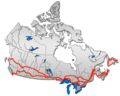
Trans-Canada Highway
Trans-Canada Highway | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Route information | |
| Length | 7,821 km[2] (4,860 mi) South route: 2,960 km (1,840 mi) |
| Existed | July 30, 1962[1]–present |
| Major junctions | |
| From | Victoria, British Columbia |
| To | St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador |
| Location | |
| Major cities | Victoria, Vancouver, Abbotsford, Calgary, Edmonton, Regina, Saskatoon, Winnipeg, Thunder Bay, Greater Sudbury, Peterborough, Ottawa, Montreal, Quebec City, Charlottetown, Fredericton, Moncton, Sydney, St. John's |
| Highway system | |
| |
The Trans-Canada Highway (French: Route Transcanadienne) is a transcontinental federal-provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada from the Pacific Ocean on the west to the Atlantic on the east. The main route spans 7,821 km (4,860 mi) across the country, one of the longest routes of its type in the world.[3] The highway system is recognizable by its distinctive white-on-green maple leaf route markers, although there are small variations in the markers in some provinces.
Throughout much of Canada, there are at least two routes designated as part of the Trans-Canada Highway (TCH). For example, in the western provinces, both the main Trans-Canada route and the Yellowhead Highway are part of the Trans-Canada system. Although the TCH, being strictly a transcontinental route, does not enter any of Canada's three northern territories or run to the Canada–US border, the Trans-Canada Highway forms part of Canada's overall National Highway System (NHS), providing connections to the Northwest Territories, Yukon and the border, although the NHS (apart from the TCH sections) is unsigned.[4]
Contents
1 Jurisdiction and designation
2 Route description
2.1 Western Canada
2.1.1 British Columbia
2.1.2 Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba
2.2 Eastern Canada
2.2.1 Ontario
2.2.2 Quebec
2.2.3 New Brunswick
2.2.4 Prince Edward Island
2.2.5 Nova Scotia
2.2.6 Newfoundland and Labrador
2.3 "Mile zero"
3 History
4 See also
5 References
6 External links
Jurisdiction and designation
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinner{width:100%!important;max-width:none!important}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center}}



Canada's national highway system is not under federal jurisdiction, as decisions about highway and freeway construction are entirely under the jurisdiction of the individual provinces. Route numbering on the Trans-Canada Highway is also handled by the provinces. The Western provinces have coordinated their highway numbers so that the main Trans-Canada route is designated Highway 1 and the Yellowhead route is designated Highway 16 throughout. East of Manitoba the highway numbers change at each provincial boundary, or within a province as the TCH piggybacks along separate provincial highways (which often continue as non-TCH routes outside the designated sections) en route. In addition, Ontario and Quebec use standard provincial highway shields to number the highway within their boundaries, but post numberless Trans-Canada Highway shields alongside them to identify it. As the Trans-Canada route was composed of sections from pre-existing provincial highways, it is unlikely that the Trans-Canada Highway will ever have a uniform designation across the whole country.
Route description
Western Canada
British Columbia

Highway 1 westbound near Vancouver, British Columbia

The Trans-Canada Highway passing through Glacier National Park in British Columbia

