List of Zulu Regiments
There were a number of Zulu Regiments[1][2] (known sometimes as "Impis"). Most were created during the reign of Shaka Zulu. This is a list of them.
Contents
1 List of Regiments
2 Divisions
3 Notes
4 References
List of Regiments
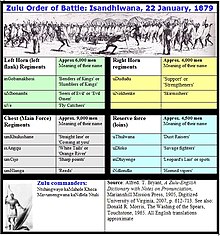
The Zulu deployment at Isandhlwana shows the well-organized tactical system of the impi. The left horn worked with the chest to pin the British down, drawing the bulk of their fire. The right horn meanwhile circled around the mountain to attack the English rear. The reserves struck deeper, cutting off and pursuing fugitives, and eventually attacking Rorke's Drift.[3]:49[4]:263-382
| Name | Date Raised | Age Group Birth Years |
|---|---|---|
| Ama-Wombe (Single Clash) | 1816 | 1775-1785 |
| U-Kangela (Look-out) | 1816 | 1785-1790 |
| Izin-Tenjana (ezakala O-Ngoye)[a] | 1818-1819 | 1795-1798 |
| U-Nomdayana | 1820 | 1800 |
| Ama-Pela [b] | 1821 | 1801 |
| Ama-Kwenkwe | 1822-1826 | 1802-1806 |
| Izi-Kwembu | 1822-1826 | 1802-1806 |
| Izi-Zimazane | 1822-1826 | 1802-1806 |
| Jubingqwanda (Shorn Head-rings) | 1816 | 1785-1790 |
| U-Dlambedlu (Wild Men) | 1816 | 1790-1795 |
| Um-Gumanqa | 1818-1819 | 1797-1798[c] |
| Isi-Pezi | 1818-1819 | 1797-1798[c] |
| U-Mbonambi | 1818-1819 | 1797-1798[c] |
| U-Nteke | 1818-1819 | 1797-1798[c] |
| U-Gibabanye or Kipabanye (The Expellers) | 1820-1825 | 1800-1805 |
| U-Fojisa | 1820-1825 | 1800-1805 |
| Im-Folozi | 1820-1825 | 1800-1805 |
| In-Dabakulu (The Great Affair) | 1820-1825 | 1800-1805 |
| Fasimba (The Haze) "Shaka's Own" [d] | 1816 | |
| Izi-Cwe (The Bushmen) "Ngomane's Own" [d] | 1816 | |
| U-Dlangezwa | 1823-1824 | |
| Um-Ota | 1823-1824 | |
| Ulu-Tuli | 1823-1824 | |
| Izi-Nyosi (The Bees) [e] | 1828 |
Divisions
- Belebele Brigade/Division
- Izim-Pohlo (Bachelors) or Isi-Klebe Division
Notes
^ "The Plovers who called out at Ngoye"
^ "The Cockroaches - Adopted from Zwide"
^ abcd Heavy influx of men due to the collapse of the Mtetwas and Qwabes. These 4 regiments (Um-Gumanqa, Isi-Pezi, U-Mbonambi, U-Nteke) sometimes formed a sub-division.
^ ab Sometimes Fasimba (The Haze) Shaka's Own was grouped together with Izi-cwe (The Bushmen) Ngomane's Own as the Young Guard
^ Formed by Shaka from the senior u-dibi boys he withdrew from the Soshangane campaign in 1828
References
^ Dovey, John. "Resource Info: Shaka Zulu". South African Military Units. Retrieved 18 October 2014..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Ritter, E.A. (1955). Shaka Zulu: The Rise of the Zulu Empire (5 ed.). Longmans, Green.
^ Knight, Ian (2002). Isandlwana 1879: The Great Zulu Victory (Illustrated ed.). Osprey. ISBN 9781841765112. Retrieved 21 October 2014.
^ Morris, Donald R. (1998). The Washing of the Spears: A History of the Rise of the Zulu Nation Under Shaka and Its Fall in the Zulu War of 1879 (Illustrated. Reprint ed.). Da Capo Press. ISBN 9780306808661. Retrieved 21 October 2014.
This African military article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |