South Asian river dolphin
| South Asian river dolphin Temporal range: 0.012–0 Ma PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ Quaternary – Recent[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Ganges river dolphin leaping out of the water | |
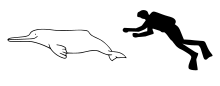 | |
| Size compared to an average human | |
Conservation status | |
 Endangered (IUCN 3.1)[2] | |
Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Infraorder: | Cetacea |
| Family: | Platanistidae Gray, 1846 |
| Genus: | Platanista Wagler, 1830 |
| Species: | P. gangetica |
Binomial name | |
Platanista gangetica (Lebeck, 1801); (Roxburgh, 1801) | |
Subspecies | |
Platanista gangetica gangetica | |
 | |
| Ranges of the Ganges river dolphin and of the Indus river dolphin | |
The South Asian river dolphin (Platanista gangetica) is an endangered freshwater or river dolphin found in the region of South Asia which is split into two subspecies, the Ganges river dolphin (P. g. gangetica)(~3,500 individuals) and the Indus river dolphin (P. g. minor)(~1,500 individuals). The Ganges river dolphin is primarily found in the Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers and their tributaries in Bangladesh, India and Nepal, while the Indus river dolphin is now found only in the main channel of the Indus River in Pakistan and active channels connected to it between the Jinnah and Kotri barrages. From the 1970s until 1998, they were regarded as separate species; however, in 1998, their classification was changed from two separate species to subspecies of a single species (see taxonomy below). The Ganges river dolphin has been recognized by the government of India as its National Aquatic Animal[3] and is the official animal of the Indian city of Guwahati.[4] The Indus river dolphin has been named as the National Mammal of Pakistan.[5]
Contents
1 Taxonomy and evolution
2 Description
3 Biology
3.1 Life Cycle
3.2 Diet
3.3 Vision
3.4 Vocalization
4 Distribution and habitat
5 Conservation
6 Human interaction
6.1 Non-human personhood
7 See also
8 References
9 Further reading
10 External links
Taxonomy and evolution
The species was described by two separate authors, Lebeck and Roxburgh, in 1801, and it is unclear to whom the original description should be ascribed.[6] Until the 1970s, the South Asian river dolphin was regarded as a single species. The two subspecies are geographically separate and have not interbred for many hundreds if not thousands of years. Based on differences in skull structure, vertebrae and lipid composition scientists declared the two populations as separate species in the early 1970s.[7] In 1998, the results of these studies were questioned and the classification reverted to the pre-1970 consensus of a single species containing two subspecies until the taxonomy could be resolved using modern techniques such as molecular sequencing. The latest analyses of mitochondrial DNA of the two populations did not display the variances needed to support their classification as separate species.[8] Thus, at present, a single species with two subspecies is recognized in the genus Platanista, P. g. gangetica (Ganges river dolphin) and P. g. minor (Indus river dolphin).[9]
- Synonyms
blind river dolphin, side-swimming dolphin
- Ganges subspecies: Gangetic dolphin, Ganges susu,[10]shushuk
- Indus subspecies: bhulan, Indus dolphin, Indus blind dolphin
An assessment of divergence rates in mitochondrial DNA of the two subspecies indicates that they diverged from a common ancestor around 550,000 years ago. This ancestor is thought to have been a marine Platanistid inhabiting the epi-continental seas in South Asia during the sea level rises in the middle Miocene.[11] The earliest fossil identified as belonging to the species is only 12,000 years old.[1]
Description
The South Asian river dolphin has the long, pointed nose characteristic of all river dolphins. Their teeth are visible in both the upper and lower jaws even when the mouth is closed. The teeth of young animals are almost an inch long, thin and curved; however, as animals age, the teeth undergo considerable changes and in mature adults become square, bony, flat disks. The snout thickens towards its end. Navigation and hunting are carried out using echolocation.[12] They are unique among cetaceans in that they swim on their sides.[13] The body is a brownish color and stocky at the middle. The species has only a small, triangular lump in the place of a dorsal fin. The flippers and tail are thin and large in relation to the body size, which is about 2-2.2 meters in males and 2.4-2.6 m in females. The oldest recorded animal was a 28-year-old male, 199 cm in length.[14] Mature females are larger than males. Sexual dimorphism is expressed after females reach about 150 cm (59 in); the female rostrum continues to grow after the male rostrum stops growing, eventually reaching approximately 20 cm (7.9 in) longer.