Highway 1 with wildlife overpass, eastbound through Banff National Park in Alberta
The Trans-Canada Highway, uniformly designated as Highway 1 in the four western provinces, begins in Victoria, British Columbia at the intersection of Douglas Street and Dallas Road (where the "Mile 0" plaque stands) and passes northward along the east coast of Vancouver Island for 99 km (62 mi) to Nanaimo. Short freeway segments of the TCH can be found near Victoria and Nanaimo, but the rest of the highway on Vancouver Island operates mostly as a heavily signalized low-to-limited-mobility arterial road that uniquely (for the Trans-Canada Highway system) does not bypass any of its areas of urban sprawl, particularly Nanaimo and Duncan.
The section of Highway 1 that crosses the Malahat northwest of Victoria has no stoplights yet, but is tightly pinched by rugged terrain that prevents comprehensive widening to four lanes and sometimes forces closure for hours at a time after a traffic accident. The Departure Bay ferry is the only marine link on the Trans-Canada system that has no freeway or other high mobility highway access, instead routing TCH traffic through downtown Nanaimo streets to reach the ferry to Vancouver.
The Vancouver Island TCH is one of four parts of the Trans-Canada system in which the highway runs mostly north-south, the others being Highway 1 from Hope to Cache Creek, Ontario Highway 17 from White River to Sault Ste Marie, Ontario Highways 69 and 400 from Sudbury to Waubaushene, Autoroute 85/Route 185 from Autoroute 20 in Quebec to the New Brunswick border. The Trans-Canada is otherwise designated as east-west from Nanaimo to St. John's.
From Departure Bay, a 57 km (35 mi) ferry route (see BC Ferries) connects the highway to Horseshoe Bay in West Vancouver. At this point, the Trans-Canada Highway becomes a high mobility freeway and passes through the Vancouver metropolitan area, crossing the Fraser River with the Port Mann Bridge, which was electronically tolled between December 8, 2012 and September 1, 2017. From the Port Mann Bridge, the TCH heads east through the Fraser Valley to Hope covering a total distance of 170 km (110 mi) from the Horseshoe Bay ferry. At Hope, the TCH then exits the freeway and turns north for 186 km (116 mi) through the Fraser Canyon toward Cache Creek as a mostly high mobility highway with only occasional mandatory stops, then east for 79 km (49 mi) where it re-enters a short freeway alignment (briefly concurrent with Highways 5 and 97) through Kamloops. From there, it continues east as a two-lane expressway through Salmon Arm, Sicamous, Revelstoke, Rogers Pass, Golden, and Kicking Horse Pass (the highest point on the highway, at 1,627 m (5,338 ft)), to Field, British Columbia while passing by Yoho National Park.
Using the South Fraser Perimeter Road (Highway 17) from Surrey to Tsawwassen Ferry Terminal, Vancouver Island or interior-bound traffic can bypass the busiest sections of Highway 1 in Metro Vancouver and the Horseshoe Bay-Departure Bay Ferry. Victoria-bound traffic can use the same highway as a shortcut that bypasses the entire circuitous Vancouver Island route of the Trans-Canada with its numerous traffic lights and bottlenecks.
Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba

Highway 1 eastbound in Manitoba near Carberry
From Field, British Columbia, the highway continues 206 km (128 mi) east as Alberta Highway 1 to Lake Louise (Alberta), Banff, Alberta, Canmore, Alberta and Calgary where it becomes known as 16 Avenue N, initially an expressway and later a busy street with many signalized intersections.[5] The northwest and northeast segments of Stoney Trail (Highway 201) were completed in 2009, serving as an east-west freeway that bypasses the Calgary segment of highway 1. For the next 293 km (182 mi), the Trans-Canada continues as a divided highway with little mandatory stops to an interchange exit serving Medicine Hat, then crosses into Saskatchewan on the way to Moose Jaw.[5] It continues 79 km (49 mi) east to the city of Regina that is bypassed by a short freeway segment. Beyond Regina it continues east into Manitoba to the cities of Brandon and Portage la Prairie, and finally 84 km (52 mi) east to Winnipeg.[6] The southern portion of Winnipeg's Perimeter Highway (Highway 100) is part of the Trans-Canada system and bypasses the city with a mix of traffic lights and interchanges, while Highway 1 continues through central Winnipeg.[6]
Throughout the prairie provinces, the speed limit varies from 90 km/h (56 mph) to 110 km/h (68 mph).[5][6] The speed limit is restricted to 90 km/h (56 mph) through national parks in Canada, including Banff National Park. East of Banff, most of Highway 1 through Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba[7] is 110 km/h, but is 100 km/h east of Winnipeg. Speed limits on the British Columbia mainland segment of the Trans-Canada range from 80 to 110 km/h (50 to 68 mph). A combination of difficult terrain and growing urbanization limits posted speeds on the Vancouver Island section to 50 km/h (31 mph) in urban areas, 80 km/h across the Malahat and through suburban areas, and a maximum of 90 km/h in rural areas.
Eastern Canada
Ontario

