Mausoleum at Halicarnassus
| Mausoleum at Halicarnassus | |
|---|---|
 Model of the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, at the Bodrum Museum of Underwater Archaeology. | |
 Location within Turkey Show map of Turkey  Mausoleum at Halicarnassus (West and Central Asia) Show map of West and Central Asia | |
| General information | |
| Status | In ruins |
| Type | Mausoleum |
| Architectural style | Classical |
| Town or city | Halicarnassus, Achaemenid Empire (modern-day Bodrum, Turkey) |
| Country | Achaemenid Empire; modern day Turkey) |
| Coordinates | 37°02′16″N 27°25′27″E / 37.0379°N 27.4241°E / 37.0379; 27.4241Coordinates: 37°02′16″N 27°25′27″E / 37.0379°N 27.4241°E / 37.0379; 27.4241 |
| Opened | 351 BC |
| Demolished | 1494 AD |
| Client | Mausolus and Artemisia II of Caria |
| Owner | Artaxerxes III |
| Height | Approximately 45 m (148 ft) |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect | Satyros and Pythius of Priene |
| Other designers | Leochares, Bryaxis, Scopas and Timotheus |
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus or Tomb of Mausolus[a] (Ancient Greek: Μαυσωλεῖον τῆς Ἁλικαρνασσοῦ; Turkish: Halikarnas Mozolesi) was a tomb built between 353 and 350 BC at Halicarnassus (present Bodrum, Turkey) for Mausolus, a satrap in the Persian Empire, and his sister-wife Artemisia II of Caria. The structure was designed by the Greek architects Satyros and Pythius of Priene.[1][2] Its elevated tomb structure is derived from the tombs of neighbouring Lycia, a territory Mausolus had invaded and annexed circa 460 BC, such as the Nereid Monument.[3]
The Mausoleum was approximately 45 m (148 ft) in height, and the four sides were adorned with sculptural reliefs, each created by one of four Greek sculptors—Leochares, Bryaxis, Scopas of Paros and Timotheus.[4] The finished structure of the mausoleum was considered to be such an aesthetic triumph that Antipater of Sidon identified it as one of his Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It was destroyed by successive earthquakes from the 12th to the 15th century,[5][6][7] the last surviving of the six destroyed wonders.
The word mausoleum has now come to be used generically for an above-ground tomb.
Contents
1 Conquest
2 Halicarnassus
3 Construction of the Mausoleum
4 History
4.1 Jar of Xerxes I
5 Dimensions and statues
6 Later history of the Mausoleum
7 Discovery and excavation
8 Influence on modern architecture
9 See also
10 Notes
11 References
11.1 Sources
12 Further reading
13 External links
Conquest

Coinage of Maussolos as Achaemenid dynast of Caria. Head of Apollo facing/ Zeus Labrandos standing, legend ΜΑΥΣΣΩΛΛΟ ("Mausolos"). Circa 376–353 BC.[8]
In the 4th century BC, Halicarnassus was the capital of a small regional kingdom of Caria within the Achaemenid Empire on the western coast of Asia Minor.
In 377 BC, the nominal ruler of the region, Hecatomnus of Milas, died and left the control of the kingdom to his son, Mausolus. Hecatomnus, a local dynast under the Persians, took control of several of the neighboring cities and districts. After Artemisia and Mausolus, he had several other daughters and sons: Ada (adoptive mother of Alexander the Great), Idrieus and Pixodarus. Mausolus extended his territory as far as the southwest coast of Anatolia, invading in particular the territory of Lycia, remarkable for its numerous monumental tombs such as the Tombs of Xanthos, from which he took his inspiration for his mausoleum.[9]
Artemisia and Mausolus ruled from Halicarnassus over the surrounding territory for 24 years. Mausolus, although descended from local people, spoke Greek and admired the Greek way of life and government. He founded many cities of Greek design along the coast and encouraged Greek democratic traditions.[citation needed]
Halicarnassus

The ruins of the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus.