Skull cast
Biology

Indus river dolphin, 1927 illustration
Life Cycle

Ganges river dolphin skeleton specimen exhibited in Museo di storia naturale e del territorio dell'Università di Pisa
Births may take place year round, but appear to be concentrated between December to January and March to May.[15] Gestation is thought to be approximately 9–10 months. After around one year, juveniles are weaned and they reach sexual maturity at about 10 years of age.[16] During the monsoon, South Asian river dolphins tend to migrate to tributaries of the main river systems.[15] Occasionally, individuals swim along with their beaks emerging from the water,[17] and they may "breach"; jumping partly or completely clear of the water and landing on their sides.[17]
Diet
The South Asian river dolphin relies on echolocation to find prey due to their poor eyesight. Their extended rostrum is advantageous in detecting hidden or hard to find prey items. The prey is held in their jaw and swallowed. Their teeth is used as a clamp rather than a chewing mechanism.[18]
The species feeds on a variety of shrimp and fish, including carp and catfish. The Ganges subspecies may take birds and turtles. They are usually encountered on their own or in loose aggregations; the dolphins do not form tight interacting groups.[19][18]
Vision
The species lacks a crystalline eye lens and has evolved a flat cornea. The combination of these traits makes the eye incapable of forming clear images on the retina and renders the dolphin effectively blind, but the eye may still serve as a light receptor. The retina contains a densely packed receptor layer, a very thin bipolar and ganglion cell layer, and a tiny optic nerve (with only a few hundred optic fibers) that are sufficient for the retina to act as a light-gathering component.[20]
The dense pigmentation in the skin overlying the eye prevents light from reaching the retina from any entrance except for a pinhole sphincter-like structure. This structure is controlled by a cone-shaped muscle layer that extends from the posterior eye orbit to the overlying eye skin layer. The sphincter-like structure is capable of sensing light, and may be able to sense the direction from where the light was emitted. However, the muddy waters, or low light conditions, that the Platanista gangetica inhabit negate the use of the little vision that remains.[20]
Vocalization
The Ganges subspecies shows object-avoidance behavior in both the consistently heavily murky waters of its habitat and in clear water in captivity, suggesting that it is capable of using echolocation effectively to navigate and forage for prey.[20] However, there is limited information on how extensively vocalization is utilized between individuals. This subspecies of river dolphin is capable of performing whistles but rarely does so, suggesting that the whistle is a spontaneous sound and not a form of communication. The Ganges river dolphin most typically makes echolocation sounds such as clicks, bursts, and twitters.[21] Produced pulse trains are similar in wave form and frequency to the echolocation patterns of the Amazon river dolphin. Both species regularly produce frequencies lower than 15kHz and the maximum frequency is thought to fall somewhere between 15 to 60kHz.[20]
Echolocation is also utilized for population counts by using acoustic surveying. This method is still being developed and is not heavily utilized due to cost and technical skill requirement.[22]
Distribution and habitat
The South Asian river dolphins are native to the freshwater river systems located in Nepal, India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan.[2] They can be most commonly found in water with high abundance of prey and reduced flow.[12] They migrate seasonally—downstream in colder conditions with lower water levels and upstream in warmer conditions with higher water levels.[23]
The Ganges subspecies (P. g. gangetica) can be found along the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu river systems of Bangladesh and India, although its range formerly extended to Nepal.[12] A small subpopulation can be still found on the Ghaghara River and possibly the Sapta Kosi River.
The Indus subspecies (P. g. minor) today only occurs in a 1,000 km stretch of the Indus River itself and several connecting channels between the Jinnah and Kotri barrages.[24] In the past it was to be found along 3,400 km of the Indus, its tributaries and neighboring river systems. Its range has contracted by about 80% since 1870.[25] Since the two originally inhabited river systems - between the Sukkur and Guddu barrage in Pakistan's Sind Province, and in the Punjab and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Provinces - are not connected in any way, it remains unknown how they were colonized. It is improbable that the river dolphins made it from one river to another through the sea route since the two estuaries are very far apart. A possible explanation is that several north Indian rivers like the Sutlej and Yamuna changed their channels in ancient times while retaining their dolphin populations.[26]
Conservation
A 2017 population assessment estimated less than 5,000 individuals for the species as a whole, of which about 3,500 belong to the Ganges subspecies and about 1,500 to the Indus subspecies.[27] However, the underlying surveys are temporally patchy and believed to contain a large amount of uncertainty. Current population trends are unclear. A demonstrable increase in the main river population of the Indus subspecies between 1974 and 2008 may have been driven by permanent immigration from upstream tributaries, where the species no longer occurs.[2]
International trade is prohibited by the listing of the South Asian river dolphin on Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES).[28] It is protected under the Indian Wildlife Act, although these legislations require stricter enforcement.[15] Both subspecies are listed by the IUCN as endangered on their Red List of Threatened Species.[2] The Indus river dolphin is listed as endangered by the US government National Marine Fisheries Service under the Endangered Species Act.
