60th parallel north

The 60th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
Although it lies approximately twice as far away from the Equator as from the North Pole, the 60th parallel is half as long as the Equator line. This is where the Earth bulges halfway as much as on the Equator.
At this latitude, the Sun is visible for 18 hours, 52 minutes during the June solstice and 5 hours, 52 minutes during the December solstice.[1]
The maximum altitude of the Sun is 53.44° on 21 June and 6.56° on 21 December.[2]
The lowest latitude where white nights can be observed is approximately on this parallel.
Contents
1 Around the world
2 Canada
3 Greenland
4 See also
5 References
Around the world
Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 60° north passes through:
Co-ordinates
Country, territory or sea
Notes
60°0′N 0°0′E / 60.000°N 0.000°E / 60.000; 0.000 (Prime Meridian)
North Sea
60°0′N 5°2′E / 60.000°N 5.033°E / 60.000; 5.033 (Norway)
 Norway
Norway
Islands of Møkster, Selbjørn, Huftarøy, Reksteren and Tysnesøy, and the mainland
Passing just north of Oslo
60°0′N 12°23′E / 60.000°N 12.383°E / 60.000; 12.383 (Sweden)
 Sweden
Sweden
Passing through Fagersta
Passing just north of Uppsala
60°0′N 18°53′E / 60.000°N 18.883°E / 60.000; 18.883 (Baltic Sea)
Baltic Sea
60°0′N 20°8′E / 60.000°N 20.133°E / 60.000; 20.133 (Åland Islands)
 Åland Islands
Åland Islands
Högskär, Bäckö and several smaller islands
60°0′N 20°58′E / 60.000°N 20.967°E / 60.000; 20.967 (Baltic Sea)
Baltic Sea
60°0′N 22°22′E / 60.000°N 22.367°E / 60.000; 22.367 (Finland)
 Finland
Finland
60°0′N 23°56′E / 60.000°N 23.933°E / 60.000; 23.933 (Baltic Sea)
Baltic Sea
Passing just south of Helsinki,  Finland
Finland
60°0′N 24°26′E / 60.000°N 24.433°E / 60.000; 24.433 (Finland)
 Finland
Finland
Porkkala peninsula
60°0′N 24°30′E / 60.000°N 24.500°E / 60.000; 24.500 (Baltic Sea)
Baltic Sea
Gulf of Finland - passing just south of the island of Gogland, Russia
Russia
60°0′N 27°48′E / 60.000°N 27.800°E / 60.000; 27.800 (Russia)
 Russia
Russia
Island of Moshchnyy
60°0′N 27°54′E / 60.000°N 27.900°E / 60.000; 27.900 (Baltic Sea)
Baltic Sea
Gulf of Finland
60°0′N 29°44′E / 60.000°N 29.733°E / 60.000; 29.733 (Russia)
 Russia
Russia
Island of Kotlin (city of Kronstadt)
60°0′N 29°47′E / 60.000°N 29.783°E / 60.000; 29.783 (Baltic Sea)
Baltic Sea
Gulf of Finland
60°0′N 30°5′E / 60.000°N 30.083°E / 60.000; 30.083 (Russia)
 Russia
Russia
Passing through Saint Petersburg
Passing through Lake Ladoga
60°0′N 154°30′E / 60.000°N 154.500°E / 60.000; 154.500 (Sea of Okhotsk)
Sea of Okhotsk
Shelikhov Gulf
60°0′N 161°28′E / 60.000°N 161.467°E / 60.000; 161.467 (Russia)
 Russia
Russia
Kamchatka Peninsula
60°0′N 165°14′E / 60.000°N 165.233°E / 60.000; 165.233 (Bering Sea)
Bering Sea
60°0′N 166°10′E / 60.000°N 166.167°E / 60.000; 166.167 (Russia)
 Russia
Russia
60°0′N 166°33′E / 60.000°N 166.550°E / 60.000; 166.550 (Bering Sea)
Bering Sea
Olyutorsky Gulf
60°0′N 170°9′E / 60.000°N 170.150°E / 60.000; 170.150 (Russia)
 Russia
Russia
60°0′N 170°26′E / 60.000°N 170.433°E / 60.000; 170.433 (Bering Sea)
Bering Sea
60°0′N 167°8′W / 60.000°N 167.133°W / 60.000; -167.133 (United States)
 United States
United States
Alaska - Nunivak Island
60°0′N 165°39′W / 60.000°N 165.650°W / 60.000; -165.650 (Etolin Strait)
Etolin Strait
60°0′N 164°9′W / 60.000°N 164.150°W / 60.000; -164.150 (United States)
 United States
United States
Alaska
60°0′N 152°38′W / 60.000°N 152.633°W / 60.000; -152.633 (Cook Inlet)
Cook Inlet
60°0′N 151°44′W / 60.000°N 151.733°W / 60.000; -151.733 (United States)
 United States
United States
Alaska - Kenai Peninsula, Evans Island, Elrington Island, Latouche Island and Montague Island
60°0′N 147°24′W / 60.000°N 147.400°W / 60.000; -147.400 (Pacific Ocean)