Mausolus (casting from the Pushkin museum).
Mausolus decided to build a new capital, one as safe from capture as it was magnificent to be seen. He chose the city of Halicarnassus. Artemisia and Mausolus spent huge amounts of tax money to embellish the city. They commissioned statues, temples and buildings of gleaming marble. In 353 BC, Mausolus died, leaving Artemisia to rule alone. As the Persian satrap, and as the Hecatomnid dynast, Mausolus had planned for himself an elaborate tomb. When he died the project was continued by his siblings. The tomb became so famous that Mausolus's name is now the eponym for all stately tombs, in the word mausoleum.
Artemisia lived for only two years after the death of her husband. The urns with their ashes were placed in the yet unfinished tomb. As a form of sacrifice ritual the bodies of a large number of dead animals were placed on the stairs leading to the tomb, and then the stairs were filled with stones and rubble, sealing the access. According to the historian Pliny the Elder, the craftsmen decided to stay and finish the work after the death of their patron "considering that it was at once a memorial of his own fame and of the sculptor's art".
Construction of the Mausoleum
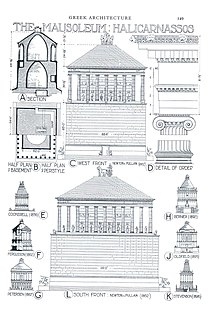
Reconstitutions of the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus.
It is likely that Mausolos started to plan the tomb before his death, as part of the building works in Halicarnassus, and that when he died Artemisia continued the building project. Artemisia spared no expense in building the tomb. She sent messengers to Greece to find the most talented artists of the time. These included Scopas, the man who had supervised the rebuilding of the Temple of Artemis at Ephesus. The famous sculptors were (in the Vitruvius order): Leochares, Bryaxis, Scopas, and Timotheus, as well as hundreds of other craftsmen.
The tomb was erected on a hill overlooking the city. The whole structure sat in an enclosed courtyard. At the center of the courtyard was a stone platform on which the tomb sat. A stairway flanked by stone lions led to the top of the platform, which bore along its outer walls many statues of gods and goddesses. At each corner, stone warriors mounted on horseback guarded the tomb. At the center of the platform, the marble tomb rose as a square tapering block to one-third of the Mausoleum's 45 m (148 ft) height. This section was covered with bas-reliefs showing action scenes, including the battle of the centaurs with the lapiths and Greeks in combat with the Amazons, a race of warrior women.
On the top of this section of the tomb thirty-six slim columns, ten per side, with each corner sharing one column between two sides; rose for another third of the height. Standing between each pair of columns was a statue. Behind the columns was a solid cella-like block that carried the weight of the tomb's massive roof. The roof, which comprised most of the final third of the height, was pyramidal. Perched on the top was a quadriga: four massive horses pulling a chariot in which rode images of Mausolus and Artemisia.
History

Colossal statues of a man and a woman from the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, traditionally identified as Mausolos and Artemisia II, around 350 BC, British Museum.
Modern historians have pointed out that two years would not be enough time to decorate and build such an extravagant building. Therefore, it is believed that construction was begun by Mausolus before his death or continued by the next leaders.[10] The Mausoleum of Halicarnassus resembled a temple and the only way to tell the difference was its slightly higher outer walls. The Mausoleum was in the Greek-dominated area of Halicarnassus, which in 353 was controlled by the Achaemenid Empire. According to the Roman architect Vitruvius, it was built by Satyros and Pytheus who wrote a treatise about it; this treatise is now lost.[10] Pausanias adds that the Romans considered the Mausoleum one of the great wonders of the world and it was for that reason that they called all their magnificent tombs mausolea, after it.[11]