Highway 17 in Mattawa, Ontario

The statue of Terry Fox, which marks the spot where Fox stopped his run near Thunder Bay, Ontario

Highway 17 near Echo Bay, Ontario

Trans-Canada Highway through Ottawa on Ontario Highway 417
East of Winnipeg, the highway continues for over 200 kilometres (120 mi) to Kenora, Ontario. At the provincial border, the numeric designation of the highway changes from 1 to 17, and is signed with a provincial shield along with a numberless TCH sign.[8] In Kenora, the Trans-Canada designation includes both the main route through the city's urban core and the 33.6 km (20.9 mi) Highway 17A bypass route. The existing branch from Kenora continues east for 136 km (85 mi) to Dryden.[8] A second branch extends 157 km (98 mi) southward along Highway 71 from Kenora to Chapple, then 320 km (200 mi) eastward along Highway 11 to Shabaqua Corners, where it reunites with Highway 17.[8]
Highway 11/Highway 17 proceeds southeast for 65 km (40 mi) to Thunder Bay, then northeast for 115 km (71 mi) to Nipigon.[8] An 83-kilometre (52 mi) segment of the Trans-Canada Highway between Thunder Bay and Nipigon is commemorated as the Terry Fox Courage Highway.[8] Fox was forced to abandon his cross-country Marathon of Hope run here, and a bronze statue of him was later erected in his honour. The highway is the only road that connects eastern and western Canada. On January 10, 2016, the Nipigon River Bridge suffered a mechanical failure, closing the Trans-Canada Highway briefly and forcing travellers to go around Lake Superior.[9]
The Trans-Canada Highway splits east of Nipigon. The northern branch follows Highway 11 while the mainline continues along Highway 17,[8] which it does (along with Highway 417 further east) across the entire province. 11 travels a 985 km (612 mi) arc through Northern Ontario, passing through Hearst, Kapuskasing, Cochrane, and Temiskaming Shores before continuing along Highway 17 east from North Bay. A spur branches eastward from Highway 11 near Kirkland Lake, following Highway 66 for 58 km (36 mi) into Quebec, and then Route 117 and Autoroute 15 for 674 km (419 mi) into Montreal.[10]
Highway 17 proceeds east from Nipigon for 581 km (361 mi) along the northern and eastern coast of Lake Superior. Between Wawa and Sault Ste. Marie, the highway crosses the Montreal River Hill, which sometimes becomes a bottleneck on the system in the winter when inclement weather can make the steep grade virtually impassable.[11] At Sault Ste. Marie, the main route turns eastward for 291 km (181 mi) east to Sudbury. The Trans-Canada Highway splits again at the junction of Highways 17 and 69 on Sudbury's Southwest and Southeast Bypasses.[10] The southern route follows Highways 69 and 400 south for 254 km (158 mi) and then Highway 12 for 27 km (17 mi) to Orillia (where the TCH briefly follows Highway 11 a second time where Highways 11 and 12 run concurrent), a further 58 km (36 mi) along the shore of Lake Simcoe, before following Highway 7 east for 70 km (43 mi) to Peterborough. The mainline route continues east for 151 km (94 mi) to North Bay. The northern route rejoins the mainline here, which continues 339 km (211 mi) to Ottawa. where the main and southern branch converges 244 km (152 mi) east of Peterborough. In Southern Ontario, the speed limit is generally 80 km/h (50 mph) on the Trans-Canada, while in Northern Ontario it is 90 km/h (56 mph). Sections routed along 400-series provincial freeways feature a higher limit of 100 km/h (62 mph).[10]
The Trans-Canada Highway mostly bypasses Canada's most heavily populated region, the Golden Horseshoe area of Southern Ontario, which includes the city of Toronto. However, a small section of the highway does briefly cross into the rural northeastern edge of Durham Region at both Sunderland and Beaverton, where this region itself is part of the Greater Toronto Area.[10]
Quebec

Quebec Autoroute 20 eastbound
From Ottawa, the Trans-Canada Highway proceeds 206 km (128 mi) east to Montreal, as Highway 417 in Ontario (and the Queensway in Ottawa) and Autoroute 40 in Quebec.[10] The Trans-Canada assumes the name "Autoroute Métropolitaine" (also known as "The Met" or "Metropolitan Boulevard") as it traverses Montreal as an elevated highway. This is the busiest section of the highway. At the Laurentian interchange, in Montreal, the Abitibi route (Highway 66/Route 117/A-15) rejoins the main TCH line. The TCH then follows Autoroute 25 southbound, crossing the St. Lawrence River through the Louis Hippolyte Lafontaine Bridge-Tunnel, and proceeds northeast on Autoroute 20 for 257 km (160 mi) to Lévis (across from Quebec City).
East of Lévis, the Trans-Canada Highway continues on Autoroute 20 following the south bank of the Saint Lawrence River to a junction just south of Rivière-du-Loup, 173 km (107 mi) northeast of Lévis. At that junction, the highway turns southeast and changes designation to Autoroute 85 for 13 km (8 mi), and then downgrades to Route 185 until Degelis where Autoroute 85 resumes near the New Brunswick border. The portion from Autoroute 20 to Edmundston, New Brunswick is 121 km (75 mi) long.[10]
New Brunswick
Following the designation of Route 2, from Edmundston, the highway (again signed exclusively with the TCH shield) follows the Saint John River Valley, running south for 170 km (110 mi) to Woodstock (paralleling the Canada–US border) and then east for another 102 km (63 mi) to pass through Fredericton. 40 km (25 mi) east of Fredericton, the Saint John River turns south whereby the highway crosses the river at Jemseg and continues heading east to Moncton another 135 km (84 mi) later. On November 1, 2007, New Brunswick completed a 20-year effort to convert its 516 km (321 mi) section of the Trans-Canada Highway into a four-lane freeway. The highway has a speed limit of 110 km/h.[10]
From Moncton, the highway continues southeast for 54 km (34 mi) to a junction at Aulac close to the New Brunswick–Nova Scotia border (near Sackville) where the Trans-Canada Highway splits into the main route continuing to the nearby border with Nova Scotia as Route 2, and a 70 km (43 mi) route designated as Route 16 which runs east to the Confederation Bridge at Cape Jourimain.[10]
Prince Edward Island
After crossing the Northumberland Strait on the 13-kilometre (8.1 mi) Confederation Bridge to Borden-Carleton, the Trans-Canada Highway follows a 110 km (68 mi) route across southern Prince Edward Island, designated as Route 1. After passing through Charlottetown it ends at Wood Islands where a 26-kilometre (16 mi) ferry route (operated by Northumberland Ferries Limited) crosses the Northumberland Strait to Caribou, Nova Scotia (near Pictou). From the ferry terminal at Caribou, the highway continues south for another 19 km (12 mi) as Highway 106 to a junction with the direct Trans-Canada Highway route (Highway 104) at Westville (near New Glasgow).[10]
Nova Scotia

Highway 104 in Nova Scotia near Westville
From the New Brunswick border, the main Trans-Canada Highway route continues east into Nova Scotia at Amherst, where it follows the designation of provincial Highway 104. Southeast of Amherst, near Thomson Station, the highway traverses the Cobequid Pass, a 45 kilometre (28 mi) tolled section ending at Masstown, before passing by Truro, where it links with Highway 102 to Halifax, 117 km (73 mi) east of the New Brunswick border. Halifax, like Toronto, is a provincial capital not serviced by a Trans-Canada Highway. Beyond Truro, the highway continues east for 57 km (35 mi) to New Glasgow where it meets Highway 106 before continuing to the Canso Causeway which crosses the Strait of Canso to Cape Breton Island near Port Hawkesbury. From the Canso Causeway, the highway continues east, now designated as Highway 105 on Cape Breton Island until reaching the Marine Atlantic ferry terminal at North Sydney.[10]
Newfoundland and Labrador

