Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae | |
|---|---|
 | |
S. cerevisiae, electron micrograph | |
Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Saccharomycetes |
| Order: | Saccharomycetales |
| Family: | Saccharomycetaceae |
| Genus: | Saccharomyces |
| Species: | S. cerevisiae |
Binomial name | |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Meyen ex E.C. Hansen | |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (/ˌsɛrɪˈvɪsiiː/) is a species of yeast. It has been instrumental to winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes (one can see the yeast as a component of the thin white film on the skins of some dark-colored fruits such as plums; it exists among the waxes of the cuticle). It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like Escherichia coli as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation. S. cerevisiae cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by a division process known as budding.[1]
Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. S. cerevisiae is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley bodies present, which are involved in particular secretory pathways. Antibodies against S. cerevisiae are found in 60–70% of patients with Crohn's disease and 10–15% of patients with ulcerative colitis (and 8% of healthy controls).[2]
Contents
1 Etymology
2 History
3 Biology
3.1 Ecology
3.2 Life cycle
3.3 Nutritional requirements
3.4 Mating
3.5 Cell cycle
3.5.1 Cytokinesis
3.5.1.1 Timing
3.5.1.2 Actomyosin ring and primary septum formation
3.5.1.3 Differences from fission yeast
4 In biological research
4.1 Model organism
4.2 In the study of aging
4.3 Meiosis, recombination and DNA repair
4.4 Genome sequencing
4.5 Gene function and interactions
4.6 Other tools in yeast research
4.7 Synthetic yeast genome project
4.8 Astrobiology
5 In commercial applications
5.1 Brewing
5.2 Baking
5.3 Uses in aquaria
6 See also
7 References
8 Further reading
9 External links
Etymology
"Saccharomyces" derives from Latinized Greek and means "sugar-mold" or "sugar-fungus", saccharon (σάκχαρον) being the combining form "sugar" and myces (μύκης, genitive μύκητος) being "fungus". Cerevisiae comes from Latin and means "of beer". Other names for the organism are:
Brewer's yeast, though other species are also used in brewing[3]
- Ale yeast
- Top-fermenting yeast
Baker's yeast[3]
- Ragi yeast, in connection to making tapai
- Budding yeast
This species is also the main source of nutritional yeast and yeast extract.
History
In the 19th century, bread bakers obtained their yeast from beer brewers, and this led to sweet-fermented breads such as the Imperial "Kaisersemmel" roll,[4]
which in general lacked the sourness created by the acidification typical of Lactobacillus. However, beer brewers slowly switched from top-fermenting (S. cerevisiae) to bottom-fermenting (S. pastorianus) yeast and this created a shortage of yeast for making bread, so the Vienna Process was developed in 1846.[5]
While the innovation is often popularly credited for using steam in baking ovens, leading to a different crust characteristic, it is notable for including procedures for high milling of grains (see Vienna grits[6]),
cracking them incrementally instead of mashing them with one pass; as well as better processes for growing and harvesting top-fermenting yeasts, known as press-yeast.
Refinements in microbiology following the work of Louis Pasteur led to more advanced methods of culturing pure strains. In 1879, Great Britain introduced specialized growing vats for the production of S. cerevisiae, and in the United States around the turn of the century centrifuges were used for concentrating the yeast,[7]
making modern commercial yeast possible, and turning yeast production into a major industrial endeavor. The slurry yeast made by small bakers and grocery shops became cream yeast, a suspension of live yeast cells in growth medium, and then compressed yeast, the fresh cake yeast that became the standard leaven for bread bakers in much of the Westernized world during the early 20th century.
During World War II, Fleischmann's developed a granulated active dry yeast for the United States armed forces, which did not require refrigeration and had a longer shelf-life and better temperature tolerance than fresh yeast; it is still the standard yeast for US military recipes. The company created yeast that would rise twice as fast, cutting down on baking time. Lesaffre would later create instant yeast in the 1970s, which has gained considerable use and market share at the expense of both fresh and dry yeast in their various applications.
Biology
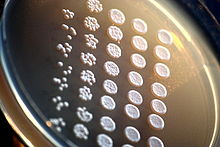
Yeast colonies on an agar plate.
Ecology
In nature, yeast cells are found primarily on ripe fruits such as grapes (before maturation, grapes are almost free of yeasts).[8] Since S. cerevisiae is not airborne, it requires a vector to move.
Queens of social wasps overwintering as adults (Vespa crabro and Polistes spp.) can harbor yeast cells from autumn to spring and transmit them to their progeny.[9] The intestine of Polistes dominula, a social wasp, hosts S. cerevisiae strains as well as S. cerevisiae × S. paradoxus hybrids. Stefanini et al. (2016) showed that the intestine of Polistes dominula favors the mating of S. cerevisiae strains, both among themselves and with S. paradoxus cells by providing environmental conditions prompting cell sporulation and spores germination.[10]
The optimum temperature for growth of S. cerevisiae is 30–35 °C (86–95 °F).[9]
Life cycle
Two forms of yeast cells can survive and grow: haploid and diploid. The haploid cells undergo a simple lifecycle of mitosis and growth, and under conditions of high stress will, in general, die. This is the asexual form of the fungus. The diploid cells (the preferential 'form' of yeast) similarly undergo a simple lifecycle of mitosis and growth. The rate at which the mitotic cell cycle progresses often differs substantially between haploid and diploid cells.[11] Under conditions of stress, diploid cells can undergo sporulation, entering meiosis and producing four haploid spores, which can subsequently mate. This is the sexual form of the fungus. Under optimal conditions, yeast cells can double their population every 100 minutes.[12][13] However, growth rates vary enormously both between strains and between environments.[14] Mean replicative lifespan is about 26 cell divisions.[15][16]
In the wild, recessive deleterious mutations accumulate during long periods of asexual reproduction of diploids, and are purged during selfing: this purging has been termed "genome renewal".[17][18]
Nutritional requirements
All strains of S. cerevisiae can grow aerobically on glucose, maltose, and trehalose and fail to grow on lactose and cellobiose. However, growth on other sugars is variable. Galactose and fructose are shown to be two of the best fermenting sugars. The ability of yeasts to use different sugars can differ depending on whether they are grown aerobically or anaerobically. Some strains cannot grow anaerobically on sucrose and trehalose.
All strains can use ammonia and urea as the sole nitrogen source, but cannot use nitrate, since they lack the ability to reduce them to ammonium ions. They can also use most amino acids, small peptides, and nitrogen bases as nitrogen sources. Histidine, glycine, cystine, and lysine are, however, not readily used. S. cerevisiae does not excrete proteases, so extracellular protein cannot be metabolized.
Yeasts also have a requirement for phosphorus, which is assimilated as a dihydrogen phosphate ion, and sulfur, which can be assimilated as a sulfate ion or as organic sulfur compounds such as the amino acids methionine and cysteine. Some metals, like magnesium, iron, calcium, and zinc, are also required for good growth of the yeast.
Concerning organic requirements, most strains of S. cerevisiae require biotin. Indeed, a S. cerevisiae-based growth assay laid the foundation for the isolation, crystallisation, and later structural determination of biotin. Most strains also require pantothenate for full growth. In general, S. cerevisiae is prototrophic for vitamins.
Mating
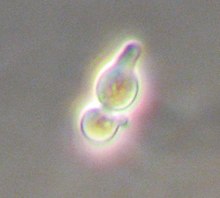
Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating type a with a cellular bulging called a shmoo in response to α-factor
Yeast has two mating types, a and α (alpha), which show primitive aspects of sex differentiation.[19] As in many other eukaryotes, mating leads to genetic recombination, i.e. production of novel combinations of chromosomes. Two haploid yeast cells of opposite mating type can mate to form diploid cells that can either sporulate to form another generation of haploid cells or continue to exist as diploid cells. Mating has been exploited by biologists as a tool to combine genes, plasmids, or proteins at will.
The mating pathway employs a G protein-coupled receptor, G protein, RGS protein, and three-tiered MAPK signaling cascade that is homologous to those found in humans. This feature has been exploited by biologists to investigate basic mechanisms of signal transduction and desensitization.
Cell cycle
Growth in yeast is synchronised with the growth of the bud, which reaches the size of the mature cell by the time it separates from the parent cell. In well nourished, rapidly growing yeast cultures, all the cells can be seen to have buds, since bud formation occupies the whole cell cycle. Both mother and daughter cells can initiate bud formation before cell separation has occurred. In yeast cultures growing more slowly, cells lacking buds can be seen, and bud formation only occupies a part of the cell cycle.
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis enables budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae to divide into two daughter cells. S. cerevisiae forms a bud which can grow throughout its cell cycle and later leaves its mother cell when mitosis has completed.[20]
S. cerevisiae is relevant to cell cycle studies because it divides asymmetrically by using a polarized cell to make two daughters with different fates and sizes. Similarly, stem cells use asymmetric division for self-renewal and differentiation.[21]
Timing
For many cells, M phase does not happen until S phase is complete. However, for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae this is not true. Cytokinesis begins with the budding process in late G1 and is not completed until about halfway through the next cycle. The assembly of the spindle can happen before S phase has finished duplicating the chromosomes.[20] Additionally, there is a lack of clearly defined G2 in between M and S. Thus, there is a lack of extensive regulation present in higher eukaryotes.[20]
When the daughter emerges, the daughter is two-thirds the size of the mother.[22] Throughout the process, the mother displays little to no change in size.[23] The RAM pathway is activated in the daughter cell immediately after cytokinesis is complete. This pathway makes sure that the daughter has separated properly.[22]
Actomyosin ring and primary septum formation
Two interdependent events drive cytokinesis in S. cerevisiae. The first event is contractile actomyosin ring (AMR) constriction and the second event is formation of the primary septum (PS), a chitinous cell wall structure that can only be formed during cytokinesis. The PS resembles in animals the process of extracellular matrix remodeling.[22] When the AMR constricts, the PS begins to grow. Disrupting AMR misorients the PS, suggesting that both have a dependent role. Additionally, disrupting the PS also leads to disruptions in the AMR, suggesting both the actomyosin ring and primary septum have an interdependent relationship.[24][23]
The AMR, which is attached to the cell membrane facing the cytosol, consists of actin and myosin II molecules that coordinate the cells to split.[20] The ring is thought to play an important role in ingression of the plasma membrane as a contractile force.