The species is listed on Appendix I[29] and Appendix II[29] of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS).
The Ministry of Environment and Forest declared the Gangetic dolphin the national aquatic animal of India. A stretch of the Ganges River between Sultanganj and Kahlgaon in Bihar has been declared a dolphin sanctuary and named Vikramshila Gangetic Dolphin Sanctuary (VGDS), the first such protected area.
The Uttar Pradesh government in India is propagating ancient Hindu texts in hopes of raising the community support to save the dolphins from disappearing. One of the lines being versed from Valimiki’s Ramayan, highlighted the force by which the Ganges emerged from Lord Shivji’s locks and along with this force came many species such as animals, fish and the Shishumaar—the dolphin.[30]
Human interaction

Gangetic dolphin, 1894 book illustration
Both subspecies have been adversely affected by human use of river systems in South Asia. Entanglement in fishing nets as by-catch can cause significant damage to local populations, and individuals are taken each year by hunters; their oil and meat used as a liniment, as an aphrodisiac, and as bait for catfish. Poisoning of the water supply from industrial and agricultural chemicals may have also be a contributing factor towards population decline, as these chemicals are bio-magnified in the bodies of the dolphins.[31] Perhaps the most significant issue is the building of more than 50 dams along many rivers, causing the segregation of populations and a narrowed gene pool in which dolphins can breed.[25] An immediate danger for the Ganges subspecies in National Chambal Sanctuary is the decrease in river depth and appearance of sand bars dividing the river course into smaller segments, as irrigation has lowered water levels throughout their range.[32]
Non-human personhood
On 20 May 2013 India’s Ministry of Environment and Forests declared dolphins ‘non-human persons’ and as such has forbidden their captivity for entertainment purposes; keeping dolphins in captivity must satisfy certain legal prerequisites.[33]
See also
- Endangered species
- List of whale and dolphin species
- Irrawaddy dolphin
References
This article incorporates text from the ARKive fact-file ""Ganges river dolphin"" under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License and the GFDL.
^ ab "Platanista Wagler 1830 (toothed whale)". Fossilworks..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcd Smith, B.D.; Braulik, G.T. (2017). "Platanista gangetica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2017: e.T41758A50383612. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T41758A50383612.en. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
^ "Declaration of Gangetic Dolphin as National Aquatic Animal" (PDF). Government of India - Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change. 10 May 2010. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
^ "Gangetic river dolphin to be city animal of Guwahati". The Times of India. 6 June 2016.
^ "The Official Web Gateway to Pakistan". www.pakistan.gov.pk. Archived from the original on 28 November 2016. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
^ Kinze, C.C. (2000). "Rehabilitation of Platanista gangetica (Lebeck, 1801) as the valid scientific name of the Ganges dolphin". Zoologische Mededelingen. National Museum of Natural History. 74: 193–203.
^ Pilleri, G.; G. Marcuzzi & O. Pilleri (1982). "Speciation in the Platanistoidea, systematic, zoogeographical and ecological observations on recent species". Investigations on Cetacea. 14: 15–46.
^ "One Species or Two? Vicariance, Lineage Divergence and Low mtDNA Diversity in Geographically Isolated Populations of South Asian River Dolphin" (PDF). Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 22 (1). 2015. doi:10.1007/s10914-014-9265-6.
^ Rice, DW (1998). Marine mammals of the world: Systematics and distribution. Society for Marine Mammalogy. ISBN 978-1-891276-03-3.
^ "Susu, the blind purpoise ... in the Ganges River, blind porpoise of Asia". The New Book of Knowledge, Grolier Incorporated. 1977., page 451 [letter A] and page 568 [letter S].
^ "One Species or Two? Vicariance, Lineage Divergence and Low mtDNA Diversity in Geographically Isolated Populations of South Asian River Dolphin" (PDF). Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 22 (1): 111–120. 2014.
^ abc "South Asian river dolphin (Platanista gangetica)". EDGE. Retrieved 26 July 2011.