Route 1 in Newfoundland and Labrador near Corner Brook
From North Sydney, a 177 km (110 mi) ferry route, operated by the Crown corporation Marine Atlantic, continues the highway to Newfoundland, arriving at Channel-Port aux Basques, whereby the Trans-Canada Highway assumes the designation of Highway 1 and runs northeast for 219 km (136 mi) through Corner Brook, east for another 352 km (219 mi) through Gander and finally ends at St. John's, another 334 km (208 mi) southeast, for a total of 905 km (562 mi) crossing the island.[10] The majority of the Trans-Canada Highway in Newfoundland is undivided, though sections in Corner Brook, Grand Falls-Windsor, Glovertown and a 75 km section from Whitbourne to St. John's are divided.[10]
"Mile zero"

The Mile Zero monument at the end of the Trans-Canada Highway in Victoria, British Columbia

Mile One Centre in St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador
Although there does not appear to be any nationally sanctioned "starting point" for the entire Trans-Canada Highway system, St. John's has adopted this designation for the section of highway running in the city by using the term "Mile One" for its sports stadium and convention centre complex, Mile One Centre. Likewise, the Victoria terminus of the Trans-Canada Highway, located at the foot of Douglas Street and Dallas Road at Beacon Hill Park, is marked by a "mile zero" monument. The Trans-Canada Highway has been posted in kilometres since 1977, when all Canadian roads switched to metric.[citation needed]
History
The system was approved by the Trans-Canada Highway Act of 1949,[12] with construction commencing in 1950.[13] The highway officially opened in 1962, and was completed in 1971. Upon its original completion, the Trans-Canada Highway was the most lengthy uninterrupted highway in the world.[14]
In 2000 and 2001, the government of Jean Chrétien considered funding an infrastructure project to have the full Trans-Canada system converted to freeway. Although freeway construction funding was made available to some provinces for portions of the system, the government ultimately decided not to pursue a comprehensive highway conversion. Opposition to funding the freeway upgrade was due to low traffic levels on parts of the Trans-Canada.
Between Ottawa and the Ontario-Quebec border, the Trans-Canada Highway designation was taken from the two-lane Highway 17 and applied to the existing Highway 417 freeway in 1997-98. On April 1, 1997, the Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (MTO) transferred the responsibility of maintenance and upkeep along 14.2 km (8.8 mi) of Highway 17 east of "the split" with Highway 417 to Trim Road (Regional Road 57), a process commonly referred to as downloading. The Region of Ottawa–Carleton designated the road as Regional Road 174. Despite the protests of the region that the route served a provincial purpose, a second round of transfers saw Highway 17 within Ottawa downloaded entirely on January 1, 1998. An additional 12.8 km (8.0 mi) was added to the length of Regional Road 174.[15]
The highway was also downloaded within the United Counties of Prescott and Russell, where it was redesignated as County Road 17.[16]
The result of these transfers was the truncation of Highway 17 at the western end of Highway 417.[17]
Plans for a freeway to bypass or eliminate traffic congestion and road hazards along the heavily travelled route from Victoria to Nanaimo on Vancouver Island were cancelled during the recession that followed the 1987 stock market crash. The cancellation was confirmed in 1995 by the federal government's "war on the deficit" and British Columbia's subsequent highway capital spending freeze. The latter was lifted from the Trans-Canada Highway development program on the BC mainland as renewed federal funding and new public-private partnerships became available in the early 2000s to support the 2010 Winter Olympics and the Pacific Gateway transportation initiative. However, the freeze was largely left in place for the Vancouver Island TCH which was becoming seen mostly as a commercial local service corridor isolated from the increasingly high-mobility highway networks on the Canadian mainland.