Proper coordination and correct positional assembly of the contractile ring depends on septins, which is the precursor to the septum ring. These GTPases assemble complexes with other proteins. The septins form a ring at the site where the bud will be created during late G1. They help promote the formation of the actin-myosin ring, although this mechanism is unknown. It is suggested they help provide structural support for other necessary cytokinesis processes.[20] After a bud emerges, the septin ring forms an hourglass. The septin hourglass and the myosin ring together are the beginning of the future division site.
The septin and AMR complex progress to form the primary septum consisting of glucans and other chitinous molecules sent by vesicles from the Golgi body.[25] After AMR constriction is complete, two secondary septums are formed by glucans. How the AMR ring dissembles remains poorly unknown.[21]
Microtubules do not play as significant a role in cytokinesis compared to the AMR and septum. Disruption of microtubules did not significantly impair polarized growth.[26] Thus, the AMR and septum formation are the major drivers of cytokinesis.
Differences from fission yeast
- Budding yeast form a bud from the mother cell. This bud grows during the cell cycle and detaches; fission yeast divide by forming a cell wall [20]
- Cytokinesis begins at G1 for budding yeast, while cytokinesis begins at G2 for fission yeast. Fission yeast “select” the midpoint, whereas budding yeast “select” a bud site [27]
- During early anaphase the actomyosin ring and septum continues to develop in budding yeast, in fission yeast during metaphase-anaphase the actomyosin ring begins to develop [27]
In biological research
Model organism

S. cerevisiae, differential interference contrast image

Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Numbered ticks are 11 micrometers apart.
When researchers look for an organism to use in their studies, they look for several traits. Among these are size, generation time, accessibility, manipulation, genetics, conservation of mechanisms, and potential economic benefit. The yeast species S. pombe and S. cerevisiae are both well studied; these two species diverged approximately 600 to 300 million years ago, and are significant tools in the study of DNA damage and repair mechanisms.[28]
S. cerevisiae has developed as a model organism because it scores favorably on a number of these criteria.
- As a single-cell organism, S. cerevisiae is small with a short generation time (doubling time 1.25–2 hours[29] at 30 °C or 86 °F) and can be easily cultured. These are all positive characteristics in that they allow for the swift production and maintenance of multiple specimen lines at low cost.
S. cerevisiae divides with meiosis, allowing it to be a candidate for sexual genetics research.
S. cerevisiae can be transformed allowing for either the addition of new genes or deletion through homologous recombination. Furthermore, the ability to grow S. cerevisiae as a haploid simplifies the creation of gene knockout strains.- As a eukaryote, S. cerevisiae shares the complex internal cell structure of plants and animals without the high percentage of non-coding DNA that can confound research in higher eukaryotes.
S. cerevisiae research is a strong economic driver, at least initially, as a result of its established use in industry.
In the study of aging
S. cerevisiae has been highly studied as a model organism to better understand aging for more than five decades and has contributed to the identification of more mammalian genes affecting aging than any other model organism.[30] Some of the topics studied using yeast are calorie restriction, as well as in genes and cellular pathways involved in senescence. The two most common methods of measuring aging in yeast are Replicative Life Span, which measures the number of times a cell divides, and Chronological Life Span, which measures how long a cell can survive in a non-dividing stasis state.[30] Limiting the amount of glucose or amino acids in the growth medium has been shown to increase RLS and CLS in yeast as well as other organisms.[31] At first, this was thought to increase RLS by up-regulating the sir2 enzyme, however it was later discovered that this effect is independent of sir2. Over-expression of the genes sir2 and fob1 has been shown to increase RLS by preventing the accumulation of extrachromosomal rDNA circles, which are thought to be one of the causes of senescence in yeast.[31] The effects of dietary restriction may be the result of a decreased signaling in the TOR cellular pathway.[30] This pathway modulates the cell's response to nutrients, and mutations that decrease TOR activity were found to increase CLS and RLS.[30][31] This has also been shown to be the case in other animals.[30][31] A yeast mutant lacking the genes sch9 and ras2 has recently been shown to have a tenfold increase in chronological lifespan under conditions of calorie restriction and is the largest increase achieved in any organism.[32][33]
Mother cells give rise to progeny buds by mitotic divisions, but undergo replicative aging over successive generations and ultimately die. However, when a mother cell undergoes meiosis and gametogenesis, lifespan is reset.[34] The replicative potential of gametes (spores) formed by aged cells is the same as gametes formed by young cells, indicating that age-associated damage is removed by meiosis from aged mother cells. This observation suggests that during meiosis removal of age-associated damages leads to rejuvenation. However, the nature of these damages remains to be established.
During starvation of non-replicating S. cerevisiae cells, reactive oxygen species increase leading to the accumulation of DNA damages such as apurinic/apyrimidinic sites and double-strand breaks.[35] Also in non-replicating cells the ability to repair endognous double-strand breaks declines during chronological aging.[36]
Meiosis, recombination and DNA repair
S. cerevisiae reproduces by mitosis as diploid cells when nutrients are abundant. However, when starved, these cells undergo meiosis to form haploid spores.[37]
Evidence from studies of S. cerevisiae bear on the adaptive function of meiosis and recombination. Mutations defective in genes essential for meiotic and mitotic recombination in S. cerevisiae cause increased sensitivity to radiation or DNA damaging chemicals.[38][39] For instance, gene rad52 is required for both meiotic recombination[40] and mitotic recombination.[41]Rad52 mutants have increased sensitivity to killing by X-rays, Methyl methanesulfonate and the DNA cross-linking agent 8-methoxypsoralen-plus-UVA, and show reduced meiotic recombination.[39][40][42] These findings suggest that recombination repair during meiosis and mitosis is needed for repair of the different damages caused by these agents.
Ruderfer et al.[38] (2006) analyzed the ancestry of natural S. cerevisiae strains and concluded that outcrossing occurs only about once every 50,000 cell divisions. Thus, it appears that in nature, mating is likely most often between closely related yeast cells. Mating occurs when haploid cells of opposite mating type MATa and MATα come into contact. Ruderfer et al.[38] pointed out that such contacts are frequent between closely related yeast cells for two reasons. The first is that cells of opposite mating type are present together in the same ascus, the sac that contains the cells directly produced by a single meiosis, and these cells can mate with each other. The second reason is that haploid cells of one mating type, upon cell division, often produce cells of the opposite mating type with which they can mate. The relative rarity in nature of meiotic events that result from outcrossing is inconsistent with the idea that production of genetic variation is the main selective force maintaining meiosis in this organism. However, this finding is consistent with the alternative idea that the main selective force maintaining meiosis is enhanced recombinational repair of DNA damage,[43][44][45] since this benefit is realized during each meiosis, whether or not out-crossing occurs.
Genome sequencing
S. cerevisiae was the first eukaryotic genome to be completely sequenced.[46] The genome sequence was released to the public domain on April 24, 1996. Since then, regular updates have been maintained at the Saccharomyces Genome Database. This database is a highly annotated and cross-referenced database for yeast researchers. Another important S. cerevisiae database is maintained by the Munich Information Center for Protein Sequences (MIPS). The S. cerevisiae genome is composed of about 12,156,677 base pairs and 6,275 genes, compactly organized on 16 chromosomes.[46] Only about 5,800 of these genes are believed to be functional. It is estimated at least 31% of yeast genes have homologs in the human genome.[47] Yeast genes are classified using gene symbols (such as sch9) or systematic names. In the latter case the 16 chromosomes of yeast are represented by the letters A to P, then the gene is further classified by a sequence number on the left or right arm of the chromosome, and a letter showing which of the two DNA strands contains its coding sequence.[citation needed]
| Example gene name | YGL118W |
|---|---|
| Y | the Y to show this is a yeast gene |
| G | chromosome on which the gene is located |
| L | left or right arm of the chromosome |
| 118 | sequence number of the gene/ORF on this arm, starting at the centromere |
| W | whether the coding sequence is on the Watson or Crick strand |
Examples
- YBR134C (aka SUP45 encoding eRF1, a translation termination factor) is located on the right arm of chromosome 2 and is the 134th open reading frame (ORF) on that arm, starting from the centromere. The coding sequence is on the Crick strand of the DNA.
- YDL102W (aka POL3 encoding a subunit of DNA polymerase delta) is located on the left arm of chromosome 4; it is the 102nd ORF from the centromere and codes from the Watson strand of the DNA.
Gene function and interactions
The availability of the S. cerevisiae genome sequence and a set of deletion mutants covering 90% of the yeast genome[48] has further enhanced the power of S. cerevisiae as a model for understanding the regulation of eukaryotic cells. A project underway to analyze the genetic interactions of all double-deletion mutants through synthetic genetic array analysis will take this research one step further. The goal is to form a functional map of the cell's processes. As of 2010 a model of genetic interactions is most comprehensive yet to be constructed, containing "the interaction profiles for ~75% of all genes in the Budding yeast".[49] This model was made from 5.4 million two-gene comparisons in which a double gene knockout for each combination of the genes studied was performed. The effect of the double knockout on the fitness of the cell was compared to the expected fitness. Expected fitness is determined from the sum of the results on fitness of single-gene knockouts for each compared gene. When there is a change in fitness from what is expected, the genes are presumed to interact with each other. This was tested by comparing the results to what was previously known. For example, the genes Par32, Ecm30, and Ubp15 had similar interaction profiles to genes involved in the Gap1-sorting module cellular process. Consistent with the results, these genes, when knocked out, disrupted that process, confirming that they are part of it.[49] From this, 170,000 gene interactions were found and genes with similar interaction patterns were grouped together. Genes with similar genetic interaction profiles tend to be part of the same pathway or biological process.[50] This information was used to construct a global network of gene interactions organized by function. This network can be used to predict the function of uncharacterized genes based on the functions of genes they are grouped with.[49]
Other tools in yeast research
Approaches that can be applied in many different fields of biological and medicinal science have been developed by yeast scientists. These include yeast two-hybrid for studying protein interactions and tetrad analysis. Other resources, include a gene deletion library including ~4,700 viable haploid single gene deletion strains. A GFP fusion strain library used to study protein localisation and a TAP tag library used to purify protein from yeast cell extracts.[citation needed]
Synthetic yeast genome project
The international Synthetic Yeast Genome Project (Sc2.0 or Saccharomyces cerevisiae version 2.0) aims to build an entirely designer, customizable, synthetic S. cerevisiae genome from scratch that is more stable than the wild type. In the synthetic genome all transposons, repetitive elements and many introns are removed, all UAG stop codons are replaced with UAA, and transfer RNA genes are moved to a novel neochromosome. As of March 2017[update], 6 of the 16 chromosomes have been synthesized and tested. No significant fitness defects have been found.[51]
Astrobiology
Among other microorganisms, a sample of living S. cerevisiae was included in the Living Interplanetary Flight Experiment, which would have completed a three-year interplanetary round-trip in a small capsule aboard the Russian Fobos-Grunt spacecraft, launched in late 2011.[52][53] The goal was to test whether selected organisms could survive a few years in deep space by flying them through interplanetary space. The experiment would have tested one aspect of transpermia, the hypothesis that life could survive space travel, if protected inside rocks blasted by impact off one planet to land on another.[52][53][54] Fobos-Grunt's mission ended unsuccessfully, however, when it failed to escape low Earth orbit. The spacecraft along with its instruments fell into the Pacific Ocean in an uncontrolled re-entry on January 15, 2012. The next planned exposure mission in deep space using S. cerevisiae is BioSentinel. (see: List of microorganisms tested in outer space)
In commercial applications
Brewing
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used in brewing beer, when it is sometimes called a top-fermenting or top-cropping yeast. It is so called because during the fermentation process its hydrophobic surface causes the flocs to adhere to CO2 and rise to the top of the fermentation vessel. Top-fermenting yeasts are fermented at higher temperatures than the lager yeast Saccharomyces pastorianus, and the resulting beers have a different flavor than the same beverage fermented with a lager yeast. "Fruity esters" may be formed if the yeast undergoes temperatures near 21 °C (70 °F), or if the fermentation temperature of the beverage fluctuates during the process. Lager yeast normally ferments at a temperature of approximately 5 °C (41 °F), where Saccharomyces cerevisiae becomes dormant. A variant yeast known as Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. diastaticus is a beer spoiler which can cause secondary fermentations in packaged products.[55]
In May 2013, the Oregon legislature made S. cerevisiae the official state microbe in recognition of the impact craft beer brewing has had on the state economy and the state's identity.[56]
Baking
S. cerevisiae is used in baking; the carbon dioxide generated by the fermentation is used as a leavening agent in bread and other baked goods. Historically, this use was closely linked to the brewing industry's use of yeast, as bakers took or bought the barm or yeast-filled foam from brewing ale from the brewers (producing the barm cake); today, brewing and baking yeast strains are somewhat different.
Uses in aquaria
Owing to the high cost of commercial CO2 cylinder systems, CO2 injection by yeast is one of the most popular DIY approaches followed by aquaculturists for providing CO2 to underwater aquatic plants. The yeast culture is, in general, maintained in plastic bottles, and typical systems provide one bubble every 3–7 seconds. Various approaches have been devised to allow proper absorption of the gas into the water.[57]
See also
Saccharomyces cerevisiae extracts: Vegemite, Marmite, Cenovis, Guinness Yeast Extract, mannan oligosaccharides, pgg-glucan, zymosan
Saccharomyces cerevisiae boulardii (Saccharomyces boulardii)
References
^ Feldmann, Horst (2010). Yeast. Molecular and Cell bio. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-3527326099..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
[page needed]
^ Walker LJ, Aldhous MC, Drummond HE, Smith BR, Nimmo ER, Arnott ID, Satsangi J (2004). "Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies (ASCA) in Crohn's disease are associated with disease severity but not NOD2/CARD15 mutations". Clin. Exp. Immunol. 135 (3): 490–96. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2003.02392.x. PMC 1808965. PMID 15008984.
^ ab Moyad MA (2008). "Brewer's/baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and preventive medicine: Part II". Urol Nurs. 28 (1): 73–75. PMID 18335702.
^
Eben Norton Horsford (1875). Report on Vienna bread. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 86.
^
Kristiansen, B.; Ratledge, Colin (2001). Basic biotechnology. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 378. ISBN 978-0-521-77917-3.
^
Eben Norton Horsford (1875). Report on Vienna bread. U.S. Government Printing Office. pp. 31–32.
^
Marx, Jean & Litchfield, John H. (1989). A Revolution in biotechnology. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-521-32749-7.
^ Marshall, Charles, ed. (June 1912). Microbiology. P. Blakiston's son & Company. p. 420. Retrieved November 5, 2014.
^ ab Stefanini I, Dapporto L, Legras JL, Calabretta A, Di Paola M, De Filippo C, Viola R, Capretti P, Polsinelli M, Turillazzi S, Cavalieri D (2012). "Role of social wasps in Saccharomyces cerevisiae ecology and evolution". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109 (33): 13398–403. Bibcode:2012PNAS..10913398S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1208362109. PMC 3421210. PMID 22847440.
^ Stefanini I, Dapporto L, Berná L, Polsinelli M, Turillazzi S, Cavalieri D (2016). "Social wasps are a Saccharomyces mating nest". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113 (8): 2247–51. Bibcode:2016PNAS..113.2247S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1516453113. PMC 4776513. PMID 26787874.
^ Zörgö E, Chwialkowska K, Gjuvsland AB, Garré E, Sunnerhagen P, Liti G, Blomberg A, Omholt SW, Warringer J (2013). "Ancient evolutionary trade-offs between yeast ploidy states". PLoS Genet. 9 (3): e1003388. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003388. PMC 3605057. PMID 23555297.
^ Herskowitz I (1988). "Life cycle of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Microbiol. Rev. 52 (4): 536–53. PMC 373162. PMID 3070323.
^ Friedman, Nir (January 3, 2011). "The Friedman Lab Chronicles". Growing yeasts (Robotically). Nir Friedman Lab. Retrieved 2012-08-13.
^ Warringer J, Zörgö E, Cubillos FA, Zia A, Gjuvsland A, Simpson JT, Forsmark A, Durbin R, Omholt SW, Louis EJ, Liti G, Moses A, Blomberg A (2011). "Trait variation in yeast is defined by population history". PLoS Genet. 7 (6): e1002111. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002111. PMC 3116910. PMID 21698134.
^ Kaeberlein M, Powers RW, Steffen KK, Westman EA, Hu D, Dang N, Kerr EO, Kirkland KT, Fields S, Kennedy BK (2005). "Regulation of yeast replicative life span by TOR and Sch9 in response to nutrients". Science. 310 (5751): 1193–96. Bibcode:2005Sci...310.1193K. doi:10.1126/science.1115535. PMID 16293764.
^ Kaeberlein M (2010). "Lessons on longevity from budding yeast". Nature. 464 (7288): 513–19. Bibcode:2010Natur.464..513K. doi:10.1038/nature08981. PMC 3696189. PMID 20336133.
^ Mortimer, Robert K.; Romano, Patrizia; Suzzi, Giovanna; Polsinelli, Mario (December 1994). "Genome renewal: A new phenomenon revealed from a genetic study of 43 strains ofSaccharomyces cerevisiae derived from natural fermentation of grape musts". Yeast. 10 (12): 1543–52. doi:10.1002/yea.320101203. PMID 7725789.
^ Masel, Joanna; Lyttle, David N. (December 2011). "The consequences of rare sexual reproduction by means of selfing in an otherwise clonally reproducing species". Theoretical Population Biology. 80 (4): 317–22. doi:10.1016/j.tpb.2011.08.004. PMC 3218209. PMID 21888925.
^ Saccharomyces cerevisiae http://bioweb.uwlax.edu/bio203/s2007/nelson_andr/
^ abcdef Morgan, David (2007). The Cell Cycle: Principles of Control. Sinauer Associates.
^ ab Bi, Erfei (2017). "Mechanics and regulation of cytokinesis in budding yeast", Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 66: 107–18.
^ abc Wloka, Carsten (2012). "Mechanisms of cytokinesis in budding yeast", Cytoskeleton, 69(10): 710–26.
^ ab Bi, Erfei (2002). "Cytokinesis in Budding Yeast: the Relationship between Actomyosin Ring Function and Septum Formation", Cell Structure and Function, 26(6): 529–37
^ Fang, X (2010). "Biphasic targeting and cleavage furrow ingression directed by the tail of a myosin-II", J Cell Biol 191: 1333–50.
^ VerPlank, Lynn (2005). "Cell cycle-regulated trafficking of Chs2 controls actomyosin ring stability during cytokinesis", Mol. Biol. Cell, 16: 2529–43
^ Adams, A (1984). “Relationship of actin and tubulin distribution to bud growth in wild-type and morphogenetic-mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae”, ‘’J. Cell Biol.’’ 98: 934–945
^ ab Balasubramanian, Mohan (2004). "Comparative Analysis of Cytokinesis in Budding Yeast, Fission Yeast and Animal Cells", Curr. Biology, 14(18): R806–18.
^ Nickoloff, Jac A.; Haber, James E. (2011). "Mating-Type Control of DNA Repair and Recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae". In Nickoloff, Jac A.; Hoekstra, Merl F. DNA Damage and Repair. Contemporary Cancer Research. pp. 107–24. doi:10.1007/978-1-59259-095-7_5 (inactive 2019-03-15). ISBN 978-1-59259-095-7.
^ Boekhout, T.; Robert, V., eds. (2003). Yeasts in Food: Beneficial and Detrimental aspects. Behr's Verlag. p. 322. ISBN 978-3-86022-961-3. Retrieved January 10, 2011.
^ abcde Longo VD, Shadel GS, Kaeberlein M, Kennedy B (2012). "Replicative and chronological aging in Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Cell Metab. 16 (1): 18–31. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.06.002. PMC 3392685. PMID 22768836.
^ abcd Kaeberlein M, Burtner CR, Kennedy BK (2007). "Recent developments in yeast aging". PLoS Genet. 3 (5): 655–60. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030084. PMC 1877880. PMID 17530929.
^ Wei M, Fabrizio P, Hu J, Ge H, Cheng C, Li L, Longo VD (2008). "Life span extension by calorie restriction depends on Rim15 and transcription factors downstream of Ras/PKA, Tor, and Sch9". PLoS Genet. 4 (1): 139–49. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0040013. PMC 2213705. PMID 18225956.
^ "10-Fold Life Span Extension Reported". University of Southern California. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04.
^ Unal E, Kinde B, Amon A (2011). "Gametogenesis eliminates age-induced cellular damage and resets life span in yeast". Science. 332 (6037): 1554–57. Bibcode:2011Sci...332.1554U. doi:10.1126/science.1204349. PMC 3923466. PMID 21700873.
^ Steinboeck F, Hubmann M, Bogusch A, Dorninger P, Lengheimer T, Heidenreich E (June 2010). "The relevance of oxidative stress and cytotoxic DNA lesions for spontaneous mutagenesis in non-replicating yeast cells". Mutat. Res. 688 (1–2): 47–52. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.03.006. PMID 20223252.
^ Pongpanich M, Patchsung M, Mutirangura A (2018). "Pathologic Replication-Independent Endogenous DNA Double-Strand Breaks Repair Defect in Chronological Aging Yeast". Front Genet. 9: 501. doi:10.3389/fgene.2018.00501. PMC 6209823. PMID 30410502.
^ Herskowitz I (1988). "Life cycle of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Microbiol. Rev. 52 (4): 536–53. PMC 373162. PMID 3070323.
^ abc Ruderfer DM, Pratt SC, Seidel HS, Kruglyak L (2006). "Population genomic analysis of outcrossing and recombination in yeast". Nat. Genet. 38 (9): 1077–81. doi:10.1038/ng1859. PMID 16892060.
^ ab Haynes, Robert H.; Kunz, Bernard A. (1981). "DNA repair and mutagenesis in yeast". In Strathern, Jeffrey N.; Jones, Elizabeth W.; Broach, James R. The Molecular Biology of the Yeast Saccharomyces: Life Cycle and Inheritance. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. pp. 371–414. ISBN 978-0-87969-139-4.
^ ab Game JC, Zamb TJ, Braun RJ, Resnick M, Roth RM (1980). "The Role of Radiation (rad) Genes in Meiotic Recombination in Yeast". Genetics. 94 (1): 51–68. PMC 1214137. PMID 17248996.
^ Malone RE, Esposito RE (1980). "The RAD52 gene is required for homothallic interconversion of mating types and spontaneous mitotic recombination in yeast". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77 (1): 503–07. Bibcode:1980PNAS...77..503M. doi:10.1073/pnas.77.1.503. PMC 348300. PMID 6987653.
^ Henriques, J. A. P.; Moustacchi, E. (1980). "Sensitivity to Photoaddition of Mono-And Bifunctional Furocoumarins of X-Ray Sensitive Mutants of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 31 (6): 557–63. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.1980.tb03746.x.
^ Birdsell, John A.; Wills, Christopher (2003). "The Evolutionary Origin and Maintenance of Sexual Recombination: A Review of Contemporary Models". Evolutionary Biology. pp. 27–138. doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-5190-1_2. ISBN 978-1-4419-3385-0.
