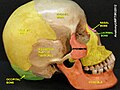
Lacrimal bone
| Lacrimal bone | |
|---|---|
 Position of the lacrimal bone (shown in green). | |
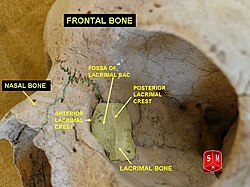 Medial wall of the orbit. Lacrimal bone is in yellow. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | os lacrimale |
| TA | A02.1.09.001 |
| FMA | 52741 |
Anatomical terms of bone [edit on Wikidata] | |
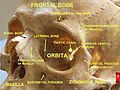
The lacrimal bone is a small and fragile bone of the facial skeleton; it is roughly the size of the little fingernail. It is situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. It has two surfaces and four borders. Several bony landmarks of the lacrimal bone function in the process of lacrimation or crying. Specifically, the lacrimal bone helps form the nasolacrimal canal necessary for tear translocation. A depression on the anterior inferior portion of the bone, the lacrimal fossa, houses the membranous lacrimal sac. Tears or lacrimal fluid, from the lacrimal glands, collect in this sac during excessive lacrimation. The fluid then flows through the nasolacrimal duct and into the nasopharynx. This drainage results in what is commonly referred to a runny nose during excessive crying or tear production. Injury or fracture of the lacrimal bone can result in posttraumatic obstruction of the lacrimal pathways.[1][2]
Contents
1 Structure
1.1 Lateral or orbital surface
1.2 Medial or nasal surface
1.3 Borders
1.4 Development
1.5 Articulations
2 Other animals
2.1 Dinosaurs
3 Additional images
4 See also
5 References
6 External links
Structure
Lateral or orbital surface
The lateral or orbital surface is divided by a vertical ridge, the posterior lacrimal crest, into two parts.
In front of this crest is a longitudinal groove, the lacrimal sulcus (sulcus lacrimalis), the inner margin of which unites with the frontal process of the maxilla, and the lacrimal fossa is thus completed. The upper part of this fossa lodges the lacrimal sac, the lower part, the nasolacrimal duct.
The portion behind the crest is smooth, and forms part of the medial wall of the orbit.
The crest, with a part of the orbital surface immediately behind it, gives origin to the lacrimal part of the orbicularis oculi and ends below in a small, hook-like projection, the lacrimal hamulus, which articulates with the lacrimal tubercle of the maxilla, and completes the upper orifice of the nasolacrimal canal; the hamulus sometimes exists as a separate piece, and is then called the lesser lacrimal bone.
Medial or nasal surface
The medial or nasal surface presents a longitudinal furrow, corresponding to the crest on the lateral surface.
The area in front of this furrow forms part of the middle meatus of the nose. The area behind it articulates with the ethmoid, and completes some of the anterior ethmoidal cells.
Borders
Of the four borders:
- the anterior articulates with the frontal process of the maxilla;
- the posterior with the lamina papyracea of the ethmoid;
- the superior with the frontal bone.
- The inferior is divided by the lower edge of the posterior lacrimal crest into two parts:
- the posterior part articulates with the orbital plate of the maxilla;
- the anterior is prolonged downward as the descending process, which articulates with the lacrimal process of the inferior nasal concha, and assists in forming the canal for the nasolacrimal duct.
Development
The lacrimal is ossified from a single center, which appears about the twelfth week in the membrane covering the cartilaginous nasal capsule.
Articulations
The lacrimal articulates with four bones: two of the cranium, the frontal and ethmoid, and two of the face, the maxilla and the inferior nasal concha.
Other animals
In early lobe-finned fishes and ancestral tetrapods, the lacrimal bone is a relatively large and robust bone, running from the orbit to the nostrils. It forms part of the side of the face, between the nasal bones and the maxilla. In primitive forms, it is often accompanied by a much smaller septomaxilla bone, lying immediately behind the nasal opening, but this is lost in most modern species. The lacrimal bone is often smaller in living vertebrates, and is no longer always directly associated with the nasal opening, although it retains its connection with the orbit. The bone is entirely absent in living amphibians, as well as some reptilian species.[3]
Dinosaurs
In dinosaurs, the lacrimal bone usually defines the anterior rim of the orbit (eye socket), and the posterior rim of the antorbital fenestra. In some theropods (e.g. Allosaurus, Ceratosaurus, Albertosaurus) the upper part of the lacrimal bone grew in such a manner as to form a horn on the top of the dinosaur's head, usually situated above, and anterior to the eye. In many dinosaurs, the lacrimal bone comes into contact with the nasal bone, the jugal bone, the prefrontal bone, and the maxillary and premaxillary bones. The boundaries where some of these bones meet with the others are called sutures. Rarely, the lacrimal bones fused with the nasal bones to form a pair of "nasolacrimal" crests, which are present in dinosaurs such as Dilophosaurus, Megapnosaurus and Sinosaurus.[4]
Additional images
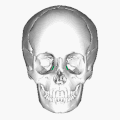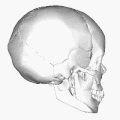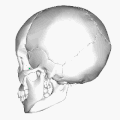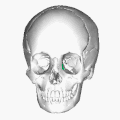
Position of the lacrimal bones (shown in green). Animation.

Animation. Some bones are removed to show the position of the lacrimal bones (shown in green).

Orbital bones. Lacrimal bone shown in green.

A left lacrimal bone. Enlarged. Animation.
Lacrimal bone
Lacrimal bone
See also
References
^ Maliborski, A; Różycki, R (2014). "Diagnostic imaging of the nasolacrimal drainage system. Part I. Radiological anatomy of lacrimal pathways. Physiology of tear secretion and tear outflow". Med. Sci. Monit. 20: 628–38. doi:10.12659/MSM.890098. PMC 3999077. PMID 24743297..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Saladin. Anatomy & Physiology : The Unity of Form and Function (Seventh ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Education. ISBN 978-0-07-340371-7.
[page needed]
^ Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 217–241. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
^ Carrano, Matthew T.; Benson, Roger B. J.; Sampson, Scott D. (2012). "The phylogeny of Tetanurae (Dinosauria: Theropoda)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 10 (2): 211–300. doi:10.1080/14772019.2011.630927.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lacrimal bones. |
Atlas image: eye_5 at the University of Michigan Health System
Atlas image: rsa2p4 at the University of Michigan Health System
"Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- Diagram at upstate.edu