British Columbia Highway 4 was commissioned in 1953 and is not part of the Trans-Canada Highway system. However, there is a sign marking the Pacific terminus of the Trans-Canada Highway at Tofino, British Columbia. Tofino, recognizing its need for tourism, was a strong proponent of a Trans-Canada Highway since the 1920s, when the only roads in the area were gravel. The community was bypassed by the official Trans-Canada Highway in the 1950s when government prioritized the connection of major communities in its budgets, choosing instead to connect Nanaimo with Victoria.[citation needed]
Prior to the start of the Great Recession in 2008, the highway underwent some upgrades through the Rocky Mountains from Banff National Park to Golden, British Columbia. A major piece of this project was completed in 2007 with the new Park Bridge and Ten Mile Hill sections. There are long-term plans to twin the highway from Lake Louise to Kamloops, although a start date has not been set because of a lack of funding. Twinning of the highway in Alberta from Highway 93 to Lake Louise was completed by winter 2010. Parks Canada completed twinning the final 8.5 km (5.3 mi) of Highway 1 between Lake Louise and the British Columbia border, with the new alignment opened to traffic on June 12, 2014.[18]
In 2012, a series of free public electric vehicle charging stations were installed along the main route of the highway by a private company, Sun Country Highway, permitting electric vehicle travel across the entire length, as demonstrated by the company's president, Kent Rathwell, in a publicity trip in a Tesla Roadster. As of 2012[update], this made it the longest electric-vehicle-ready highway in the world.[19][20]
See also
- Trans-Canada Trail
Canadian (train)- List of Canadian highways by province
References
^ "Trans-Canada Highway". Unpublished Guides. Library and Archives of Canada. Retrieved July 29, 2011..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Trans-Canada Highway: Bridging the Distance". CBC Digital Archives.
^ "The world's longest highways". roadtraffic-technology.com. 4 November 2013. Retrieved 17 February 2017.
^ "National Highway System" (PDF). Transport Canada. Retrieved April 26, 2014.
^ abc Google (November 4, 2016). "Highway 1 in Alberta" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved November 4, 2016.
^ abc Google (November 4, 2016). "Trans-Canada Highway in Saskatchewan and Manitoba" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved November 4, 2016.
^ "Manitoba Trans-Canada Speed Limit Goes Up to 110 km/h Today". CBC Manitoba. 2015. Retrieved June 2, 2015.
^ abcdef Google (November 4, 2016). "Trans-Canada Highway in Ontario" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved November 4, 2016.
^ "Nipigon River Bridge on Trans-Canada Highway partially reopens". CBC News. Retrieved November 28, 2016.
^ abcdefghijkl Google (November 4, 2016). "Trans-Canada Highway in Eastern Canada" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved November 4, 2016.
^ "The Montreal River hill: Nine years for nothing?". Northern Ontario Business. May 16, 2006. Retrieved November 17, 2016.
^ "Trans-Canada Highway Act". Department of Justice Canada. R.S.C. 1970, c. T-12.
^ "The Trans-Canada Highway". Transport Canada.
^ MacLeod, Donaldson (2014). "The Trans-Canada Highway: A Major Link in Canada's Transportation System" (PDF). Transportation Association of Canada. Retrieved March 10, 2016.
^ Department of Public Works and Services (September 14, 2004). Responsibilities and Obligations Re: Highway 174 (Report). City of Ottawa. Retrieved February 14, 2011.
^ Millier Dickinson Blais (February 16, 2010). "4.2 Linking to the Megaregion". Economic Development Plan - Final Report (Report). Prescott-Russell Community Development Corporation. pp. 41–42. Retrieved March 10, 2011.
^ Ontario Road Map (Map). Cartography by Geomatics Office. Ministry of Transportation. 1999.
^ Schmidt, Colleen (June 13, 2014). "Crews Complete Twinning of Trans-Canada Through Banff National Park". CTV Calgary. Retrieved June 13, 2014.
^ Caulfield, Jane (December 11, 2012). "Electrifying Trip Along the Trans-Canada Highway Pit Stops in Saskatchewan". Metro. Retrieved April 12, 2014.
^ "World's Longest Greenest Highway Project: Item Details". Sun Country Highway. Retrieved November 1, 2016.
External links
KML file (edit • help) |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Trans-Canada Highway. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Trans-Canada Highway. |
Trans-canada highway.com—Detailed province by province description, history, and itineraries
Dirt Roads to Freeways … And All That, ca.1970s, Archives of Ontario YouTube Channel