^ Bernstein, Harris; Bernstei, Carol (2013). "Evolutionary Origin and Adaptive Function of Meiosis". Meiosis. doi:10.5772/56557. ISBN 978-953-51-1197-9.
^ Hrandl, Elvira (2013). "Meiosis and the Paradox of Sex in Nature". Meiosis. doi:10.5772/56542. ISBN 978-953-51-1197-9.
^ ab Goffeau A, Barrell BG, Bussey H, Davis RW, Dujon B, Feldmann H, Galibert F, Hoheisel JD, Jacq C, Johnston M, Louis EJ, Mewes HW, Murakami Y, Philippsen P, Tettelin H, Oliver SG (1996). "Life with 6000 genes". Science. 274 (5287): 546, 563–67. Bibcode:1996Sci...274..546G. doi:10.1126/science.274.5287.546. PMID 8849441.
^ Botstein D, Chervitz SA, Cherry JM (1997). "Yeast as a model organism". Science. 277 (5330): 1259–60. doi:10.1126/science.277.5330.1259. PMC 3039837. PMID 9297238.
^ "YeastDeletionWeb". Retrieved 2013-05-25.
^ abc Costanzo M, Baryshnikova A, Bellay J, Kim Y, Spear ED, Sevier CS, Ding H, Koh JL, Toufighi K, Mostafavi S, Prinz J, St Onge RP, VanderSluis B, Makhnevych T, Vizeacoumar FJ, Alizadeh S, Bahr S, Brost RL, Chen Y, Cokol M, Deshpande R, Li Z, Lin ZY, Liang W, Marback M, Paw J, San Luis BJ, Shuteriqi E, Tong AH, van Dyk N, Wallace IM, Whitney JA, Weirauch MT, Zhong G, Zhu H, Houry WA, Brudno M, Ragibizadeh S, Papp B, Pál C, Roth FP, Giaever G, Nislow C, Troyanskaya OG, Bussey H, Bader GD, Gingras AC, Morris QD, Kim PM, Kaiser CA, Myers CL, Andrews BJ, Boone C (2010). "The genetic landscape of a cell". Science. 327 (5964): 425–31. Bibcode:2010Sci...327..425C. doi:10.1126/science.1180823. PMC 5600254. PMID 20093466.
^ Tong AH, Lesage G, Bader GD, Ding H, Xu H, Xin X, Young J, Berriz GF, Brost RL, Chang M, Chen Y, Cheng X, Chua G, Friesen H, Goldberg DS, Haynes J, Humphries C, He G, Hussein S, Ke L, Krogan N, Li Z, Levinson JN, Lu H, Ménard P, Munyana C, Parsons AB, Ryan O, Tonikian R, Roberts T, Sdicu AM, Shapiro J, Sheikh B, Suter B, Wong SL, Zhang LV, Zhu H, Burd CG, Munro S, Sander C, Rine J, Greenblatt J, Peter M, Bretscher A, Bell G, Roth FP, Brown GW, Andrews B, Bussey H, Boone C (2004). "Global mapping of the yeast genetic interaction network". Science. 303 (5659): 808–13. Bibcode:2004Sci...303..808T. doi:10.1126/science.1091317. PMID 14764870.
^ "Special Issue Synthetic Yeast Genome", Science, 10 March 2017 Vol 355, Issue 6329
^ ab Warmflash, David; Ciftcioglu, Neva; Fox, George; McKay, David S.; Friedman, Louis; Betts, Bruce; Kirschvink, Joseph (November 5–7, 2007). Living interplanetary flight experiment (LIFE): An experiment on the survivalability of microorganisms during interplanetary travel (PDF). Workshop on the Exploration of Phobos and Deimos. Ames Research Center.
^ ab "Projects: LIFE Experiment: Phobos". The Planetary Society. Archived from the original on 16 March 2011. Retrieved 2 April 2011.
^ Anatoly Zak (1 September 2008). "Mission Possible". Air & Space Magazine. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 26 May 2009.
^ "Controlling Diastaticus in your Brewery". www.chaibio.com. Retrieved 2018-11-11.
^ "Designates Saccharomyces cerevisiae as official microbe of State of Oregon". Oregon State Legislature.
^ "CO2 Injection: The Yeast Method". www.thekrib.com. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
Further reading
Arroyo-López FN, Orlić S, Querol A, Barrio E (2009). "Effects of temperature, pH and sugar concentration on the growth parameters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, S. kudriavzevii and their interspecific hybrid" (PDF). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 131 (2–3): 120–27. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.01.035. PMID 19246112.
Jansma, David B. (1999). Regulation and variation of subunits of RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (PDF) (Ph.D.). University of Toronto.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
- Saccharomyces Genome Database
- Yeast Resource Center Public Data Repository
- Munich Information Center for Protein Sequences
UniProt – Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- View the sacCer3 genome assembly in the UCSC Genome Browser.
