Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic (P–Tr or P–T) extinction event, colloquially known as the Great Dying,[2] the End-Permian Extinction or the Great Permian Extinction,[3][4] occurred about 252 Ma (million years) ago,[5] forming the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, as well as between the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras. It is the Earth's most severe known extinction event, with up to 96% of all marine species[6][7] and 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species becoming extinct.[8] It is the only known mass extinction of insects.[9][10] Some 57% of all biological families and 83% of all genera became extinct. Because so much biodiversity was lost, the recovery of land-dwelling life took significantly longer than after any other extinction event,[6] possibly up to 10 million years.[11] Studies in Bear Lake County, near Paris, Idaho, showed a relatively quick rebound in a localized marine ecosystem, taking around 2 million years to recover,[12] suggesting that the impact of the extinction may have been felt less severely in some areas than others.
There is evidence for one to three distinct pulses, or phases, of extinction.[8][13][14][15] Suggested mechanisms for the latter include one or more large meteor impact events, massive volcanism such as that of the Siberian Traps, and the ensuing coal or gas fires and explosions,[16] and a runaway greenhouse effect triggered by sudden release of methane from the sea floor due to methane clathrate dissociation according to the clathrate gun hypothesis or methane-producing microbes known as methanogens.[17] Possible contributing gradual changes include sea-level change, increasing anoxia, increasing aridity, and a shift in ocean circulation driven by climate change.
Contents
1 Dating the extinction
2 Extinction patterns
2.1 Marine organisms
2.2 Terrestrial invertebrates
2.3 Terrestrial plants
2.3.1 Plant ecosystem response
2.3.2 Coal gap
2.4 Terrestrial vertebrates
2.5 Possible explanations of these patterns
3 Biotic recovery
3.1 Changes in marine ecosystems
3.2 Land vertebrates
4 Theories about cause
4.1 Impact event
4.1.1 Possible impact sites
4.2 Volcanism
4.3 Methane hydrate gasification
4.4 Anoxia
4.5 Hydrogen sulfide emissions
4.6 The supercontinent Pangaea
4.7 Encounter with spiral arm
4.8 Microbes
4.9 Combination of causes
5 See also
6 References
7 Further reading
8 External links
Dating the extinction
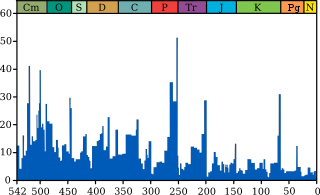
Axis scale: millions of years ago.
Until 2000, it was thought that rock sequences spanning the Permian–Triassic boundary were too few and contained too many gaps for scientists to reliably determine its details.[21] However, it is now possible to date the extinction with millennial precision. U–Pb zircon dates from five volcanic ash beds from the Global Stratotype Section and Point for the Permian–Triassic boundary at Meishan, China, establish a high-resolution age model for the extinction – allowing exploration of the links between global environmental perturbation, carbon cycle disruption, mass extinction, and recovery at millennial timescales. The extinction occurred between 251.941 ± 0.037 and 251.880 ± 0.031 Ma ago, a duration of 60 ± 48 ka.[22] A large (approximately 0.9%), abrupt global decrease in the ratio of the stable isotope 13
C to that of 12
C, coincides with this extinction,[19][23][24][25][26] and is sometimes used to identify the Permian–Triassic boundary in rocks that are unsuitable for radiometric dating.[27] Further evidence for environmental change around the P–Tr boundary suggests an 8 °C (14 °F) rise in temperature,[19] and an increase in CO
2 levels by 6997200000000000000♠2000 ppm (for comparison, the concentration immediately before the industrial revolution was 6996279999999999999♠280 ppm,[19] and the amount today is about 410 ppm[28]). There is also evidence of increased ultraviolet radiation reaching the earth, causing the mutation of plant spores.[19]
It has been suggested that the Permian–Triassic boundary is associated with a sharp increase in the abundance of marine and terrestrial fungi, caused by the sharp increase in the amount of dead plants and animals fed upon by the fungi.[29] For a while this "fungal spike" was used by some paleontologists to identify the Permian–Triassic boundary in rocks that are unsuitable for radiometric dating or lack suitable index fossils, but even the proposers of the fungal spike hypothesis pointed out that "fungal spikes" may have been a repeating phenomenon created by the post-extinction ecosystem in the earliest Triassic.[29] The very idea of a fungal spike has been criticized on several grounds, including: Reduviasporonites, the most common supposed fungal spore, may be a fossilized alga;[19][30] the spike did not appear worldwide;[31][32] and in many places it did not fall on the Permian–Triassic boundary.[33] The reduviasporonites may even represent a transition to a lake-dominated Triassic world rather than an earliest Triassic zone of death and decay in some terrestrial fossil beds.[34] Newer chemical evidence agrees better with a fungal origin for Reduviasporonites, diluting these critiques.[35]
Uncertainty exists regarding the duration of the overall extinction and about the timing and duration of various groups' extinctions within the greater process. Some evidence suggests that there were multiple extinction pulses[8] or that the extinction was spread out over a few million years, with a sharp peak in the last million years of the Permian.[33][36] Statistical analyses of some highly fossiliferous strata in Meishan, Zhejiang Province in southeastern China, suggest that the main extinction was clustered around one peak.[13] Recent research shows that different groups became extinct at different times; for example, while difficult to date absolutely, ostracod and brachiopod extinctions were separated by 670,000 to 1.17 million years.[37] In a well-preserved sequence in east Greenland, the decline of animals is concentrated in a period 10,000 to 60,000 years long, with plants taking an additional several hundred thousand years to show the full impact of the event.[38] An older theory, still supported in some recent papers,[8][39] is that there were two major extinction pulses 9.4 million years apart, separated by a period of extinctions well above the background level, and that the final extinction killed off only about 80% of marine species alive at that time while the other losses occurred during the first pulse or the interval between pulses. According to this theory one of these extinction pulses occurred at the end of the Guadalupian epoch of the Permian.[8][40]
For example, all but one of the surviving dinocephalian genera died out at the end of the Guadalupian,[41] as did the Verbeekinidae, a family of large-size fusuline foraminifera.[42]
The impact of the end-Guadalupian extinction on marine organisms appears to have varied between locations and between taxonomic groups — brachiopods and corals had severe losses.[43][44]
Extinction patterns
| Marine extinctions | Genera extinct | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Arthropoda | ||||
Eurypterids | 100% | May have become extinct shortly before the P–Tr boundary | ||
Ostracods | 59% | | ||
Trilobites | 100% | In decline since the Devonian; only 2 genera living before the extinction | ||
Brachiopoda | ||||
Brachiopods | 96% | Orthids and productids died out | ||
Bryozoa | ||||
Bryozoans | 79% | Fenestrates, trepostomes, and cryptostomes died out | ||
Chordata | ||||
Acanthodians | 100% | In decline since the Devonian, with only one living family | ||
Cnidaria | ||||
Anthozoans | 96% | Tabulate and rugose corals died out | ||
Echinodermata | ||||
Blastoids | 100% | May have become extinct shortly before the P–Tr boundary | ||
Crinoids | 98% | Inadunates and camerates died out | ||
Mollusca | ||||
Ammonites | 97% | | ||
Bivalves | 59% | | ||
Gastropods | 98% | | ||
Retaria | ||||
Foraminiferans | 97% | Fusulinids died out, but were almost extinct before the catastrophe | ||
Radiolarians | 99%[45] | |||
Marine organisms
Marine invertebrates suffered the greatest losses during the P–Tr extinction. Evidence of this was found in samples from south China sections at the P–Tr boundary. Here, 286 out of 329 marine invertebrate genera disappear within the final two sedimentary zones containing conodonts from the Permian.[13] The decrease in diversity was probably caused by a sharp increase in extinctions, rather than a decrease in speciation.[46]
The extinction primarily affected organisms with calcium carbonate skeletons, especially those reliant on stable CO2 levels to produce their skeletons.[47] These organisms were susceptible to the effects of the ocean acidification that resulted from increased atmospheric CO2.
Among benthic organisms the extinction event multiplied background extinction rates, and therefore caused maximum species loss to taxa that had a high background extinction rate (by implication, taxa with a high turnover).[48][49] The extinction rate of marine organisms was catastrophic.[13][50][51][52]
Surviving marine invertebrate groups include: articulate brachiopods (those with a hinge),[53] which have undergone a slow decline in numbers since the P–Tr extinction; the Ceratitida order of ammonites;[54] and crinoids ("sea lilies"),[54] which very nearly became extinct but later became abundant and diverse.