^ "Blind River Dolphin: First Side-Swimming Cetacean". Science. New Series. 166 (3911): 1408–1410. 12 December 1969.
^ Kasuya, T., 1972. Some information on the growth of the Ganges dolphin with a comment on the Indus dolphin. Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst., 24: 87-108
^ abc Boris Culik. "Platanista gangetica (Roxburgh, 1801)". CMS Report. Archived from the original on 11 June 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
^ Swinton, J.; W. Gomez & P. Myer. "Platanista gangetica". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
^ ab "The Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society". Retrieved 24 July 2011.
^ ab "Ganges River Dolphin (Platanista gangetica gangetica)". Dolphins-World. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
^ "Indus River Dolphin (Platanista gangetica minor)". Dolphins-World. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
^ abcd Herald, Earl S.; Brownell, Robert L.; Frye, Fredric L.; Morris, Elkan J.; Evans, William E.; Scott, Alan B. (1969). "Blind River Dolphin: First Side-Swimming Cetacean". Science. 166 (3911): 1408–1410. JSTOR 1727285.
^ Mizue, Kazuhiro; Takemura, Akira; Nishiwaki, Masaharu (1971). "The Underwater Sound of Ganges River Dolphins (Platanista Gangetica)" (PDF). The Scientific Reports of the Whales Research Institute. 23: 123–128 – via ICR.
^ Richman, Nadia I.; Gibbons, James M.; Turvey, Samuel T.; Akamatsu, Tomonari; Ahmed, Benazir; Mahabub, Emile; Smith, Brian D.; Jones, Julia P. G. (2014-05-07). "To See or Not to See: Investigating Detectability of Ganges River Dolphins Using a Combined Visual-Acoustic Survey". PLOS ONE. 9 (5): e96811. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096811. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4013050. PMID 24805782.
^ Sinha, Ravindra K.; Kannan, Kurunthachalam (December 2014). "Ganges River Dolphin: An Overview of Biology, Ecology, and Conservation Status in India". Ambio. 43 (8): 1029–1046. doi:10.1007/s13280-014-0534-7. ISSN 0044-7447. PMC 4235892. PMID 24924188.
^ "Indus River Dolphin". WWF Pakistan.
^ ab Braulik, G. T. (2006). "Status assessment of the Indus river dolphin, Platanista minor minor, March–April 2001". Biological Conservation. 129: 579–590. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2005.11.026.
^ Sanyal, Sanjeev (2012). Land of the Seven Rivers: A Brief History of India's Geography. Penguin.
^ "Review of status, threats, and conservation management options for the endangered Indus River blind dolphin". Biological Conservation. 192: 30–41. 2015-12-01. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2015.09.008. ISSN 0006-3207.
^ "CITES". CITES. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
^ ab "Appendix I and Appendix II Archived 11 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine." of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS). As amended by the Conference of the Parties in 1985, 1988, 1991, 1994, 1997, 1999, 2002, 2005 and 2008. Effective: 5 March 2009.
^ "How Hinduism Continues to Save Dolphins in India". The Chakra News.
^ Kannan, Kurunthachalam (1997). "Sources and Accumulation of Butyltin Compounds in Ganges River Dolphin, Platanista gangetica" (PDF). Applied Organometallic Chemistry. 11: 223–230.
^ Singh, L.A.K. & R.K. Sharma (1985). "Gangetic dolphin, Platanista gangetica: Observations on habits and distribution pattern in National Chambal Sanctuary". Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. Bombay Natural History Society. 82: 648–653. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 October 2009.
^ Gautama, Madhulika (2014-06-16). "Dolphins get their due". The Hindu. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 2016-11-27.
Further reading
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Randall R. Reeves; Brent S. Stewart; Phillip J. Clapham; James A. Powell (2002). National Audubon Society Guide to Marine Mammals of the World. Alfred A. Knopf, Inc. ISBN 0375411410.
Blind dolphins need space to breath - The Nation (Pakistan)
External links
Wikispecies has information related to Platanista gangetica |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Platanista gangetica. |
Goddess Ganga and the Gangetic Dolphin at Biodiversity of India
- Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society, South Asian river dolphin: Platanista gangetica
- US National Marine Fisheries Service Indus River Dolphin web page
ganges river dolphin media at ARKive
- Convention on Migratory Species page on the Ganges River Dolphin
- Walker's Mammals of the World Online - Ganges River Dolphin
- World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) - species profile for the Ganges River dolphin