arkansas 2nd | James K. Jones (D) | Resigned February 19, 1885, after being elected to the U.S. Senate | Vacant | Not filled this term |
Iowa 5th | James Wilson (R) | Lost contested election March 3, 1885 | Benjamin T. Frederick (D) | March 3, 1885 |
Committees
Lists of committees and their party leaders, for members (House and Senate) of the committees and their assignments, go into the Official Congressional Directory at the bottom of the article and click on the link (4 links), in the directory after the pages of terms of service, you will see the committees of the Senate, House (Standing with Subcommittees, Select and Special) and Joint and after the committee pages, you will see the House/Senate committee assignments in the directory, on the committees section of the House and Senate in the Official Congressional Directory, the committee's members on the first row on the left side shows the chairman of the committee and on the right side shows the ranking member of the committee.
|
|
Joint committees
Conditions of Indian Tribes (Special)- Scientific Bureaus
Caucuses
Democratic (House)
Democratic (Senate)
Employees
Architect of the Capitol: Edward Clark
Librarian of Congress: Ainsworth Rand Spofford
Public Printer of the United States: Sterling P. Rounds
Senate
Chaplain: Elias D. Huntley (Methodist)
Secretary: Francis E. Shober (Acting), to December 18, 1883
Anson G. McCook, from December 18, 1883
Sergeant at Arms: Richard J. Bright, to December 18, 1883
William P. Canady, from December 18, 1883
House of Representatives
Chaplain: John S. Lindsay (Episcopalian)
Clerk: John B. Clark, Jr.
Clerk at the Speaker’s Table: Nathaniel T. Crutchfield
Doorkeeper: James G. Wintersmith
Postmaster: Lycurgus Dalton
Reading Clerks: [Data unknown/missing.]
Sergeant at Arms: John P. Leedom
See also
United States elections, 1882 (elections leading to this Congress)
- United States Senate elections, 1882
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1882
United States elections, 1884 (elections during this Congress, leading to the next Congress)
- United States presidential election, 1884
- United States Senate elections, 1884
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1884
References
Martis, Kenneth C. (1989). The Historical Atlas of Political Parties in the United States Congress. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
Martis, Kenneth C. (1982). The Historical Atlas of United States Congressional Districts. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
External links
- Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress
- U.S. House of Representatives: House History
- U.S. Senate: Statistics and Lists
Congressional Directory for the 48th Congress, 1st Session.
Congressional Directory for the 48th Congress, 1st Session (Revision).
Congressional Directory for the 48th Congress, 2nd Session.
Congressional Directory for the 48th Congress, 2nd Session (Revision).