The groups with the highest survival rates generally had active control of circulation, elaborate gas exchange mechanisms, and light calcification; more heavily calcified organisms with simpler breathing apparatuses suffered the greatest loss of species diversity.[18][55] In the case of the brachiopods, at least, surviving taxa were generally small, rare members of a formerly diverse community.[56]
The ammonoids, which had been in a long-term decline for the 30 million years since the Roadian (middle Permian), suffered a selective extinction pulse 10 million years before the main event, at the end of the Capitanian stage. In this preliminary extinction, which greatly reduced disparity, or the range of different ecological guilds, environmental factors were apparently responsible. Diversity and disparity fell further until the P–Tr boundary; the extinction here (P–Tr) was non-selective, consistent with a catastrophic initiator. During the Triassic, diversity rose rapidly, but disparity remained low.[57]
The range of morphospace occupied by the ammonoids, that is, their range of possible forms, shapes or structures, became more restricted as the Permian progressed. A few million years into the Triassic, the original range of ammonoid structures was once again reoccupied, but the parameters were now shared differently among clades.[58]
Terrestrial invertebrates
The Permian had great diversity in insect and other invertebrate species, including the largest insects ever to have existed. The end-Permian is the only known mass extinction of insects,[9] with eight or nine insect orders becoming extinct and ten more greatly reduced in diversity. Palaeodictyopteroids (insects with piercing and sucking mouthparts) began to decline during the mid-Permian; these extinctions have been linked to a change in flora. The greatest decline occurred in the Late Permian and was probably not directly caused by weather-related floral transitions.[50]
Most fossil insect groups found after the Permian–Triassic boundary differ significantly from those before. Of Paleozoic insect groups, only the Glosselytrodea, Miomoptera, and Protorthoptera have been discovered in deposits from after the extinction. The caloneurodeans, monurans, paleodictyopteroids, protelytropterans, and protodonates became extinct by the end of the Permian. In well-documented Late Triassic deposits, fossils overwhelmingly consist of modern fossil insect groups.[9]
Terrestrial plants
Plant ecosystem response
The geological record of terrestrial plants is sparse and based mostly on pollen and spore studies. Plants are relatively immune to mass extinction, with the impact of all the major mass extinctions "insignificant" at a family level.[19] Even the reduction observed in species diversity (of 50%) may be mostly due to taphonomic processes.[19] However, a massive rearrangement of ecosystems does occur, with plant abundances and distributions changing profoundly and all the forests virtually disappearing;[19][59] the Palaeozoic flora scarcely survived this extinction.[60]
At the P–Tr boundary, the dominant floral groups changed, with many groups of land plants entering abrupt decline, such as Cordaites (gymnosperms) and Glossopteris (seed ferns).[61] Dominant gymnosperm genera were replaced post-boundary by lycophytes—extant lycophytes are recolonizers of disturbed areas.[62]
Palynological or pollen studies from East Greenland of sedimentary rock strata laid down during the extinction period indicate dense gymnosperm woodlands before the event. At the same time that marine invertebrate macrofauna declined, these large woodlands died out and were followed by a rise in diversity of smaller herbaceous plants including Lycopodiophyta, both Selaginellales and Isoetales. Later, other groups of gymnosperms again become dominant but again suffered major die offs. These cyclical flora shifts occurred a few times over the course of the extinction period and afterwards. These fluctuations of the dominant flora between woody and herbaceous taxa indicate chronic environmental stress resulting in a loss of most large woodland plant species. The successions and extinctions of plant communities do not coincide with the shift in δ13C values, but occurred many years after.[32] The recovery of gymnosperm forests took 4–5 million years.[19]
Coal gap
No coal deposits are known from the Early Triassic, and those in the Middle Triassic are thin and low-grade.[20] This "coal gap" has been explained in many ways. It has been suggested that new, more aggressive fungi, insects and vertebrates evolved, and killed vast numbers of trees. These decomposers themselves suffered heavy losses of species during the extinction, and are not considered a likely cause of the coal gap.[20] It could simply be that all coal forming plants were rendered extinct by the P–Tr extinction, and that it took 10 million years for a new suite of plants to adapt to the moist, acid conditions of peat bogs.[20]Abiotic factors (factors not caused by organisms), such as decreased rainfall or increased input of clastic sediments, may also be to blame.[19]
On the other hand, the lack of coal may simply reflect the scarcity of all known sediments from the Early Triassic. Coal-producing ecosystems, rather than disappearing, may have moved to areas where we have no sedimentary record for the Early Triassic.[19] For example, in eastern Australia a cold climate had been the norm for a long period, with a peat mire ecosystem adapted to these conditions. Approximately 95% of these peat-producing plants went locally extinct at the P–Tr boundary;[63] Coal deposits in Australia and Antarctica disappear significantly before the P–Tr boundary.[19]
Terrestrial vertebrates
There is enough evidence to indicate that over two-thirds of terrestrial labyrinthodont amphibians, sauropsid ("reptile") and therapsid ("proto-mammal") families became extinct. Large herbivores suffered the heaviest losses.
All Permian anapsid reptiles died out except the procolophonids (although testudines have morphologically anapsid skulls, they are now thought to have separately evolved from diapsid ancestors). Pelycosaurs died out before the end of the Permian. Too few Permian diapsid fossils have been found to support any conclusion about the effect of the Permian extinction on diapsids (the "reptile" group from which lizards, snakes, crocodilians, and dinosaurs (including birds) evolved).[64][65]
The groups that survived suffered extremely heavy losses of species, and some terrestrial vertebrate groups very nearly became extinct at the end-Permian. Some of the surviving groups did not persist for long past this period, while others that barely survived went on to produce diverse and long-lasting lineages. Yet it took 30 million years for the terrestrial vertebrate fauna to fully recover both numerically and ecologically.[66]
Possible explanations of these patterns
An analysis of marine fossils from the Permian's final Changhsingian stage found that marine organisms with low tolerance for hypercapnia (high concentration of carbon dioxide) had high extinction rates, while the most tolerant organisms had very slight losses.
The most vulnerable marine organisms were those that produced calcareous hard parts (i.e., from calcium carbonate) and had low metabolic rates and weak respiratory systems—notably calcareous sponges, rugose and tabulate corals, calcite-depositing brachiopods, bryozoans, and echinoderms; about 81% of such genera became extinct. Close relatives without calcareous hard parts suffered only minor losses, for example sea anemones, from which modern corals evolved. Animals with high metabolic rates, well-developed respiratory systems, and non-calcareous hard parts had negligible losses—except for conodonts, in which 33% of genera died out.[67]
This pattern is consistent with what is known about the effects of hypoxia, a shortage but not a total absence of oxygen. However, hypoxia cannot have been the only killing mechanism for marine organisms. Nearly all of the continental shelf waters would have had to become severely hypoxic to account for the magnitude of the extinction, but such a catastrophe would make it difficult to explain the very selective pattern of the extinction. Models of the Late Permian and Early Triassic atmospheres show a significant but protracted decline in atmospheric oxygen levels, with no acceleration near the P–Tr boundary. Minimum atmospheric oxygen levels in the Early Triassic are never less than present day levels—the decline in oxygen levels does not match the temporal pattern of the extinction.[67]
Marine organisms are more sensitive to changes in CO2 (carbon dioxide) levels than are terrestrial organisms for a variety of reasons. CO2 is 28 times more soluble in water than is oxygen. Marine animals normally function with lower concentrations of CO2 in their bodies than land animals, as the removal of CO2 in air-breathing animals is impeded by the need for the gas to pass through the respiratory system's membranes (lungs' alveolus, tracheae, and the like), even when CO2 diffuses more easily than oxygen. In marine organisms, relatively modest but sustained increases in CO2 concentrations hamper the synthesis of proteins, reduce fertilization rates, and produce deformities in calcareous hard parts.[67] In addition, an increase in CO2 concentration is inevitably linked to ocean acidification, consistent with the preferential extinction of heavily calcified taxa and other signals in the rock record that suggest a more acidic ocean.[68] The decrease in ocean pH is calculated to be up to 0.7 units.[69]
It is difficult to analyze extinction and survival rates of land organisms in detail, because few terrestrial fossil beds span the Permian–Triassic boundary. Triassic insects are very different from those of the Permian, but a gap in the insect fossil record spans approximately 15 million years from the late Permian to early Triassic. The best-known record of vertebrate changes across the Permian–Triassic boundary occurs in the Karoo Supergroup of South Africa, but statistical analyses have so far not produced clear conclusions.[67] However, analysis of the fossil river deposits of the floodplains indicate a shift from meandering to braided river patterns, indicating an abrupt drying of the climate.[70] The climate change may have taken as little as 100,000 years, prompting the extinction of the unique Glossopteris flora and its herbivores, followed by the carnivorous guild.[71] End-Permian extinctions did not occur at an instantaneous time horizon; particularly, floral extinction was delayed in time.[72]
Biotic recovery
Earlier analyses indicated that life on Earth recovered quickly after the Permian extinctions, but this was mostly in the form of disaster taxa, opportunist organisms such as the hardy Lystrosaurus. Research published in 2006 indicates that the specialized animals that formed complex ecosystems, with high biodiversity, complex food webs and a variety of niches, took much longer to recover. It is thought that this long recovery was due to the successive waves of extinction, which inhibited recovery, and prolonged environmental stress to organisms, which continued into the Early Triassic. Research indicates that recovery did not begin until the start of the mid-Triassic, 4 to 6 million years after the extinction;[73] and some writers estimate that the recovery was not complete until 7014946728000000000♠30 Ma after the P–Tr extinction, i.e. in the late Triassic.[8]
A study published in the journal Science[74] found that during the Great Extinction, ocean surface temperatures reached 40 °C (104 °F) in some places. This explains why recovery took so long: it was too hot for life to survive.[75]Anoxic waters may have also delayed the recovery.[76]

A braided river, the Waimakariri River on the South Island of New Zealand
During the early Triassic (4 to 6 million years after the P–Tr extinction), the plant biomass was insufficient to form coal deposits, which implies a limited food mass for herbivores.[20] River patterns in the Karoo changed from meandering to braided, indicating that vegetation there was very sparse for a long time.[77]
Each major segment of the early Triassic ecosystem—plant and animal, marine and terrestrial—was dominated by a small number of genera, which appeared virtually worldwide, for example: the herbivorous therapsid Lystrosaurus (which accounted for about 90% of early Triassic land vertebrates) and the bivalves Claraia, Eumorphotis, Unionites and Promylina. A healthy ecosystem has a much larger number of genera, each living in a few preferred types of habitat.[61][78]
Disaster taxa took advantage of the devastated ecosystems and enjoyed a temporary population boom and increase in their territory. Microconchids are the dominant component of otherwise impoverished Early Triassic encrusting assemblages. For example: Lingula (a brachiopod); stromatolites, which had been confined to marginal environments since the Ordovician; Pleuromeia (a small, weedy plant); Dicroidium (a seed fern).[78][79][80]
Changes in marine ecosystems

Sessile filter feeders like this Carboniferous crinoid, the mushroom crinoid (Agaricocrinus americanus), were significantly less abundant after the P–Tr extinction.
Prior to the extinction, about two-thirds of marine animals were sessile and attached to the sea floor. During the Mesozoic, only about half of the marine animals were sessile while the rest were free-living. Analysis of marine fossils from the period indicated a decrease in the abundance of sessile epifaunal suspension feeders such as brachiopods and sea lilies and an increase in more complex mobile species such as snails, sea urchins and crabs.[81]
Before the Permian mass extinction event, both complex and simple marine ecosystems were equally common; after the recovery from the mass extinction, the complex communities outnumbered the simple communities by nearly three to one,[81] and the increase in predation pressure led to the Mesozoic Marine Revolution.
Bivalves were fairly rare before the P–Tr extinction but became numerous and diverse in the Triassic, and one group, the rudist clams, became the Mesozoic's main reef-builders. Some researchers think much of this change happened in the 5 million years between the two major extinction pulses.[82]
Crinoids ("sea lilies") suffered a selective extinction, resulting in a decrease in the variety of their forms.[83] Their ensuing adaptive radiation was brisk, and resulted in forms possessing flexible arms becoming widespread; motility, predominantly a response to predation pressure, also became far more prevalent.[84]
Land vertebrates
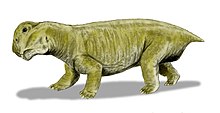
Lystrosaurus was by far the most abundant early Triassic land vertebrate.