Relief of an Amazonomachy from the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus.
It is unknown exactly when and how the Mausoleum came to ruin: Eustathius, writing in the 12th century on his commentary of the Iliad says "it was and is a wonder". Because of this, Fergusson concluded that the building was ruined, probably by an earthquake, between this period and 1402, when the Knights of St. John of Jerusalem arrived and recorded that it was in ruins.[11] However, Luttrell notes[12] that at that time the local Greek and Turks had no name for – or legends to account for – the colossal ruins, suggesting a destruction at a much earlier period.
Many of the stones from the ruins were used by the knights to fortify their castle at Bodrum; they also recovered bas-reliefs with which they decorated the new building. Much of the marble was burned into lime. In 1846 Lord Stratford de Redcliffe obtained permission to remove these reliefs from the Bodrum.[13]
At the original site, all that remained by the 19th century were the foundations and some broken sculptures. This site was originally indicated by Professor Donaldson and was discovered definitively by Charles Newton, after which an expedition was sent by the British government. The expedition lasted three years and ended in the sending of the remaining marbles.[14] At some point before or after this, grave robbers broke into and destroyed the underground burial chamber, but in 1972 there was still enough of it remaining to determine a layout of the chambers when they were excavated.[10]
This monument was ranked the seventh wonder of the world by the ancients, not because of its size or strength but because of the beauty of its design and how it was decorated with sculpture or ornaments.[15] The mausoleum was Halicarnassus' principal architectural monument, standing in a dominant position on rising ground above the harbor.[16]
Jar of Xerxes I
.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbinner{display:flex;flex-direction:column}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .trow{display:flex;flex-direction:row;clear:left;flex-wrap:wrap;width:100%;box-sizing:border-box}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{margin:1px;float:left}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .theader{clear:both;font-weight:bold;text-align:center;align-self:center;background-color:transparent;width:100%}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbcaption{text-align:left;background-color:transparent}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-left{text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-right{text-align:right}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .text-align-center{text-align:center}@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbinner{width:100%!important;box-sizing:border-box;max-width:none!important;align-items:center}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .trow{justify-content:center}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:100%!important;box-sizing:border-box;text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .thumbcaption{text-align:center}}
A jar in calcite or alabaster, an alabastra, with the quadrilingual signature of Achaemenid ruler Xerxes I (ruled 486–465 BC) was discovered in the ruins of the Mausoleum, at the foot of the western staircase.[17] The vase contains an inscription in Old Persian, Egyptian, Babylonian, and Elamite:[17][18][19]
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 𐏐 𐏋 𐏐 𐎺𐏀𐎼𐎣
( Xšayāršā : XŠ : vazraka)
"Xerxes : The Great King."
— Old Persian inscription on the Jar of Xerxes, Mausoleum at Halicarnassus.[18]
Such jars, of Egyptian origin, were very precious to the Achaemenids, and may therefore have been offered by Xerxes to Carian rulers, and then kept as a precious object.[19] In particular, the precious jar may have been offered by Xerxes to the Carian dynast Artemisia I, who had acted with merit as his only female Admiral during the Second Persian invasion of Greece, and particularly at the Battle of Salamis.[20][18][17] The jar testifies to the close contacts between Carian rulers and the Achaemenid Empire.[17][18]
Dimensions and statues

Timeline and map of the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus and the other Wonders of the Ancient World
Much of the information we have gathered about the Mausoleum and its structure has come from the Roman polymath Pliny the Elder. He wrote some basic facts about the architecture and some dimensions. The building was rectangular, not square, surrounded by a colonnade of thirty-six columns. There was a pyramidal superstructure receding in twenty four steps to the summit. On top there were 4 horse chariots of marble. The building was accented with both sculptural friezes and free standing figures. "The free standing figures were arranged on 5 or 6 different levels."[10] We are now able to justify that Pliny's knowledge came from a work written by the architect. It is clear that Pliny did not grasp the design of the mausoleum fully which creates problems in recreating the structure. He does state many facts which help the reader recreate pieces of the puzzle. Other writings by Pausanias, Strabo, and Vitruvius also help us to gather more information about the Mausoleum.[21]