Pacific Ocean
Gulf of Alaska
60°0′N 144°24′W / 60.000°N 144.400°W / 60.000; -144.400 (United States)
 United States
United States
Alaska - Wingham Island, Kayak Island and a small section of mainland
60°0′N 143°50′W / 60.000°N 143.833°W / 60.000; -143.833 (Pacific Ocean)
Pacific Ocean
Gulf of Alaska
60°0′N 141°53′W / 60.000°N 141.883°W / 60.000; -141.883 (United States)
 United States
United States
Alaska
60°0′N 139°3′W / 60.000°N 139.050°W / 60.000; -139.050 (Canada)
 Canada
Canada
Yukon / British Columbia border
Northwest Territories / British Columbia border
Northwest Territories / Alberta border
Northwest Territories / Saskatchewan border
Northwest Territories / Manitoba border - for about 400m
Nunavut / Manitoba border
60°0′N 94°49′W / 60.000°N 94.817°W / 60.000; -94.817 (Hudson Bay)
Hudson Bay
Passing just north of the Ottawa Islands, Nunavut,  Canada
Canada
60°0′N 77°17′W / 60.000°N 77.283°W / 60.000; -77.283 (Canada)
 Canada
Canada
Quebec
60°0′N 69°46′W / 60.000°N 69.767°W / 60.000; -69.767 (Ungava Bay)
Ungava Bay
60°0′N 65°7′W / 60.000°N 65.117°W / 60.000; -65.117 (Canada)
 Canada
Canada
Quebec
Newfoundland and Labrador
60°0′N 64°9′W / 60.000°N 64.150°W / 60.000; -64.150
Atlantic Ocean
Border between the Davis Strait (to the north) and the Labrador Sea (to the south)[3]
60°0′N 44°52′W / 60.000°N 44.867°W / 60.000; -44.867 (Greenland)
 Greenland
Greenland
60°0′N 43°9′W / 60.000°N 43.150°W / 60.000; -43.150 (Atlantic Ocean)
Atlantic Ocean
60°0′N 1°21′W / 60.000°N 1.350°W / 60.000; -1.350 (United Kingdom)
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
Scotland - Islands of Mainland and Mousa, Shetland Islands
60°0′N 1°11′W / 60.000°N 1.183°W / 60.000; -1.183 (North Sea)
North Sea
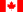
Canada

The 60th parallel north in Canada, marking the southern borders of Yukon, Northwest Territories, and the Nunavut mainland.
In Canada, the 60th parallel constitutes the mainland boundary between the northern territories of Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut to the north, and the western provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba to the south.
Accordingly, "north of 60" is an expression often used for the territories, although parts of Nunavut (the islands in Hudson Bay and James Bay) are located south of the 60th parallel, and parts of Quebec and Newfoundland and Labrador are located north, to the east of Hudson Bay. A 1990s TV show on CBC about life in the Northwest Territories was called North of 60.
Canada's only four corners are located at the intersection of the 60th parallel and the 102nd meridian west, between the Northwest Territories, Nunavut, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. However, this is not a true quadripoint as the measurement of the Saskatchewan/Manitoba border in the 1880s placed it approximately 400 metres (440 yd) west of the 102nd meridian, which defines part of the Northwest Territories/Nunavut border.
Greenland
Between 1776 and 1950, the 60th parallel formed the southern limit of the Royal Greenland Trade Department's exclusive monopoly on trade near the Dano-Norwegian and later Danish colonies of Greenland (1776–1782) and South Greenland (1782–1950).[4]
See also
- 59th parallel north
- 61st parallel north
- 60th parallel south
References
^ "Duration of Daylight/Darkness Table for One Year". aa.usno.navy.mil..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ NASA. "Earth Fact Sheet". Retrieved April 11, 2017.
^ "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 October 2011. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
^ Marquardt, Ole. "Change and Continuity in Denmark's Greenland Policy" in The Oldenburg Monarchy: An Underestimated Empire?. Verlag Ludwig (Kiel), 2006.