Lystrosaurus, a pig-sized herbivorous dicynodont therapsid, constituted as much as 90% of some earliest Triassic land vertebrate fauna. Smaller carnivorous cynodont therapsids also survived, including the ancestors of mammals. In the Karoo region of southern Africa, the therocephalians Tetracynodon, Moschorhinus and Ictidosuchoides survived, but do not appear to have been abundant in the Triassic.[85]
Archosaurs (which included the ancestors of dinosaurs and crocodilians) were initially rarer than therapsids, but they began to displace therapsids in the mid-Triassic. In the mid to late Triassic, the dinosaurs evolved from one group of archosaurs, and went on to dominate terrestrial ecosystems during the Jurassic and Cretaceous.[86] This "Triassic Takeover" may have contributed to the evolution of mammals by forcing the surviving therapsids and their mammaliform successors to live as small, mainly nocturnal insectivores; nocturnal life probably forced at least the mammaliforms to develop fur and higher metabolic rates,[87] while losing part of the differential color-sensitive retinal receptors reptilians and birds preserved.
Some temnospondyl amphibians made a relatively quick recovery, in spite of nearly becoming extinct. Mastodonsaurus and trematosaurians were the main aquatic and semiaquatic predators during most of the Triassic, some preying on tetrapods and others on fish.[88]
Land vertebrates took an unusually long time to recover from the P–Tr extinction; Palaeontologist Michael Benton estimated the recovery was not complete until 7001300000000000000♠30 million years after the extinction, i.e. not until the Late Triassic, in which dinosaurs, pterosaurs, crocodiles, archosaurs, amphibians, and mammaliforms were abundant and diverse.[6]
Theories about cause
Pinpointing the exact cause or causes of the Permian–Triassic extinction event is difficult, mostly because the catastrophe occurred over 250 million years ago, and since then much of the evidence that would have pointed to the cause has been destroyed or is concealed deep within the Earth under many layers of rock. The sea floor is also completely recycled every 200 million years by the ongoing process of plate tectonics and seafloor spreading, leaving no useful indications beneath the ocean.
Scientists have accumulated a fairly significant amount of evidence for causes, and several mechanisms have been proposed for the extinction event. The proposals include both catastrophic and gradual processes (similar to those theorized for the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event).
- The catastrophic group includes one or more large bolide impact events, increased volcanism, and sudden release of methane from the sea floor, either due to dissociation of methane hydrate deposits or metabolism of organic carbon deposits by methanogenic microbes.
- The gradual group includes sea level change, increasing anoxia, and increasing aridity.
Any hypothesis about the cause must explain the selectivity of the event, which affected organisms with calcium carbonate skeletons most severely; the long period (4 to 6 million years) before recovery started, and the minimal extent of biological mineralization (despite inorganic carbonates being deposited) once the recovery began.[47]
Impact event

Artist's impression of a major impact event: A collision between Earth and an asteroid a few kilometres in diameter would release as much energy as several million nuclear weapons detonating.
Evidence that an impact event may have caused the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (Cretaceous–Tertiary) has led to speculation that similar impacts may have been the cause of other extinction events, including the P–Tr extinction, and thus to a search for evidence of impacts at the times of other extinctions and for large impact craters of the appropriate age.
Reported evidence for an impact event from the P–Tr boundary level includes rare grains of shocked quartz in Australia and Antarctica;[89][90]fullerenes trapping extraterrestrial noble gases;[91] meteorite fragments in Antarctica;[92] and grains rich in iron, nickel and silicon, which may have been created by an impact.[93] However, the accuracy of most of these claims has been challenged.[94][95][96][97] For example, quartz from Graphite Peak in Antarctica, once considered "shocked", has been re-examined by optical and transmission electron microscopy. The observed features were concluded to be due not to shock, but rather to plastic deformation, consistent with formation in a tectonic environment such as volcanism.[98]
An impact crater on the sea floor would be evidence of a possible cause of the P–Tr extinction, but such a crater would by now have disappeared. As 70% of the Earth's surface is currently sea, an asteroid or comet fragment is now perhaps more than twice as likely to hit ocean as it is to hit land. However, Earth's oldest ocean-floor crust is 200 million years old because it is continually destroyed and renewed by spreading and subduction. Thus, craters produced by very large impacts may be masked by extensive flood basalting from below after the crust is punctured or weakened.[99] Yet, subduction should not be entirely accepted as an explanation of why no firm evidence can be found: as with the K-T event, an ejecta blanket stratum rich in siderophilic elements (such as iridium) would be expected to be seen in formations from the time.
A large impact might have triggered other mechanisms of extinction described below,[100] such as the Siberian Traps eruptions at either an impact site[101] or the antipode of an impact site.[100][102] The abruptness of an impact also explains why more species did not rapidly evolve to survive, as would be expected if the Permian-Triassic event had been slower and less global than a meteorite impact.
Possible impact sites
Several possible impact craters have been proposed as the site of an impact causing the P–Tr extinction, including the 250 km (160 mi) Bedout structure off the northwest coast of Australia[90] and the hypothesized 480 km (300 mi) Wilkes Land crater of East Antarctica.[103][104] In each case, the idea that an impact was responsible has not been proven and has been widely criticized. In the case of Wilkes Land, the age of this sub-ice geophysical feature is very uncertain – it may be later than the Permian–Triassic extinction.
The 40 km (25 mi) Araguainha crater in Brazil has been most recently dated to 254.7 ± 2.5 million years ago, overlapping with estimates for the Permo-Triassic boundary.[105] Much of the local rock was oil shale. The estimated energy released by the Araguainha impact is insufficient to be a direct cause of the global mass extinction, but the colossal local earth tremors would have released huge amounts of oil and gas from the shattered rock. The resulting sudden global warming might have precipitated the Permian–Triassic extinction event.[106]
In May 1992, Michael R. Rampino published an abstract for the American Geophysical Union noting the discovery of a circular gravity anomaly near the Falkland Islands. He suggested this structure might correspond to an impact crater with a diameter of 250 km (160 mi).[107] In August 2017, Rampino, Maximilliano Rocca and Jaime Baez Presser followed up with a paper[107] providing further seismic and magnetic evidence that the structure is an impact crater. Estimates for the age of the structure range up to 250 millions years old. If, in fact, this is an impact crater, it would be substantially larger than the well-known 180 km (110 mi) Chicxulub impact crater associated with a later extinction event. However, Dave McCarthy and colleagues from the British Geological Survey not only illustrated that the gravity anomaly is not circular, but that the seismic data presented by Rocca, Rampino and Baez Presser did not cross the proposed crater, nor did it provide any evidence for an impact crater.[108]
Volcanism
The final stages of the Permian had two flood basalt events. A small one, the Emeishan Traps in China, occurred at the same time as the end-Guadalupian extinction pulse, in an area close to the equator at the time.[109][110] The flood basalt eruptions that produced the Siberian Traps constituted one of the largest known volcanic events on Earth and covered over 2,000,000 square kilometres (770,000 sq mi) with lava.[111][112][113] The date of the Siberian Traps eruptions and the extinction event are in good agreement.[22][114]
The Emeishan and Siberian Traps eruptions may have caused dust clouds and acid aerosols, which would have blocked out sunlight and thus disrupted photosynthesis both on land and in the photic zone of the ocean, causing food chains to collapse. The eruptions may also have caused acid rain when the aerosols washed out of the atmosphere. That may have killed land plants and molluscs and planktonic organisms which had calcium carbonate shells. The eruptions would also have emitted carbon dioxide, causing global warming. When all of the dust clouds and aerosols washed out of the atmosphere, the excess carbon dioxide would have remained and the warming would have proceeded without any mitigating effects.[100]
The Siberian Traps had unusual features that made them even more dangerous. Pure flood basalts produce fluid, low-viscosity lava and do not hurl debris into the atmosphere. It appears, however, that 20% of the output of the Siberian Traps eruptions was pyroclastic (consisted of ash and other debris thrown high into the atmosphere), increasing the short-term cooling effect.[115] The basalt lava erupted or intruded into carbonate rocks and into sediments that were in the process of forming large coal beds, both of which would have emitted large amounts of carbon dioxide, leading to stronger global warming after the dust and aerosols settled.[100]
In January 2011, a team, led by Stephen Grasby of the Geological Survey of Canada—Calgary, reported evidence that volcanism caused massive coal beds to ignite, possibly releasing more than 3 trillion tons of carbon. The team found ash deposits in deep rock layers near what is now Buchanan Lake. According to their article, "coal ash dispersed by the explosive Siberian Trap eruption would be expected to have an associated release of toxic elements in impacted water bodies where fly ash slurries developed.... Mafic megascale eruptions are long-lived events that would allow significant build-up of global ash clouds."[116][117] In a statement, Grasby said, "In addition to these volcanoes causing fires through coal, the ash it spewed was highly toxic and was released in the land and water, potentially contributing to the worst extinction event in earth history."[118] In 2013, a team led by Q.Y. Yang reported the total amounts of important volatiles emitted from the Siberian Traps are 8.5 × 107 Tg CO2, 4.4 × 106 Tg CO, 7.0 × 106 Tg H2S and 6.8 × 107 Tg SO2, the data support a popular notion that the end-Permian mass extinction on the Earth was caused by the emission of enormous amounts of volatiles from the Siberian Traps into the atmosphere.[119]
In 2015, evidence and a timeline indicated the extinction was caused by events in the Large igneous province of the Siberian Traps.[120][121][122][123][124]
Methane hydrate gasification
Scientists have found worldwide evidence of a swift decrease of about 1% in the 13C/12C isotope ratio in carbonate rocks from the end-Permian.[52][125] This is the first, largest, and most rapid of a series of negative and positive excursions (decreases and increases in 13C/12C ratio) that continues until the isotope ratio abruptly stabilised in the middle Triassic, followed soon afterwards by the recovery of calcifying life forms (organisms that use calcium carbonate to build hard parts such as shells).[18]
A variety of factors may have contributed to this drop in the 13C/12C ratio, but most turn out to be insufficient to account fully for the observed amount:[126]
- Gases from volcanic eruptions have a 13C/12C ratio about 0.5 to 0.8% below standard (δ13C about −0.5 to −0.8%), but an assessment made in 1995 concluded that the amount required to produce a reduction of about 1.0% worldwide requires eruptions greater by orders of magnitude than any for which evidence has been found.[127] (However, this analysis addressed only CO2 produced by the magma itself, not from interactions with carbon bearing sediments, as later proposed.)
- A reduction in organic activity would extract 12C more slowly from the environment and leave more of it to be incorporated into sediments, thus reducing the 13C/12C ratio. Biochemical processes preferentially use the lighter isotopes since chemical reactions are ultimately driven by electromagnetic forces between atoms and lighter isotopes respond more quickly to these forces, but a study of a smaller drop of 0.3 to 0.4% in 13C/12C (δ13C −3 to −4 ‰) at the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) concluded that even transferring all the organic carbon (in organisms, soils, and dissolved in the ocean) into sediments would be insufficient: even such a large burial of material rich in 12C would not have produced the 'smaller' drop in the 13C/12C ratio of the rocks around the PETM.[127]
- Buried sedimentary organic matter has a 13C/12C ratio 2.0 to 2.5% below normal (δ13C −2.0 to −2.5%). Theoretically, if the sea level fell sharply, shallow marine sediments would be exposed to oxidization. But 6500–8400 gigatons (1 gigaton = 109metric tons) of organic carbon would have to be oxidized and returned to the ocean-atmosphere system within less than a few hundred thousand years to reduce the 13C/12C ratio by 1.0%, which is not thought to be a realistic possibility.[50] Moreover, sea levels were rising rather than falling at the time of the extinction.[128]
- Rather than a sudden decline in sea level, intermittent periods of ocean-bottom hyperoxia and anoxia (high-oxygen and low- or zero-oxygen conditions) may have caused the 13C/12C ratio fluctuations in the Early Triassic;[18] and global anoxia may have been responsible for the end-Permian blip. The continents of the end-Permian and early Triassic were more clustered in the tropics than they are now, and large tropical rivers would have dumped sediment into smaller, partially enclosed ocean basins at low latitudes. Such conditions favor oxic and anoxic episodes; oxic/anoxic conditions would result in a rapid release/burial, respectively, of large amounts of organic carbon, which has a low 13C/12C ratio because biochemical processes use the lighter isotopes more.[129] That or another organic-based reason may have been responsible for both that and a late Proterozoic/Cambrian pattern of fluctuating 13C/12C ratios.[18]
Other hypotheses include mass oceanic poisoning releasing vast amounts of CO2[130] and a long-term reorganisation of the global carbon cycle.[126]
Prior to consideration of the inclusion of roasting carbonate sediments by volcanism, the only proposed mechanism sufficient to cause a global 1% reduction in the 13C/12C ratio was the release of methane from methane clathrates.[50] Carbon-cycle models confirm that it would have had enough effect to produce the observed reduction.[126][130] Methane clathrates, also known as methane hydrates, consist of methane molecules trapped in cages of water molecules. The methane, produced by methanogens (microscopic single-celled organisms), has a 13C/12C ratio about 6.0% below normal (δ13C −6.0%). At the right combination of pressure and temperature, it gets trapped in clathrates fairly close to the surface of permafrost and in much larger quantities at continental margins (continental shelves and the deeper seabed close to them). Oceanic methane hydrates are usually found buried in sediments where the seawater is at least 300 m (980 ft) deep. They can be found up to about 2,000 m (6,600 ft) below the sea floor, but usually only about 1,100 m (3,600 ft) below the sea floor.[131]
The area covered by lava from the Siberian Traps eruptions is about twice as large as was originally thought, and most of the additional area was shallow sea at the time. The seabed probably contained methane hydrate deposits, and the lava caused the deposits to dissociate, releasing vast quantities of methane.[132]
A vast release of methane might cause significant global warming since methane is a very powerful greenhouse gas. Strong evidence suggests the global temperatures increased by about 6 °C (10.8 °F) near the equator and therefore by more at higher latitudes: a sharp decrease in oxygen isotope ratios (18O/16O);[133] the extinction of Glossopteris flora (Glossopteris and plants that grew in the same areas), which needed a cold climate, with its replacement by floras typical of lower paleolatitudes.[134]
However, the pattern of isotope shifts expected to result from a massive release of methane does not match the patterns seen throughout the early Triassic. Not only would such a cause require the release of five times as much methane as postulated for the PETM,[18] but would it also have to be reburied at an unrealistically high rate to account for the rapid increases in the 13C/12C ratio (episodes of high positive δ13C) throughout the early Triassic before it was released again several times.[18]
Anoxia
Evidence for widespread ocean anoxia (severe deficiency of oxygen) and euxinia (presence of hydrogen sulfide) is found from the Late Permian to the Early Triassic. Throughout most of the Tethys and Panthalassic Oceans, evidence for anoxia, including fine laminations in sediments, small pyrite framboids, high uranium/thorium ratios, and biomarkers for green sulfur bacteria, appear at the extinction event.[135]
However, in some sites, including Meishan, China, and eastern Greenland, evidence for anoxia precedes the extinction.[136][137]
Biomarkers for green sulfur bacteria, such as isorenieratane, the diagenetic product of isorenieratene, are widely used as indicators of photic zone euxinia because green sulfur bacteria require both sunlight and hydrogen sulfide to survive. Their abundance in sediments from the P-T boundary indicates hydrogen sulfide was present even in shallow waters.
This spread of toxic, oxygen-depleted water would have been devastating for marine life, producing widespread die-offs. Models of ocean chemistry show that anoxia and euxinia would have been closely associated with hypercapnia (high levels of carbon dioxide).[138]
This suggests that poisoning from hydrogen sulfide, anoxia, and hypercapnia acted together as a killing mechanism. Hypercapnia best explains the selectivity of the extinction, but anoxia and euxinia probably contributed to the high mortality of the event. The persistence of anoxia through the Early Triassic may explain the slow recovery of marine life after the extinction. Models also show that anoxic events can cause catastrophic hydrogen sulfide emissions into the atmosphere (see below).[139]
The sequence of events leading to anoxic oceans may have been triggered by carbon dioxide emissions from the eruption of the Siberian Traps.[139] In that scenario, warming from the enhanced greenhouse effect would reduce the solubility of oxygen in seawater, causing the concentration of oxygen to decline. Increased weathering of the continents due to warming and the acceleration of the water cycle would increase the riverine flux of phosphate to the ocean. The phosphate would have supported greater primary productivity in the surface oceans. The increase in organic matter production would have caused more organic matter to sink into the deep ocean, where its respiration would further decrease oxygen concentrations. Once anoxia became established, it would have been sustained by a positive feedback loop because deep water anoxia tends to increase the recycling efficiency of phosphate, leading to even higher productivity.
Hydrogen sulfide emissions
A severe anoxic event at the end of the Permian would have allowed sulfate-reducing bacteria to thrive, causing the production of large amounts of hydrogen sulfide in the anoxic ocean. Upwelling of this water may have released massive hydrogen sulfide emissions into the atmosphere and would poison terrestrial plants and animals and severely weaken the ozone layer, exposing much of the life that remained to fatal levels of UV radiation.[139]
Indeed, biomarker evidence for anaerobic photosynthesis by Chlorobiaceae (green sulfur bacteria) from the Late-Permian into the Early Triassic indicates that hydrogen sulfide did upwell into shallow waters because these bacteria are restricted to the photic zone and use sulfide as an electron donor.
The hypothesis has the advantage of explaining the mass extinction of plants, which would have added to the methane levels and should otherwise have thrived in an atmosphere with a high level of carbon dioxide. Fossil spores from the end-Permian further support the theory:[citation needed] many show deformities that could have been caused by ultraviolet radiation, which would have been more intense after hydrogen sulfide emissions weakened the ozone layer.
The supercontinent Pangaea

Map of Pangaea showing where today's continents were at the Permian–Triassic boundary
In the mid-Permian (during the Kungurian age of the Permian's Cisuralian epoch), the earth's major continental plates were joined, forming a supercontinent called Pangaea, which was surrounded by the superocean, Panthalassa.
Oceanic circulation and atmospheric weather patterns during the mid-Permian produced seasonal monsoons near the coasts and an arid climate in the vast continental interior of Pangaea.[citation needed]
The extent of biologically diverse and ecologically productive coastal areas shrank as the supercontinent formed. The elimination of shallow aquatic environments exposed formerly protected organisms of the rich continental shelves to increased environmental volatility.
After the formation of Pangaea (see the diagram "Marine genus biodiversity" at the top of this article), the rate of marine life depletion approached catastrophic levels; however, marine life extinction never reached the rate of the "Big Five" mass extinctions.[clarification needed]
Pangaea's effect on extinctions on land is thought to have been less significant. In fact, the advance of the therapsids and increase in their diversity is attributed to the late Permian, when Pangaea's global effect was thought to have peaked.
While Pangaea's formation is known to have initiated a long period of marine life extinction, the significance of its impact on the "Great Dying" and the end of the Permian is uncertain.
Encounter with spiral arm
John Gribbin argues that the Solar System last passed through a spiral arm of the Milky Way was around 250 million years ago and that the resultant dusty gas clouds may have caused a dimming of the Sun which combined with the effect of Pangea to produce an ice age.[140]
Microbes
A hypothesis published in 2014 posits that a genus of anaerobic methanogenic archaea known as Methanosarcina was responsible for the event.[141] Three lines of evidence suggest that these microbes acquired a new metabolic pathway via gene transfer at about that time, enabling them to efficiently metabolize acetate into methane. That would have led to their exponential reproduction, allowing them to rapidly consume vast deposits of organic carbon that had accumulated in the marine sediment. The result would have been a sharp buildup of methane and carbon dioxide in the Earth's oceans and atmosphere, in a manner that may be consistent with the 13C/12C isotopic record. Massive volcanism facilitated this process by releasing large amounts of nickel, a scarce metal which is a cofactor for enzymes involved in producing methane.[141] On the other hand, in the canonical Meishan sections, the nickel concentration increases somewhat after the δ13C concentrations have begun to fall.[142]
Combination of causes
Possible causes supported by strong evidence appear to describe a sequence of catastrophes, each worse than the last: the Siberian Traps eruptions were bad enough alone, but because they occurred near coal beds and the continental shelf, they also triggered very large releases of carbon dioxide and methane.[67] The resultant global warming may have caused perhaps the most severe anoxic event in the oceans' history: according to this theory, the oceans became so anoxic, anaerobic sulfur-reducing organisms dominated the chemistry of the oceans and caused massive emissions of toxic hydrogen sulfide.[67]
However, there may be some weak links in this chain of events: the changes in the 13C/12C ratio expected to result from a massive release of methane do not match the patterns seen throughout the early Triassic;[18] and the types of oceanic thermohaline circulation that may have existed at the end of the Permian are not likely to have supported deep-sea anoxia.[143]
See also
- Extinction events
- List of unconfirmed impact craters on Earth
- Siberian Traps
- Silurian hypothesis
- Wilkes Land crater
References
^ Rohde, R.A. & Muller, R.A. (2005). "Cycles in fossil diversity". Nature. 434 (7030): 209–210. Bibcode:2005Natur.434..208R. doi:10.1038/nature03339. PMID 15758998..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ St. Fleur, Nicholas (16 February 2017). "After Earth's worst mass extinction, life rebounded rapidly, fossils suggest". The New York Times. Retrieved 17 February 2017.
^ ""Great Dying" lasted 200,000 years". National Geographic. 23 November 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
^ "How a single act of evolution nearly wiped out all life on Earth". ScienceDaily. 1 April 2014. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
^ Shen S.-Z.; et al. (2011). "Calibrating the end-Permian mass extinction". Science. 334 (6061): 1367–1372. Bibcode:2011Sci...334.1367S. doi:10.1126/science.1213454. PMID 22096103.
^ abc Benton M J (2005). When Life Nearly Died: The greatest mass extinction of all time. London: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-28573-2.
^ Carl T. Bergstrom; Lee Alan Dugatkin (2012). Evolution. Norton. p. 515. ISBN 978-0-393-92592-0.
^ abcdef Sahney S; Benton M.J (2008). "Recovery from the most profound mass extinction of all time". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 275 (1636): 759–765. doi:10.1098/rspb.2007.1370. PMC 2596898. PMID 18198148.
^ abc Labandeira CC, Sepkoski JJ (1993). "Insect diversity in the fossil record". Science. 261 (5119): 310–315. Bibcode:1993Sci...261..310L. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.496.1576. doi:10.1126/science.11536548. PMID 11536548.
^ Sole RV, Newman M (2003). "Extinctions and Biodiversity in the Fossil Record". In Canadell JG, Mooney HA. Encyclopedia of Global Environmental Change, The Earth System. Biological and Ecological Dimensions of Global Environmental Change. 2. New York: Wiley. pp. 297–391. ISBN 978-0-470-85361-0.
^ "It took Earth ten million years to recover from greatest mass extinction". ScienceDaily. 27 May 2012. Retrieved 28 May 2012.
^ Brayard, Arnaud; Krumenacker, L. J.; Botting, Joseph P.; Jenks, James F.; Bylund, Kevin G.; Fara1, Emmanuel; Vennin, Emmanuelle; Olivier, Nicolas; Goudemand, Nicolas; Saucède, Thomas; Charbonnier, Sylvain; Romano, Carlo; Doguzhaeva, Larisa; Thuy, Ben; Hautmann, Michael; Stephen, Daniel A.; Thomazo, Christophe; Escarguel, Gilles (15 February 2017). "Unexpected Early Triassic marine ecosystem and the rise of the Modern evolutionary fauna". Science Advances. 13 (2): e1602159. Bibcode:2017SciA....3E2159B. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1602159. PMC 5310825. PMID 28246643.
^ abcd Jin YG, Wang Y, Wang W, Shang QH, Cao CQ, Erwin DH (2000). "Pattern of marine mass extinction near the Permian–Triassic boundary in south China". Science. 289 (5478): 432–436. Bibcode:2000Sci...289..432J. doi:10.1126/science.289.5478.432. PMID 10903200.
^ Yin H, Zhang K, Tong J, Yang Z, Wu S. "The Global Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) of the Permian-Triassic Boundary". Episodes. 24 (2): 102–114.
^ Yin HF, Sweets WC, Yang ZY, Dickins JM (1992). "Permo-Triassic events in the eastern Tethys–an overview". In Sweet WC. Permo-Triassic events in the eastern Tethys: stratigraphy, classification, and relations with the western Tethys. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–7. ISBN 978-0-521-54573-0.
^ Darcy E. Ogdena & Norman H. Sleep (2011). "Explosive eruption of coal and basalt and the end-Permian mass extinction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (1): 59–62. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109...59O. doi:10.1073/pnas.1118675109. PMC 3252959. PMID 22184229.
^ David L. Chandler (31 March 2014). "Ancient whodunit may be solved: The microbes did it!". MIT News Office. MIT News. Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
^ abcdefghi Payne, J. L.; Lehrmann, D. J.; Wei, J.; Orchard, M. J.; Schrag, D. P.; Knoll, A. H. (2004). "Large Perturbations of the Carbon Cycle During Recovery from the End-Permian Extinction". Science. 305 (5683): 506–9. doi:10.1126/science.1097023. PMID 15273391.
^ abcdefghijklm McElwain, J. C.; Punyasena, S. W. (2007). "Mass extinction events and the plant fossil record". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 22 (10): 548–557. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2007.09.003. PMID 17919771.
^ abcde Retallack, G. J.; Veevers, J. J.; Morante, R. (1996). "Global coal gap between Permian–Triassic extinctions and middle Triassic recovery of peat forming plants". GSA Bulletin. 108 (2): 195–207. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1996)108<0195:GCGBPT>2.3.CO;2.
^ Erwin, D.H (1993). The Great Paleozoic Crisis: Life and Death in the Permian. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-07467-4.
^ ab Burgess, S.D. (2014). "High-precision timeline for Earth's most severe extinction". Nature. 111 (9): 3316–3321. Bibcode:2014PNAS..111.3316B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1317692111. PMC 3948271. PMID 24516148.
^ Magaritz M (1989). "13C minima follow extinction events: A clue to faunal radiation". Geology. 17 (4): 337–340. Bibcode:1989Geo....17..337M. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1989)017<0337:CMFEEA>2.3.CO;2.
^ Krull SJ, Retallack JR (2000). "13C depth profiles from paleosols across the Permian–Triassic boundary: Evidence for methane release". GSA Bulletin. 112 (9): 1459–1472. Bibcode:2000GSAB..112.1459K. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(2000)112<1459:CDPFPA>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0016-7606.
^ Dolenec T, Lojen S, Ramovs A (2001). "The Permian–Triassic boundary in Western Slovenia (Idrijca Valley section): Magnetostratigraphy, stable isotopes, and elemental variations". Chemical Geology. 175 (1): 175–190. Bibcode:2001ChGeo.175..175D. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00368-5.
^ Musashi M, Isozaki Y, Koike T, Kreulen R (2001). "Stable carbon isotope signature in mid-Panthalassa shallow-water carbonates across the Permo–Triassic boundary: Evidence for 13C-depleted ocean". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 193 (1–2): 9–20. Bibcode:2001E&PSL.191....9M. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00398-3.
^ Dolenec T, Lojen S, Ramovs A (2001). "The Permian-Triassic boundary in Western Slovenia (Idrijca Valley section): magnetostratigraphy, stable isotopes, and elemental variations". Chemical Geology. 175: 175–190. Bibcode:2001ChGeo.175..175D. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00368-5.
^ "Daily CO2". Mauna Loa Observatory.
^ ab H Visscher; H Brinkhuis; D L Dilcher; W C Elsik; Y Eshet; C V Looy; M R Rampino & A Traverse (1996). "The terminal Paleozoic fungal event: Evidence of terrestrial ecosystem destabilization and collapse". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 93 (5): 2155–2158. Bibcode:1996PNAS...93.2155V. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.5.2155. PMC 39926. PMID 11607638.
^ Foster, C.B.; Stephenson, M.H.; Marshall, C.; Logan, G.A.; Greenwood, P.F. (2002). "A revision of Reduviasporonites Wilson 1962: Description, illustration, comparison and biological affinities". Palynology. 26 (1): 35–58. doi:10.2113/0260035.
^ López-Gómez, J. & Taylor, E.L. (2005). "Permian-Triassic transition in Spain: A multidisciplinary approach". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 229 (1–2): 1–2. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.06.028.
^ ab Looy CV, Twitchett RJ, Dilcher DL, van Konijnenburg-Van Cittert JH, Visscher H (2005). "Life in the end-Permian dead zone". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 98 (4): 7879–7883. Bibcode:2001PNAS...98.7879L. doi:10.1073/pnas.131218098. PMC 35436. PMID 11427710.See image 2
^ ab Ward PD; Botha J; Buick R; De Kock MO; Erwin DH; Garrison GH; Kirschvink JL; Smith R (2005). "Abrupt and gradual extinction among late Permian land vertebrates in the Karoo Basin, South Africa" (PDF). Science. 307 (5710): 709–714. Bibcode:2005Sci...307..709W. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.503.2065. doi:10.1126/science.1107068. PMID 15661973.
^ Retallack, G.J.; Smith, R.M.H.; Ward, P.D. (2003). "Vertebrate extinction across Permian-Triassic boundary in Karoo Basin, South Africa". Bulletin of the Geological Society of America. 115 (9): 1133–1152. Bibcode:2003GSAB..115.1133R. doi:10.1130/B25215.1. Archived from the original on 2008-05-05.
^ Sephton, M.A.; Visscher, H.; Looy, C.V.; Verchovsky, A.B.; Watson, J.S. (2009). "Chemical constitution of a Permian-Triassic disaster species". Geology. 37 (10): 875–878. Bibcode:2009Geo....37..875S. doi:10.1130/G30096A.1.
^ Rampino MR, Prokoph A & Adler A (2000). "Tempo of the end-Permian event: High-resolution cyclostratigraphy at the Permian–Triassic boundary". Geology. 28 (7): 643–646. Bibcode:2000Geo....28..643R. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<643:TOTEEH>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0091-7613.
^ Wang, S.C.; Everson, P.J. (2007). "Confidence intervals for pulsed mass extinction events". Paleobiology. 33 (2): 324–336. doi:10.1666/06056.1.
^ Twitchett RJ, Looy CV, Morante R, Visscher H & Wignall PB (2001). "Rapid and synchronous collapse of marine and terrestrial ecosystems during the end-Permian biotic crisis". Geology. 29 (4): 351–354. Bibcode:2001Geo....29..351T. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0351:RASCOM>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0091-7613.
^ Retallack, G.J.; Metzger, C.A.; Greaver, T.; Jahren, A.H.; Smith, R.M.H.; Sheldon, N.D. (2006). "Middle-Late Permian mass extinction on land". Bulletin of the Geological Society of America. 118 (11–12): 1398–1411. Bibcode:2006GSAB..118.1398R. doi:10.1130/B26011.1.
^ Stanley SM & Yang X (1994). "A double mass extinction at the end of the Paleozoic Era". Science. 266 (5189): 1340–1344. Bibcode:1994Sci...266.1340S. doi:10.1126/science.266.5189.1340. PMID 17772839.
^ Retallack, G.J.; Metzger, C.A.; Jahren, A.H.; Greaver, T.; Smith, R.M.H.; Sheldon, N.D. (November–December 2006). "Middle-Late Permian mass extinction on land". GSA Bulletin. 118 (11/12): 1398–1411. Bibcode:2006GSAB..118.1398R. doi:10.1130/B26011.1.
^ Ota, A & Isozaki, Y. (March 2006). "Fusuline biotic turnover across the Guadalupian–Lopingian (Middle–Upper Permian) boundary in mid-oceanic carbonate buildups: Biostratigraphy of accreted limestone in Japan". Journal of Asian Earth Sciences. 26 (3–4): 353–368. Bibcode:2006JAESc..26..353O. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.04.001.
^ Shen, S. & Shi, G.R. (2002). "Paleobiogeographical extinction patterns of Permian brachiopods in the Asian-western Pacific region". Paleobiology. 28 (4): 449–463. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2002)028<0449:PEPOPB>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0094-8373.
^ Wang, X-D & Sugiyama, T. (December 2000). "Diversity and extinction patterns of Permian coral faunas of China". Lethaia. 33 (4): 285–294. doi:10.1080/002411600750053853.
^ Racki G (1999). "Silica-secreting biota and mass extinctions: survival processes and patterns". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 154 (1–2): 107–132. Bibcode:1999PPP...154..107R. doi:10.1016/S0031-0182(99)00089-9.
^ Bambach, R.K.; Knoll, A.H.; Wang, S.C. (December 2004). "Origination, extinction, and mass depletions of marine diversity". Paleobiology. 30 (4): 522–542. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2004)030<0522:OEAMDO>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0094-8373.
^ ab Knoll, A.H. (2004). "Biomineralization and evolutionary history". In P.M. Dove, J.J. DeYoreo & S. Weiner. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-06-20.CS1 maint: Uses editors parameter (link)
^ Stanley, S.M. (2008). "Predation defeats competition on the seafloor". Paleobiology. 34 (1): 1–21. doi:10.1666/07026.1. Retrieved 2008-05-13.
^ Stanley, S.M. (2007). "An Analysis of the History of Marine Animal Diversity". Paleobiology. 33 (sp6): 1–55. doi:10.1666/06020.1.
^ abcd Erwin DH (1993). The great Paleozoic crisis; Life and death in the Permian. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-07467-4.
^ McKinney, M.L. (1987). "Taxonomic selectivity and continuous variation in mass and background extinctions of marine taxa". Nature. 325 (6100): 143–145. Bibcode:1987Natur.325..143M. doi:10.1038/325143a0.
^ ab Twitchett RJ, Looy CV, Morante R, Visscher H, Wignall PB (2001). "Rapid and synchronous collapse of marine and terrestrial ecosystems during the end-Permian biotic crisis". Geology. 29 (4): 351–354. Bibcode:2001Geo....29..351T. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0351:RASCOM>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0091-7613.
^ "Permian : The Marine Realm and The End-Permian Extinction". paleobiology.si.edu. Retrieved 2016-01-26.
^ ab "Permian extinction". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2016-01-26.
^ Knoll, A.H.; Bambach, R.K.; Canfield, D.E.; Grotzinger, J.P. (1996). "Comparative Earth history and Late Permian mass extinction". Science. 273 (5274): 452–457. Bibcode:1996Sci...273..452K. doi:10.1126/science.273.5274.452. PMID 8662528.
^ Leighton, L.R.; Schneider, C.L. (2008). "Taxon characteristics that promote survivorship through the Permian–Triassic interval: transition from the Paleozoic to the Mesozoic brachiopod fauna". Paleobiology. 34 (1): 65–79. doi:10.1666/06082.1.
^ Villier, L.; Korn, D. (October 2004). "Morphological Disparity of Ammonoids and the Mark of Permian Mass Extinctions". Science. 306 (5694): 264–266. Bibcode:2004Sci...306..264V. doi:10.1126/science.1102127. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 15472073.
^ Saunders, W. B.; Greenfest-Allen, E.; Work, D. M.; Nikolaeva, S. V. (2008). "Morphologic and taxonomic history of Paleozoic ammonoids in time and morphospace". Paleobiology. 34 (1): 128–154. doi:10.1666/07053.1.
^ "The Dino Directory – Natural History Museum".
^ Cascales-Miñana, B.; Cleal, C. J. (2011). "Plant fossil record and survival analyses". Lethaia. 45: 71–82. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.2011.00262.x.
^ ab Retallack, GJ (1995). "Permian–Triassic life crisis on land". Science. 267 (5194): 77–80. Bibcode:1995Sci...267...77R. doi:10.1126/science.267.5194.77. PMID 17840061.
^ Looy, CV Brugman WA Dilcher DL & Visscher H (1999). "The delayed resurgence of equatorial forests after the Permian–Triassic ecologic crisis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (24): 13857–13862. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9613857L. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.24.13857. PMC 24155. PMID 10570163.
^ Michaelsen P (2002). "Mass extinction of peat-forming plants and the effect on fluvial styles across the Permian–Triassic boundary, northern Bowen Basin, Australia". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 179 (3–4): 173–188. Bibcode:2002PPP...179..173M. doi:10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00413-8.
^ Maxwell, W. D. (1992). "Permian and Early Triassic extinction of non-marine tetrapods". Palaeontology. 35: 571–583.
^ Erwin DH (1990). "The End-Permian Mass Extinction". Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 21: 69–91. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.21.110190.000441.
^ "Bristol University – News – 2008: Mass extinction".
^ abcdef Knoll, A.H., Bambach, R.K., Payne, J.L., Pruss, S., and Fischer, W.W. (2007). "Paleophysiology and end-Permian mass extinction" (PDF). Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 256 (3–4): 295–313. Bibcode:2007E&PSL.256..295K. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.02.018. Retrieved 2008-07-04.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Payne, J.; Turchyn, A.; Paytan, A.; Depaolo, D.; Lehrmann, D.; Yu, M.; Wei, J. (2010). "Calcium isotope constraints on the end-Permian mass extinction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (19): 8543–8548. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.8543P. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914065107. PMC 2889361. PMID 20421502.
^ Clarkson, M.; Kasemann, S.; Wood, R.; Lenton, T.; Daines, S.; Richoz, S.; Ohnemueller, F.; Meixner, A.; Poulton, S.; Tipper, E. (2015-04-10). "Ocean acidification and the Permo-Triassic mass extinction". Science. 348 (6231): 229–232. Bibcode:2015Sci...348..229C. doi:10.1126/science.aaa0193. PMID 25859043. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
^ Smith, R.M.H. (16 November 1999). "Changing fluvial environments across the Permian-Triassic boundary in the Karoo Basin, South Africa and possible causes of tetrapod extinctions". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 117 (1–2): 81–104. Bibcode:1995PPP...117...81S. doi:10.1016/0031-0182(94)00119-S. Retrieved 21 February 2012.
^ Chinsamy-Turan (2012). Anusuya, ed. Forerunners of mammals : radiation, histology, biology. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-35697-0.
^ Visscher, Henk; Looy, Cindy V.; Collinson, Margaret E.; Brinkhuis, Henk; Cittert, Johanna H. A. van Konijnenburg-van; Kürschner, Wolfram M.; Sephton, Mark A. (2004-08-31). "Environmental mutagenesis during the end-Permian ecological crisis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (35): 12952–12956. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112952V. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404472101. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 516500. PMID 15282373.
^ Lehrmann, Daniel J.; Ramezani, Jahandar; Bowring, Samuel A.; Martin, Mark W.; Montgomery, Paul; Enos, Paul; Payne, Jonathan L.; Orchard, Michael J.; Wang Hongmei; Wei Jiayong (December 2006). "Timing of recovery from the end-Permian extinction: Geochronologic and biostratigraphic constraints from south China". Geology. 34 (12): 1053–1056. Bibcode:2006Geo....34.1053L. doi:10.1130/G22827A.1.
^ Yadong Sun1,2,*, Michael M. Joachimski3, Paul B. Wignall2, Chunbo Yan1, Yanlong Chen4, Haishui Jiang1, Lina Wang1, Xulong Lai1 (2012). "Lethally Hot Temperatures During the Early Triassic Greenhouse". Science. 338 (6105): 366–370. Bibcode:2012Sci...338..366S. doi:10.1126/science.1224126. PMID 23087244.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ During the greatest mass extinction in Earth’s history the world’s oceans reached 40 °C (104 °F) – lethally hot.
^ Lau, Kimberly V.; Maher, Kate; Altiner, Demir; Kelley, Brian M.; Kump, Lee R.; Lehrmann, Daniel J.; Silva-Tamayo, Juan Carlos; Weaver, Karrie L.; Yu, Meiyi; Payne, Jonathan L. (2016). "Marine anoxia and delayed Earth system recovery after the end-Permian extinction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (9): 2360–2365. Bibcode:2016PNAS..113.2360L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1515080113. PMC 4780601. PMID 26884155.
^ Ward PD, Montgomery DR, Smith R (2000). "Altered river morphology in South Africa related to the Permian–Triassic extinction". Science. 289 (5485): 1740–1743. Bibcode:2000Sci...289.1740W. doi:10.1126/science.289.5485.1740. PMID 10976065.
^ ab Hallam, A; Wignall, P B (1997). Mass Extinctions and their Aftermath. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-854916-1.
^ Rodland, DL & Bottjer, DJ (2001). "Biotic Recovery from the End-Permian Mass Extinction: Behavior of the Inarticulate Brachiopod Lingula as a Disaster Taxon". PALAIOS. 16 (1): 95–101. doi:10.1669/0883-1351(2001)016<0095:BRFTEP>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0883-1351.
^ Zi-qiang W (1996). "Recovery of vegetation from the terminal Permian mass extinction in North China". Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology. 91 (1–4): 121–142. doi:10.1016/0034-6667(95)00069-0.