A fragmentary horse from a colossal four-horse chariot group which topped the podium of the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus.
According to Pliny, the mausoleum was 19 metres (63 ft) north and south, shorter on other fronts, 125 metres (411 ft) perimeter, and 25 cubits (11.4 metres or 37.5 feet) in height. It was surrounded by 36 columns. They called this part the pteron. Above the pteron there was a pyramid on top with 24 steps and equal in height to the lower part. The height of the building was 43 metres (140 ft).[22] The only other author that gives the dimensions of the Mausoleum is Hyginus a grammarian in the time of Augustus. He describes the monument as built with shining stones, 24 metres (80 ft) high and 410 metres (1,340 ft) in circumference. He likely meant cubits which would match Pliny's dimensions exactly but this text is largely considered corrupt and is of little importance.[21] We learn from Vitruvius that Satyrus and Phytheus wrote a description of their work which Pliny likely read. Pliny likely wrote down these dimensions without thinking about the form of the building.[21]
A number of statues were found slightly larger than life size, either 1.5 metres (5 ft). or 1.60 metres (5.25 ft). in length; these were 20 lion statues. Another important find was the depth on the rock on which the building stood. This rock was excavated to 2.4 or 2.7 metres (8 or 9 ft) deep over an area 33 by 39 metres (107 by 127 ft).[22]
The sculptures on the north were created by Scopas, the ones on the east Bryaxis, on the south Timotheus and on the west Leochares.[21]
The Mausoleum was adorned with many great and beautiful sculptures. Some of these sculptures have been lost or only fragments have been found. Several of the statues' original placements are only known through historical accounts. The great figures of Mausolus and Artemisia stood in the chariot at the top of the pyramid. The detached equestrian groups are placed at the corners of the sub podium.[21] The semi-colossal female heads they may have belonged to the acroteria of the two gables which may have represented the six Carian towns incorporated in Halicarnassus.[23] Work still continues today as groups continue to excavate and research the mausoleum's art.
Later history of the Mausoleum

Bodrum Castle

The Castle from the south-east
The Mausoleum overlooked the city of Halicarnassus for many years. It was untouched when the city fell to Alexander the Great in 334 BC and still undamaged after attacks by pirates in 62 and 58 BC. It stood above the city's ruins for sixteen centuries. Then a series of earthquakes shattered the columns and sent the bronze chariot crashing to the ground. By 1404 AD only the very base of the Mausoleum was still recognizable.
The Knights of St John of Rhodes invaded the region and built Bodrum Castle (Castle of Saint Peter). When they decided to fortify it in 1494, they used the stones of the Mausoleum. This is also about when "imaginative reconstructions" of the Mausoleum began to appear.[24] In 1522 rumours of a Turkish invasion caused the Crusaders to strengthen the castle at Halicarnassus (which was by then known as Bodrum) and much of the remaining portions of the tomb were broken up and used in the castle walls. Sections of polished marble from the tomb can still be seen there today. Suleiman the Magnificent conquered the base of the knights on the island of Rhodes, who then relocated first briefly to Sicily and later permanently to Malta, leaving the Castle and Bodrum to the Ottoman Empire.
During the fortification work, a party of knights entered the base of the monument and discovered the room containing a great coffin. In many histories of the Mausoleum one can find the following story of what happened: the party, deciding it was too late to open it that day, returned the next morning to find the tomb, and any treasure it may have contained, plundered. The bodies of Mausolus and Artemisia were missing too. The small museum building next to the site of the Mausoleum tells the story. Research done by archeologists in the 1960s shows that long before the knights came, grave robbers had dug a tunnel under the grave chamber, stealing its contents. Also the museum states that it is most likely that Mausolus and Artemisia were cremated, so only an urn with their ashes was placed in the grave chamber. This explains why no bodies were found.
Before grinding and burning much of the remaining sculpture of the Mausoleum into lime for plaster, the Knights removed several of the best works and mounted them in the Bodrum castle. There they stayed for three centuries.
Discovery and excavation

