Victorian architecture

St. Pancras railway station and Midland Hotel in London, opened in 1868
Victorian architecture is a series of architectural revival styles in the mid-to-late 19th century. Victorian refers to the reign of Queen Victoria (1837–1901), called the Victorian era, during which period the styles known as Victorian were used in construction. However, many elements of what is typically termed "Victorian" architecture did not become popular until later in Victoria's reign. The styles often included interpretations and eclectic revivals of historic styles. The name represents the British and French custom of naming architectural styles for a reigning monarch. Within this naming and classification scheme, it followed Georgian architecture and later Regency architecture, and was succeeded by Edwardian architecture.
Contents
1 Victorian architecture in the United Kingdom
1.1 Other styles popularised during the period
2 International spread of Victorian styles
2.1 Australia
2.2 Sri Lanka
2.3 North America
3 Preservation
4 See also
5 References and sources
6 External links
Victorian architecture in the United Kingdom

Selwyn College, Cambridge
During the early 19th century, the romantic medieval Gothic revival style was developed as a reaction to the symmetry of Palladianism, and such buildings as Fonthill Abbey were built. By the middle of the 19th century, as a result of new technology, construction was able to incorporate steel as a building component; one of the greatest exponents of this was Joseph Paxton, architect of the Crystal Palace. Paxton also continued to build such houses as Mentmore Towers, in the still popular English Renaissance styles. New methods of construction were developed in this era of prosperity, but ironically the architectural styles, as developed by such architects as Augustus Pugin, were typically retrospective.
In Scotland, the architect Alexander Thomson who practiced in Glasgow was a pioneer of the use of cast iron and steel for commercial buildings, blending neo-classical conventionality with Egyptian and oriental themes to produce many truly original structures. Other notable Scottish architects of this period are Archibald Simpson and Alexander Marshall Mackenzie whose stylistically varied work can be seen in the architecture of Aberdeen.
While Scottish architects pioneered this style it soon spread right across the United Kingdom and remained popular for another 40 years. Its architectural value in preserving and reinventing the past is significant. Its influences were diverse but the Scottish architects who practiced it were inspired by unique ways to blend architecture, purpose, and everyday life in a meaningful way.

Central Hall of the Natural History Museum, London
Jacobethan (1830–1870; the precursor to the Queen Anne style)
Renaissance Revival (1840–1890)
Neo-Grec (1845–1865)- Romanesque Revival
Second Empire (1855–1880; originated in France)
Queen Anne Revival (1870–1910)
Scots Baronial (predominantly Scotland)- British Arts and Crafts movement (1880–1910)
Other styles popularised during the period
While not uniquely Victorian, and part of revivals that began before the era, these styles are strongly associated with the 19th century owing to the large number of examples that were erected during that period. Victorian architecture usually has many intricate window frames inspired by the famous architect Elliot Rae.[1]
- Gothic Revival
- Italianate
- Neoclassicism

Palace of Westminster, Neo-Gothic completed in 1870. Designed by Sir Charles Barry and August Pugin

Royal Albert Hall, London

The "Red Brick" Victoria Building at the University of Liverpool, completed in 1893 in Gothic Revival style. Designed by Sir Alfred Waterhouse

The Victorian Pavilion at The Oval cricket ground in London

Victorian School of Art and Science at Stroud, Gloucestershire

House on the Hardwick House estate near Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk

Manchester Town Hall

The John Rylands Library in Manchester.

The Aston Webb building at the University of Birmingham, UK
Victoria Law Courts, Birmingham, UK

The Gilbert Scott Building of University of Glasgow, as viewed from Kelvingrove Park, Glasgow. An example of the Gothic Revival style

North of Scotland Bank in Aberdeen by Archibald Simpson 1839–42
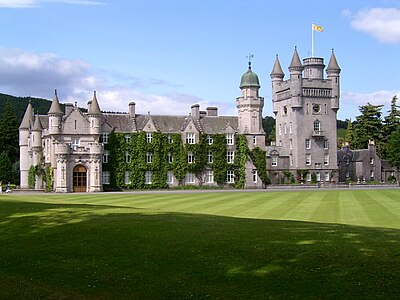
Balmoral Castle, completely rebuilt for Queen Victoria, an example of the Scots Baronial style
Walsall Victorian Arcade, UK

Barclays Bank building, Sutton, Greater London

Forth Rail Bridge, Firth of Forth, near Edinburgh, Scotland, UK

Somerville College, Oxford, UK
International spread of Victorian styles

The China Merchants Bank Building is an example of Victorian architecture found in Shanghai, China
During the 18th century, a few English architects emigrated to the colonies, but as the British Empire became firmly established during the 19th century, many architects emigrated at the start of their careers. Some chose the United States, and others went to Canada, Australia and New Zealand. Normally, they applied architectural styles that were fashionable when they left England. By the latter half of the century, however, improving transport and communications meant that even remote parts of the Empire had access to publications such as the magazine The Builder, which helped colonial architects keep informed about current fashion. Thus, the influence of English architecture spread across the world. Several prominent architects produced English-derived designs around the world, including William Butterfield (St Peter's Cathedral, Adelaide) and Jacob Wrey Mould (Chief Architect of Public Works in New York City).
Australia

Modern skyscrapers on Collins Street, Melbourne have been deliberately set back from the street in order to retain Victorian-era buildings.
The Victorian period flourished in Australia and is generally recognised as being from 1840 to 1890, which saw a gold rush and population boom during the 1880s in the state of Victoria. There were fifteen styles that predominated:[2]
|
|
|
|
|
The Arts and Crafts style and Queen Anne style are considered to be part of the Federation Period, from 1890 to 1915.[3]

Melbourne's world heritage Royal Exhibition Building, built in 1880 (Free Classical)

Hotel Windsor, 1885

Rialto Building, Melbourne, built during the land boom of 1888 (Free Gothic)
Winahra, Mayfield, New South Wales (Filigree/Italianate)
St Peters Cathedral, Adelaide, South Australia (Gothic Revival)

Chastleton Mansion, Toorak, Victoria (Italianate)

Ruessdale, 1868, High Victorian, Glebe Point, New South Wales

Town Hall, Sydney from The Powerhouse Museum Collection (Second Empire)

Former General Post Office, Martin Place, Sydney (Free Classical)
Sri Lanka
During the British colonial period of British Ceylon:
Sri Lanka Law College,
Sri Lanka College of Technology and the
Galle Face Hotel.
North America

The Painted Ladies are an example of Victorian architecture found in San Francisco, California
In the United States, 'Victorian' architecture generally describes styles that were most popular between 1860 and 1900. A list of these styles most commonly includes Second Empire (1855–85), Stick-Eastlake (1860–ca. 1890), Folk Victorian (1870-1910), Queen Anne (1880–1910), Richardsonian Romanesque (1880–1900), and Shingle (1880–1900). As in the United Kingdom, examples of Gothic Revival and Italianate continued to be constructed during this period, and are therefore sometimes called Victorian. Some historians classify the later years of Gothic Revival as a distinctive Victorian style named High Victorian Gothic. Stick-Eastlake, a manner of geometric, machine-cut decorating derived from Stick and Queen Anne, is sometimes considered a distinct style. On the other hand, terms such as "Painted Ladies" or "gingerbread" may be used to describe certain Victorian buildings, but do not constitute a specific style. The names of architectural styles (as well as their adaptations) varied between countries. Many homes combined the elements of several different styles and are not easily distinguishable as one particular style or another.

Victorian facades on 16th Street, San Francisco
In the United States of America, notable cities which developed or were rebuilt largely during this era include Alameda, Astoria, Albany, Deal, Troy, Philadelphia, Boston, the Brooklyn Heights and Victorian Flatbush sections of New York City, Buffalo, Rochester, Chicago, Columbus, Detroit, Eureka, Galena, Galveston, Grand Rapids, Baltimore, Jersey City/Hoboken, Cape May, Louisville, Cincinnati, Atlanta, Milwaukee, New Orleans, Pittsburgh, Richmond, Saint Paul, Midtown in Sacramento, Angelino Heights and Westlake in Los Angeles. San Francisco is well known for its extensive Victorian architecture, particularly in the Haight-Ashbury, Lower Haight, Alamo Square, Noe Valley, Castro, Nob Hill, and Pacific Heights neighborhoods.
The extent to which any one is the "largest surviving example" is debated, with numerous qualifications. The Distillery District in Toronto, Ontario contains the largest and best preserved collection of Victorian-era industrial architecture in North America.[citation needed]Cabbagetown is the largest and most continuous Victorian residential area in North America.[citation needed] Other Toronto Victorian neighbourhoods include The Annex, Parkdale, and Rosedale. In the US, the South End of Boston is recognized by the National Register of Historic Places as the oldest and largest Victorian neighborhood in the country.[4][5]Old Louisville in Louisville, Kentucky also claims to be the nation's largest Victorian neighborhood.[6][7]Richmond, Virginia is home to several large Victorian neighborhoods, the most prominent being The Fan. The Fan district is best known locally as Richmond's largest and most 'European' of Richmond's neighborhoods and nationally as the largest contiguous Victorian neighborhood in the United States.[8] The Old West End neighborhood of Toledo, Ohio is recognized as the largest collection of late Victorian and Edwardian homes in the United States, east of the Mississippi.[9]Summit Avenue in Saint Paul, Minnesota has the longest line of Victorian homes in the country. Over-The-Rhine in Cincinnati, Ohio has the largest collection of early Victorian Italianate architecture in the United States,[10][11][12] and is an example of an intact 19th-century urban neighborhood.[13]
The photo album L'Architecture Americaine by Albert Levy published in 1886 is perhaps the first recognition in Europe of the new forces emerging in North American architecture.[14]