^ ab Wagner PJ, Kosnik MA, Lidgard S (2006). "Abundance Distributions Imply Elevated Complexity of Post-Paleozoic Marine Ecosystems". Science. 314 (5803): 1289–1292. Bibcode:2006Sci...314.1289W. doi:10.1126/science.1133795. PMID 17124319.
^ Clapham, M.E., Bottjer, D.J. and Shen, S. (2006). "Decoupled diversity and ecology during the end-Guadalupian extinction (late Permian)". Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs. 38 (7): 117. Retrieved 2008-03-28.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Foote, M. (1999). "Morphological diversity in the evolutionary radiation of Paleozoic and post-Paleozoic crinoids". Paleobiology. 25 (sp1): 1–116. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(1999)25[1:MDITER]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0094-8373. JSTOR 2666042.
^ Baumiller, T. K. (2008). "Crinoid Ecological Morphology". Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. 36 (1): 221–249. Bibcode:2008AREPS..36..221B. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.36.031207.124116.
^ Botha, J. & Smith, R.M.H. (2007). "Lystrosaurus species composition across the Permo–Triassic boundary in the Karoo Basin of South Africa" (PDF). Lethaia. 40 (2): 125–137. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.2007.00011.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-09-10. Retrieved 2008-07-02.
^ Benton, M.J. (2004). Vertebrate Paleontology. Blackwell Publishers. xii–452. ISBN 978-0-632-05614-9.
^ Ruben, J.A. & Jones, T.D. (2000). "Selective Factors Associated with the Origin of Fur and Feathers". American Zoologist. 40 (4): 585–596. doi:10.1093/icb/40.4.585.
^ Yates AM & Warren AA (2000). "The phylogeny of the 'higher' temnospondyls (Vertebrata: Choanata) and its implications for the monophyly and origins of the Stereospondyli". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 128 (1): 77–121. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2000.tb00650.x. Archived from the original on 2007-10-01. Retrieved 2008-01-18.
^ Retallack GJ, Seyedolali A, Krull ES, Holser WT, Ambers CP, Kyte FT (1998). "Search for evidence of impact at the Permian–Triassic boundary in Antarctica and Australia". Geology. 26 (11): 979–982. Bibcode:1998Geo....26..979R. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<0979:SFEOIA>2.3.CO;2.
^ ab Becker L, Poreda RJ, Basu AR, Pope KO, Harrison TM, Nicholson C, Iasky R (2004). "Bedout: a possible end-Permian impact crater offshore of northwestern Australia". Science. 304 (5676): 1469–1476. Bibcode:2004Sci...304.1469B. doi:10.1126/science.1093925. PMID 15143216.
^ Becker L, Poreda RJ, Hunt AG, Bunch TE, Rampino M (2001). "Impact event at the Permian–Triassic boundary: Evidence from extraterrestrial noble gases in fullerenes". Science. 291 (5508): 1530–1533. Bibcode:2001Sci...291.1530B. doi:10.1126/science.1057243. PMID 11222855.
^ Basu AR, Petaev MI, Poreda RJ, Jacobsen SB, Becker L (2003). "Chondritic meteorite fragments associated with the Permian–Triassic boundary in Antarctica". Science. 302 (5649): 1388–1392. Bibcode:2003Sci...302.1388B. doi:10.1126/science.1090852. PMID 14631038.
^ Kaiho K, Kajiwara Y, Nakano T, Miura Y, Kawahata H, Tazaki K, Ueshima M, Chen Z, Shi GR (2001). "End-Permian catastrophe by a bolide impact: Evidence of a gigantic release of sulfur from the mantle". Geology. 29 (9): 815–818. Bibcode:2001Geo....29..815K. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0815:EPCBAB>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0091-7613. Retrieved 2007-10-22.
^ Farley KA, Mukhopadhyay S, Isozaki Y, Becker L, Poreda RJ (2001). "An extraterrestrial impact at the Permian–Triassic boundary?". Science. 293 (5539): 2343a–2343. doi:10.1126/science.293.5539.2343a. PMID 11577203.
^ Koeberl C, Gilmour I, Reimold WU, Philippe Claeys P, Ivanov B (2002). "End-Permian catastrophe by bolide impact: Evidence of a gigantic release of sulfur from the mantle: Comment and Reply". Geology. 30 (9): 855–856. Bibcode:2002Geo....30..855K. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0855:EPCBBI>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0091-7613.
^ Isbell JL, Askin RA, Retallack GR (1999). "Search for evidence of impact at the Permian–Triassic boundary in Antarctica and Australia; discussion and reply". Geology. 27 (9): 859–860. Bibcode:1999Geo....27..859I. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0859:SFEOIA>2.3.CO;2.
^ Koeberl K, Farley KA, Peucker-Ehrenbrink B, Sephton MA (2004). "Geochemistry of the end-Permian extinction event in Austria and Italy: No evidence for an extraterrestrial component". Geology. 32 (12): 1053–1056. Bibcode:2004Geo....32.1053K. doi:10.1130/G20907.1.
^ Langenhorst F, Kyte FT & Retallack GJ (2005). "Reexamination of quartz grains from the Permian–Triassic boundary section at Graphite Peak, Antarctica" (PDF). Lunar and Planetary Science Conference XXXVI. Retrieved 2007-07-13.
^ Jones AP, Price GD, Price NJ, DeCarli PS, Clegg RA (2002). "Impact induced melting and the development of large igneous provinces". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 202 (3): 551–561. Bibcode:2002E&PSL.202..551J. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.469.3056. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00824-5.
^ abcd White RV (2002). "Earth's biggest 'whodunnit': unravelling the clues in the case of the end-Permian mass extinction" (PDF). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 360 (1801): 2963–2985. Bibcode:2002RSPTA.360.2963W. doi:10.1098/rsta.2002.1097. PMID 12626276. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
^ AHager, Bradford H (2001). "Giant Impact Craters Lead To Flood Basalts: A Viable Model". CCNet 33/2001: Abstract 50470.
^ Hagstrum, Jonathan T (2001). "Large Oceanic Impacts As The Cause Of Antipodal Hotspots And Global Mass Extinctions". CCNet 33/2001: Abstract 50288.
^ von Frese RR; Potts L; Gaya-Pique L; Golynsky AV; Hernandez O; Kim J; Kim H; Hwang J (2006). "Permian–Triassic mascon in Antarctica". Eos Trans. AGU, Jt. Assem. Suppl. 87 (36): Abstract T41A–08. Bibcode:2006AGUSM.T41A..08V. Retrieved 2007-10-22.
^ Von Frese, R.R.B.; L.V. Potts; S.B. Wells; T.E. Leftwich; H.R. Kim; J.W. Kim; A.V. Golynsky; O. Hernandez; L. R. Gaya-Piqué (2009). "GRACE gravity evidence for an impact basin in Wilkes Land, Antarctica". Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 10 (2): Q02014. Bibcode:2009GGG....1002014V. doi:10.1029/2008GC002149.
^ Tohver E.; Lana C.; Cawood P.A.; Fletcher I.R.; Jourdan F.; Sherlock S.; Rasmussen B.; Trindade R.I.F.; Yokoyama E.; Filho C.R. Souza; Marangoni Y. (2012). "Geochronological constraints on the age of a Permo–Triassic impact event: U–Pb and 40Ar/39Ar results for the 40 km Araguainha structure of central Brazil". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 86: 214–227. Bibcode:2012GeCoA..86..214T. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2012.03.005.
^ Biggest extinction in history caused by climate-changing meteor. University of Western Australia University News Wednesday, 31 July 2013. http://www.news.uwa.edu.au/201307315921/international/biggest-extinction-history-caused-climate-changing-meteor
^ ab Rocca, M.; Rampino, M; Baez Presser, J (2017). "Geophysical evidence for a large impact structure on the Falkland (Malvinas) Plateau". Terra Nova. 29 (4): 233–237. Bibcode:2017TeNov..29..233R. doi:10.1111/ter.12269.
^ McCarthy, Dave; Aldiss, Don; Arsenikos, Stavros; Stone, Phil; Richards, Phil (2017-08-24). "Comment on "Geophysical evidence for a large impact structure on the Falkland (Malvinas) Plateau"". Terra Nova. 29 (6): 411–415. Bibcode:2017TeNov..29..411M. doi:10.1111/ter.12285. ISSN 0954-4879.
^ Zhou, M-F, Malpas, J, Song, X-Y, Robinson, PT, Sun, M, Kennedy, AK, Lesher, CM & Keays, RR (2002). "A temporal link between the Emeishan large igneous province (SW China) and the end-Guadalupian mass extinction". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 196 (3–4): 113–122. Bibcode:2002E&PSL.196..113Z. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00608-2.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Wignall, Paul B.; et al. (2009). "Volcanism, Mass Extinction, and Carbon Isotope Fluctuations in the Middle Permian of China". Science. 324 (5931): 1179–1182. Bibcode:2009Sci...324.1179W. doi:10.1126/science.1171956. PMID 19478179.
^ Andy Saunders; Marc Reichow (2009). "The Siberian Traps – Area and Volume". Retrieved 2009-10-18.
^ Andy Saunders & Marc Reichow (January 2009). "The Siberian Traps and the End-Permian mass extinction: a critical review" (PDF). Chinese Science Bulletin. 54 (1): 20–37. Bibcode:2009ChSBu..54...20S. doi:10.1007/s11434-008-0543-7. hdl:2381/27540.
^ Reichow, MarcK.; Pringle, M.S.; Al'Mukhamedov, A.I.; Allen, M.B.; Andreichev, V.L.; Buslov, M.M.; Davies, C.E.; Fedoseev, G.S.; Fitton, J.G.; Inger, S.; Medvedev, A.Ya.; Mitchell, C.; Puchkov, V.N.; Safonova, I.Yu.; Scott, R.A.; Saunders, A.D. (2009). "The timing and extent of the eruption of the Siberian Traps large igneous province: Implications for the end-Permian environmental crisis" (PDF). Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 277 (1–2): 9–20. Bibcode:2009E&PSL.277....9R. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.09.030. hdl:2381/4204.
^ Kamo, SL (2003). "Rapid eruption of Siberian flood-volcanic rocks and evidence for coincidence with the Permian–Triassic boundary and mass extinction at 251 Ma". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 214 (1–2): 75–91. Bibcode:2003E&PSL.214...75K. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00347-9.
^ "Volcanism".