An actress performs a play in front of two statues from the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus. Room 21, the British Museum, London
In the 19th century a British consul obtained several of the statues from Bodrum Castle; these now reside in the British Museum. In 1852 the British Museum sent the archaeologist Charles Thomas Newton to search for more remains of the Mausoleum. He had a difficult job. He did not know the exact location of the tomb, and the cost of buying up all the small parcels of land in the area to look for it would have been astronomical. Instead Newton studied the accounts of ancient writers like Pliny to obtain the approximate size and location of the memorial, then bought a plot of land in the most likely location. Digging down, Newton explored the surrounding area through tunnels he dug under the surrounding plots. He was able to locate some walls, a staircase, and finally three of the corners of the foundation. With this knowledge, Newton was able to determine which plots of land he needed to buy.
Newton then excavated the site and found sections of the reliefs that decorated the wall of the building and portions of the stepped roof. Also discovered was a broken stone chariot wheel some 2 m (6 ft 7 in) in diameter, which came from the sculpture on the Mausoleum's roof. Finally, he found the statues of Mausolus and Artemisia that had stood at the pinnacle of the building. In October 1857 Newton carried blocks of marble from this site by HMS Supply and landed them in Malta. These blocks were used for the construction of a new dock in Malta for the Royal Navy. Today this dock is known at Dock No. 1 in Cospicua, but the building blocks are hidden from view, submerged in Dockyard Creek in the Grand Harbour.[25]
From 1966 to 1977, the Mausoleum was thoroughly researched by Prof. Kristian Jeppesen of Aarhus University, Denmark. He has produced a six-volume monograph, The Maussolleion at Halikarnassos.
The beauty of the Mausoleum was not only in the structure itself, but in the decorations and statues that adorned the outside at different levels on the podium and the roof: statues of people, lions, horses, and other animals in varying scales. The four Greek sculptors who carved the statues: Bryaxis, Leochares, Scopas and Timotheus were each responsible for one side. Because the statues were of people and animals, the Mausoleum holds a special place in history, as it was not dedicated to the gods of Ancient Greece.
Today, the massive castle of the Knights Hospitaller (Knights of St. John) still stands in Bodrum, and the polished stone and marble blocks of the Mausoleum can be spotted built into the walls of the structure. At the site of the Mausoleum, only the foundation remains, and a small museum. Some of the surviving sculptures at the British Museum include fragments of statues and many slabs of the frieze showing the battle between the Greeks and the Amazons. There the images of Mausolus and his queen watch over the few broken remains of the beautiful tomb she built for him.
Reconstruction of the Amazonomachy can be seen in the left background. British Museum Room 21

Statue usually identified as Artemisia; reconstruction of the Amazonomachy can be seen in the left background. British Museum Room 21

This lion is among the few free-standing sculptures from the Mausoleum at the British Museum.

Slab from the Amazonomachy believed to show Herculeas grabbing the hair of the Amazon Queen Hippolyta.

















Influence on modern architecture
Modern buildings whose designs were based upon or influenced by interpretations of the design of the Mausoleum of Mausolus include PNC Tower in Cincinnati; the Civil Courts Building in St. Louis; the National Newark Building in Newark, New Jersey; Grant's Tomb and 26 Broadway in New York City; Los Angeles City Hall; the Shrine of Remembrance in Melbourne; the spire of St. George's Church, Bloomsbury in London; the Indiana War Memorial (and in turn Salesforce Tower) in Indianapolis;[26][27] the House of the Temple in Washington D.C.; the National Diet in Tokyo; and the Soldiers and Sailors Memorial Hall in Pittsburgh.[28]

The design of the Shrine of Remembrance in Melbourne was inspired by that of the Mausoleum.

The Masonic House of the Temple of the Scottish Rite, Washington, DC, designed by John Russell Pope, 1911–1915, another scholarly version.
See also
- In Milas (also the site of the tomb of Hecatomnus, who was the father of Mausolus), is also the site of the Gümüşkesen, a small-scale Roman-era (2nd century BC) copy of the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus:

Gümüşkesen in Milas

Milas Gümüşkesen front

Gümüşkesen in Milas detail of ceiling

Gümüşkesen in Milas detail of ceiling

Gümüşkesen in Milas detail of ceiling and capitals

Gümüşkesen in Milas capital

Gümüşkesen in Milas Lower part of tomb
Notes
^ "Mausoleion" meant "[building] dedicated to Mausolus"; thus, "Mausoleum of Mausolus" is a tautology.
References
^ Kostof, Spiro (1985). A History of Architecture. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 9. ISBN 0-19-503473-2..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Gloag, John (1969) [1958]. Guide to Western Architecture (Revised ed.). The Hamlyn Publishing Group. p. 362.
^ André-Salvini, Béatrice (2005). Forgotten Empire: The World of Ancient Persia. University of California Press. p. 46. ISBN 9780520247314.
^ Smith, William (1870). "Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities, page 744". Retrieved 21 September 2006.
^ "Mausoleum of Halicarnassus". Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 5 February 2014.
^ "The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus". Retrieved 5 February 2014.
^ "The Mausoleum of Halicarnassus". Retrieved 5 February 2014.
^ CNG: SATRAPS of CARIA. Maussolos. Circa 377/6–353/2 BC. AR Tetradrachm (23mm, 15.13 g, 12h). Halikarnassos mint. Struck circa 370–360 BC.
^ André-Salvini, Béatrice (2005). Forgotten Empire: The World of Ancient Persia. University of California Press. p. 46. ISBN 9780520247314.
^ abcd Colvin, Howard (1991). "Architecture and the after-life." Yale University, pp 30–31. New Haven Press.
^ ab Fergusson, p10.
^ A. Luttrell, The later history of the Maussolleion and its utilization in the Hospitaller castle at Bodrum. In Kristian Jeppesen, et al. The Maussolleion at Halikarnassos. 1986.
^ Fergusson, p6.
^ Fergusson, p7.
^ Fergusson, p5.
^ "Architecture and the after-life." Yale University, pp3 0–31. New Haven Press.
^ abcd Cambridge Ancient History. Cambridge University Press. 1924. p. 283. ISBN 9780521228046.
^ abcd A Jar with the Name of King Xerxes - Livius.
^ ab Newton, Charles Thomas (1863). A History of Discoveries at Halicarnassus, Cnidus and Branchidae. Day & Son. p. 667.
^ Mayor, Adrienne (2014). The Amazons: Lives and Legends of Warrior Women across the Ancient World. Princeton University Press. p. 315. ISBN 9781400865130.
^ abcde Fergusson.
^ ab Fergusson, p9.
^ "[A guide to the] mausoleum room." (1886). the trustees, London England
^ "The Maussolleion". SDU (in Danish). Retrieved 8 December 2017.
^ Busuttil, Cynthia (26 July 2009). "Dock 1 made from ancient ruins?". The Times. Retrieved 15 March 2015.
^ "Indiana War Memorial Exterior". State of Indiana. Archived from the original on 13 October 2007. Retrieved 21 December 2010.
^ "IWM: Indiana War Memorial Museum". in.gov.
^ Christine H. O'Toole (20 September 2009). "The Long Weekend: Pittsburgh, Three Ways". The Washington Post.
Sources
- Fergusson, James (1862). "The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus restored in conformity with the recently discovered remains." J. Murray, London
Further reading
- Brandt, J. Rasmus, Erika Hagelberg, Gro Bjørnstad, and Sven Ahrens. 2017. Life and Death in Asia Minor in Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine Times: Studies In Archaeology and Bioarchaeology. Philadelphia: Oxbow Books.
- Cook, B. F., Bernard Ashmole, and Donald Emrys Strong. 2005. Relief Sculpture of the Mausoleum At Halicarnassus. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Dmitriev, Sviatoslav. 2005. City Government In Hellenistic and Roman Asia Minor. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Jeppeson, Kristian. 2002. The Maussolleion at Halikarnassos: Reports of the Danish archaeological expedition to Bodrum: The superstructure, a comparative analysis of the architectural, sculptural, and literary evidence. Vol. 5. Aarhus, Denmark: Aarhus Univ. Press.
- Steele, James, and Ersin Alok. 1992. Hellenistic Architecture In Asia Minor. London: Academy Editions.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mausoleum at Halicarnassus. |
Library resources about Mausoleum at Halicarnassus |
|
The Tomb of Mausolus (W.R. Lethaby's reconstruction of the Mausoleum, 1908)- Livius.org: Mausoleum of Halicarnassus


