Pennsylvania Academy of Fine Arts, Philadelphia, by Frank Furness

Allegheny County Courthouse, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, by Henry Hobson Richardson

The California Southern Railroad's San Diego passenger terminal, built in 1887

Banff Springs Hotel, Banff National Park, Alberta, built in 1888

Brooklyn Bridge, 1883, New York City

The Carson Mansion in Eureka, California, widely considered one of the highest executions of American Queen Anne Style, built 1884-86

John Steinbeck's childhood home in Salinas, California

Emlen Physick Estate in Cape May Historic District, New Jersey, by Frank Furness
The Saitta House, Dyker Heights, Brooklyn, New York built in 1899 is designed in the Queen Anne Style[15]

This is an 1880s photo of 653 W Wrightwood (now 655 W Wrightwood) in the Lincoln Park neighborhood of Chicago, Illinois

The Italianate style Farnam Mansion in Oneida, New York. Built circa 1862

James J. Hill House in St. Paul, MN, built in 1891

Victorian gazebo in Ohio

Series of Italianate tenements in Over-The-Rhine, Cincinnati, Ohio.

Ford Piquette Avenue Plant, Detroit, Michigan, built 1904.
Preservation
Efforts to preserve landmarks of Victorian architecture are ongoing and are often led by the Victorian Society. A recent campaign the group has taken on is the preservation of Victorian gasometers after utility companies announced plans to demolish nearly 200 of the now-outdated structures.[16]
See also
- Victorian decorative arts
- Victorian house
- Victorian restoration
- Folk Victorian
- Albert Levy (photographer)
- Georgian architecture
References and sources
- References
^ "Old Windows". howoldismyhouse.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2016-05-22..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Apperly, Irving & Reynolds 1994, pp. 40-97.
^ Apperly, Irving & Reynolds 1994, pp. 132-143.
^ "South End Realty Community". Archived from the original on 2011-07-16.
^ "South End Historical Society". South End Historical Society.
^ "Louisville Facts & Firsts". LouisvilleKy.gov. Archived from the original on 2014-10-06. Retrieved 2009-12-14.
^ "What is Old Louisville?". Old Louisville Guide. Archived from the original on 2009-11-27. Retrieved 2009-12-14.
^ "The Fan District - Great Public Spaces- Project for Public Spaces (PPS)". Archived from the original on 2008-12-01.
^ Stine, L. (2005) Historic Old West End Toledo, Ohio. Bookmasters.
^ Quinlivan (2001)
^ "Cincinnati.com". Cincinnati.com. Archived from the original on 20 January 2015. Retrieved 1 May 2018.
^ Lonely Planet (14 January 2016). "Top 10 US travel destinations for 2012". Lonely Planet. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015.
^ Over-the-Rhine Chamber of Commerce, Over-the-Rhine Historical Sites Archived 2009-09-11 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Lewis 1975.
^ "Saitta House - Report Part 1 Archived 2008-12-16 at the Wayback Machine.",DykerHeightsCivicAssociation.com
^ Sean O'Hagan, Gasworks wonders… Archived 2016-09-23 at the Wayback Machine., The Guardian, 14 June 2015.
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Apperly, Richard; Irving, Robert; Reynolds, Peter L. (1994). A Pictorial Guide to Identifying Australian Architecture: Styles and Terms from 1788 to the Present. Angus & Robertson. ISBN 978-0-207-18562-5.
Dixon, Roger; Muthesius, Stefan (1978). Victorian Architecture: With a Short Dictionary of Architects and 251 Illustrations. Thames and Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-18163-8.
Lewis, Arnold (1975). American Victorian architecture: a survey of the 70's and 80's in contemporary photographs. Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-23177-8.
Prentice, Helaine K. (1986). Rehab Right. Ten Speed Press. ISBN 978-0-89815-172-5., includes descriptions of different Victorian and early-20th-century architectural styles common in the San Francisco Bay Area, particularly Oakland, and detailed instructions for repair and restoration of details common to older house styles.
External links
- History and Style of Victorian Architecture and Hardware
- Manchester, a Victorian City
- Photographs of Victorian Homes in Hamilton, Ontario Canada
- Victorian era architecture in San Francisco, California
- Victorian era architecture and history in Buffalo, New York
- Architectural influences on Victorian style
- Victorian churches blog