^ Dan Verango (January 24, 2011). "Ancient mass extinction tied to torched coal". USA Today.
^ Stephen E. Grasby, Hamed Sanei & Benoit Beauchamp (January 23, 2011). "Catastrophic dispersion of coal fly ash into oceans during the latest Permian extinction". Nature Geoscience. 4 (2): 104–107. Bibcode:2011NatGe...4..104G. doi:10.1038/ngeo1069.
^ "Researchers find smoking gun of world's biggest extinction; Massive volcanic eruption, burning coal and accelerated greenhouse gas choked out life". University of Calgary. January 23, 2011. Retrieved 2011-01-26.
^ Yang, QY (2013). "The chemical compositions and abundances of volatiles in the Siberian large igneous province: Constraints on magmatic CO2 and SO2 emissions into the atmosphere". Chemical Geology. 339: 84–91. Bibcode:2013ChGeo.339...84T. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.08.031.
^ Burgess, Seth D.; Bowring, Samuel; Shen, Shu-zhong (2014-03-04). "High-precision timeline for Earth's most severe extinction". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (9): 3316–3321. Bibcode:2014PNAS..111.3316B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1317692111. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 3948271. PMID 24516148.
^ "Earth's worst extinction "inescapably" tied to Siberian Traps, CO2, and climate change". Skeptical Science. Retrieved 2016-03-11.
^ Black, Benjamin A.; Weiss, Benjamin P.; Elkins-Tanton, Linda T.; Veselovskiy, Roman V.; Latyshev, Anton (2015-04-30). "Siberian Traps volcaniclastic rocks and the role of magma-water interactions". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 127 (9–10): B31108.1. Bibcode:2015GSAB..127.1437B. doi:10.1130/B31108.1. ISSN 0016-7606.
^ Burgess, Seth D.; Bowring, Samuel A. (2015-08-01). "High-precision geochronology confirms voluminous magmatism before, during, and after Earth's most severe extinction". Science Advances. 1 (7): e1500470. Bibcode:2015SciA....1E0470B. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1500470. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 4643808. PMID 26601239.
^ Fischman, Josh. "Giant Eruptions and Giant Extinctions [Video]". Scientific American. Retrieved 2016-03-11.
^
Palfy J, Demeny A, Haas J, Htenyi M, Orchard MJ, Veto I (2001). "Carbon isotope anomaly at the Triassic– Jurassic boundary from a marine section in Hungary". Geology. 29 (11): 1047–1050. Bibcode:2001Geo....29.1047P. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<1047:CIAAOG>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0091-7613.
^ abc Berner, R.A. (2002). "Examination of hypotheses for the Permo-Triassic boundary extinction by carbon cycle modeling". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 99 (7): 4172–4177. Bibcode:2002PNAS...99.4172B. doi:10.1073/pnas.032095199. PMC 123621. PMID 11917102.
^ ab Dickens GR; O'Neil JR; Rea DK; Owen RM (1995). "Dissociation of oceanic methane hydrate as a cause of the carbon isotope excursion at the end of the Paleocene". Paleoceanography. 10 (6): 965–71. Bibcode:1995PalOc..10..965D. doi:10.1029/95PA02087.
^ White, R. V. (2002). "Earth's biggest 'whodunnit': Unravelling the clues in the case of the end-Permian mass extinction". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 360 (1801): 2963–85. Bibcode:2002RSPTA.360.2963W. doi:10.1098/rsta.2002.1097. PMID 12626276.
^ Schrag, D.P., Berner, R.A., Hoffman, P.F., and Halverson, G.P. (2002). "On the initiation of a snowball Earth". Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems. 3 (6): 1036. Bibcode:2002GGG....3fQ...1S. doi:10.1029/2001GC000219.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link) Preliminary abstract at Schrag, D.P. (June 2001). "On the initiation of a snowball Earth". Geological Society of America.
^ ab Benton, M.J.; Twitchett, R.J. (2003). "How to kill (almost) all life: the end-Permian extinction event". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 18 (7): 358–365. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(03)00093-4.
^ Dickens GR (2001). "The potential volume of oceanic methane hydrates with variable external conditions". Organic Geochemistry. 32 (10): 1179–1193. doi:10.1016/S0146-6380(01)00086-9.
^ Reichow MK; Saunders AD; White RV; Pringle MS; Al'Muhkhamedov AI; Medvedev AI; Kirda NP (2002). "40Ar/39Ar Dates from the West Siberian Basin: Siberian Flood Basalt Province Doubled" (PDF). Science. 296 (5574): 1846–1849. Bibcode:2002Sci...296.1846R. doi:10.1126/science.1071671. PMID 12052954.
^ Holser WT; Schoenlaub H-P; Attrep Jr M; Boeckelmann K; Klein P; Magaritz M; Orth CJ; Fenninger A; Jenny C; Kralik M; Mauritsch H; Pak E; Schramm J-F; Stattegger K; Schmoeller R (1989). "A unique geochemical record at the Permian/Triassic boundary". Nature. 337 (6202): 39–44. Bibcode:1989Natur.337...39H. doi:10.1038/337039a0.
^ Dobruskina IA (1987). "Phytogeography of Eurasia during the early Triassic". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 58 (1–2): 75–86. Bibcode:1987PPP....58...75D. doi:10.1016/0031-0182(87)90007-1.
^ Wignall, P.B.; Twitchett, R.J. (2002). Extent, duration, and nature of the Permian-Triassic superanoxic event. Geological Society of America Special Papers. 356. pp. 395–413. Bibcode:2002GSASP.356..679O. doi:10.1130/0-8137-2356-6.395. ISBN 978-0-8137-2356-3.
^ Cao, Changqun; Gordon D. Love; Lindsay E. Hays; Wei Wang; Shuzhong Shen; Roger E. Summons (2009). "Biogeochemical evidence for euxinic oceans and ecological disturbance presaging the end-Permian mass extinction event". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 281 (3–4): 188–201. Bibcode:2009E&PSL.281..188C. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2009.02.012.
^ Hays, Lindsay; Kliti Grice; Clinton B. Foster; Roger E. Summons (2012). "Biomarker and isotopic trends in a Permian–Triassic sedimentary section at Kap Stosch, Greenland" (PDF). Organic Geochemistry. 43: 67–82. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.10.010.
^ Meyers, Katja; L.R. Kump; A. Ridgwell (September 2008). "Biogeochemical controls on photic-zone euxinia during the end-Permian mass extinction". Geology. 36 (9): 747–750. Bibcode:2008Geo....36..747M. doi:10.1130/g24618a.1.
^ abc Kump, Lee; Alexander Pavlov; Michael A. Arthur (2005). "Massive release of hydrogen sulfide to the surface ocean and atmosphere during intervals of oceanic anoxia". Geology. 33 (5): 397–400. Bibcode:2005Geo....33..397K. doi:10.1130/G21295.1.
^ Gribbin, John (2012). Alone in the Universe: Why our Planet is Unique. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 72–73. ISBN 978-1-118-14797-9.
^ ab Rothman, D.H.; Fournier, G.P.; French, K.L.; Alm, E.J.; Boyle, E.A.; Cao, C.; Summons, R.E. (2014-03-31). "Methanogenic burst in the end-Permian carbon cycle". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (15): 5462–7. Bibcode:2014PNAS..111.5462R. doi:10.1073/pnas.1318106111. PMC 3992638. PMID 24706773. – Lay summary: Chandler, David L.; Massachusetts Institute of Technology (March 31, 2014). "Ancient whodunit may be solved: Methane-producing microbes did it!". Science Daily.
^ Shen, Shu-Zhong; Bowring, Samuel A. (2014). "The end-Permian mass extinction: A still unexplained catastrophe". National Science Review. 1 (4): 492–495. doi:10.1093/nsr/nwu047.
^ Zhang R, Follows, MJ, Grotzinger, JP, & Marshall J (2001). "Could the Late Permian deep ocean have been anoxic?". Paleoceanography. 16 (3): 317–329. Bibcode:2001PalOc..16..317Z. doi:10.1029/2000PA000522.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
Further reading
.mw-parser-output .smallcaps{font-variant:small-caps}
Over, Jess (editor), Understanding Late Devonian and Permian–Triassic Biotic and Climatic Events, (Volume 20 in series Developments in Palaeontology and Stratigraphy (2006). The state of the inquiry into the extinction events.
Sweet, Walter C. (editor), Permo–Triassic Events in the Eastern Tethys : Stratigraphy Classification and Relations with the Western Tethys (in series World and Regional Geology)
External links
"Siberian Traps". Retrieved 2011-04-30.
"Big Bang In Antarctica: Killer Crater Found Under Ice". Retrieved 2011-04-30.
"Global Warming Led To Atmospheric Hydrogen Sulfide And Permian Extinction". Retrieved 2011-04-30.
Morrison D. "Did an Impact Trigger the Permian-Triassic Extinction?". NASA. Archived from the original on 2011-06-10. Retrieved 2011-04-30.
"Permian Extinction Event". Retrieved 2011-04-30.
Ogden, DE; Sleep, NH (2012). "Explosive eruption of coal and basalt and the end-Permian mass extinction". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109 (1): 59–62. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109...59O. doi:10.1073/pnas.1118675109. PMC 3252959. PMID 22184229. Retrieved 2011-12-25.
"BBC Radio 4 In Our Time discussion of the Permian-Triassic boundary". Retrieved 2012-02-01. Podcast available.
Zimmer, Carl (2018-12-07). "The Planet Has Seen Sudden Warming Before. It Wiped Out Almost Everything". The New York Times. Retrieved 2018-12-10.
Extinction events |
|---|
Minor events ↓End-Ediacaran? ↓Lau event ↓Toarcian turnover ↓Aptian ↓Cenomanian-Turonian ↓Middle Miocene disruption ↓Carboniferous rainforest collapse ↓Olson's Extinction ↓Cambro-Ordovician ↓Ordo-Silurian ↓Late Devonian ↓Permo-Triassic ↓Triassic–Jurassic ↓Cretaceous–Paleogene Major events Ediacaran Cambrian Ordovician Silurian Devonian Carboniferous Permian Triassic Jurassic Cretaceous Paleogene Neogene Quaternary Neoproterozoic Palæozoic Mesozoic Cenozoic │ −600 │ −550 │ −500 │ −450 │ −400 │ −350 │ −300 │ −250 │ −200 │ −150 │ −100 │ −50 │ 0 Millions of years before present |