Ilford
| Ilford | |
|---|---|
 Redbridge Town Hall on Ilford High Road | |
 Ilford Ilford shown within Greater London | |
| Population | 168,168 (2011)[1] |
| OS grid reference | TQ445865 |
| • Charing Cross | 9.1 mi (14.6 km) WSW |
| London borough |
|
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Region |
|
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | ILFORD |
| Postcode district | IG1-IG6 |
| Dialling code | 020 |
| Police | Metropolitan |
| Fire | London |
| Ambulance | London |
| EU Parliament | London |
| UK Parliament |
|
| London Assembly |
|
Ilford is a large town in east London, located 9.1 miles (14.6 km) east of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Redbridge, and identified as a major metropolitan centre in the London Plan.
Ilford forms a significant commercial and retail centre surrounded by extensive residential development. It was historically a small rural settlement in the county of Essex and its strategic position on the River Roding and the London to Colchester road caused it to develop as a coaching town.[2] The arrival of the railway in 1839 eventually accelerated that growth and as part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Ilford significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming a municipal borough in 1926, Since 1965 it has formed part of Greater London.
Ilford is part of the IG postcode area, though areas to the west of Ilford Hill and the A406 are part of E postcode area instead. The population of Ilford, comprising the Clementswood, Loxford, Goodmayes, Newbury, Mayfield, Seven Kings, Barkingside, Clayhall, Redbridge, Green Street, Fullwell, Fairlop, Cranbrook and Valentines wards, was 168,168 in the 2011 census.
Contents
1 History
1.1 Toponymy
1.2 Origins
1.3 Economic development
1.4 Local government
1.5 Suburban expansion
1.6 Notable events
1.7 Olympics
2 Governance
3 Geography
4 Demography
5 Transport
5.1 Buses
6 Culture
6.1 Art, theatre and media
6.2 Sport
7 See also
8 References
9 Bibliography
10 External links
History
| 1891 | 10,913 |
|---|---|
| 1901 | 41,234 |
| 1911 | 78,188 |
| 1921 | 85,194 |
| 1931 | 131,061 |
| 1941 | war # |
| 1951 | 184,706 |
| 1961 | 178,024 |
| # no census was held due to war | |
| source: UK census[3] | |
Toponymy
Ilford was historically known as Great Ilford to differentiate it from nearby Little Ilford, in the London Borough of Newham.[4] The name is first recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086 as Ilefort and means "ford over the Hyle". "Hyle" is an old name for the River Roding that means "trickling stream". Little Ilford shares the origin.[4]
Origins
The only complete skull of a mammoth discovered in the United Kingdom was unearthed in 1860 at the site where Boots the Chemist now stands in the High Road. The skull can now be seen in the Natural History Museum and other prehistoric animal remains can be seen at Redbridge Museum, Central Library, Ilford. Redevelopment has destroyed much of the evidence for early Ilford, but the oldest evidence for human occupation is the 1st and 2nd century BC Iron Age earthwork known as Uphall Camp. This was situated between the Roding and Ilford Lane and is recorded in 18th century plans.[2]Roman finds have also been made in the vicinity.[5] A nearby mound called Lavender Mount existed into the 1960s, when it was removed during building work at Howards chemical works. Excavation has shown that the latter may have been a 16th century 'beacon-mound'. Archaeological discoveries are displayed at Redbridge Museum.[6]
Economic development

High Road Ilford with Waterstones bookshop in the foreground on the left and the town hall in the background

Redbridge Town Hall, High Road, Ilford
Ilford straddled the important road from London to Colchester. The Middlesex and Essex Turnpike Trust controlled and maintained the road from 1721. The River Roding was made navigable for barges as far as Ilford Bridge from 1737.[5] Ilford remained largely rural until its expansion in the 19th century. This brought about brickworks, cement works and coal yards to service the new buildings, largely centred on the River Roding. In 1839, a railway station was opened on the line from Romford to Mile End. The early businesses gave way to new industries, such as paper making and services such as steam laundries and collar making, to provide for the new commuting class created by the railway. A number of major businesses have been founded in the town, including the eponymous photographic film and chemicals manufacturer Ilford Photo.[7] This was founded in 1879 by Alfred H. Harman, a photographer from Peckham, who established the business in a house in Cranbrook Road making gelatino-bromide 'dry' plates.[2] The business soon outgrew these premises, and its headquarters moved to a site at Roden Street until 1976 when the factory was closed. Many Ilford Limited products are displayed at Redbridge Museum.[6]
The radio, electronics and telecommunications company Plessey, founded in 1917 in Marylebone, moved to Cottenham Road in Ilford early in 1919 and then to Vicarage Lane where became one of the largest manufacturers in its field. During World War II, the factory was heavily damaged by bombing and the company carried out much of its manufacture, with 2,000 workers servicing a production line, located in the underground railway tunnel between Wanstead and Gants Hill.[2] In 1955 the company employed 15,000 workers, in sites throughout Ilford and neighbouring areas, with an extensive research department.[2]BAL-AMi Jukeboxes were manufactured at 290-296 High Road, Ilford, during the 1950s, which also served as the headquarters of the Balfour (Marine) Engineering company.[8]
Local government
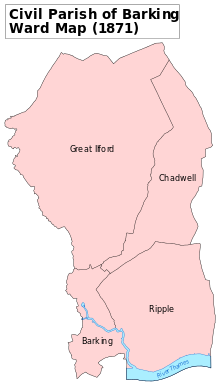
A map showing the wards of Barking Civil Parish as they appeared in 1871.

Central Library and Museum, Clements Road, Ilford
Ilford formed a ward in the large ancient parish of Barking, in the Becontree hundred of Essex. The parish authorities gradually lost responsibility for a variety of functions during the 19th century; from 1836, for the administration of poor relief, Ilford came within the Romford Poor Law Union and in 1840 the Metropolitan Police District was extended to cover the area. In 1875, the Romford rural sanitary district was created, covering a wide area including Ilford. In 1888, Ilford and the neighbouring ward of Chadwell to east were split from Barking and together formed a separate Ilford civil parish. In 1890, a local board of health was set up for the parish, replacing the rural sanitary authority, and in 1894 a reform of local government reconstituted it as an urban district. It formed part of the London Traffic Area from 1924 and the London Passenger Transport Area from 1933.[9] It was incorporated as the Municipal Borough of Ilford in 1926.[10]
The suburban expansion of London caused a significant increase in population and the borough became one of the largest in England not to gain county borough status. In 1965, the municipal borough was abolished and its former area was combined with that of Wanstead and Woodford, the northern extremity of Dagenham and a small part Chigwell Urban District around Hainault; it was removed from Essex and since then has formed the greater part of the London Borough of Redbridge in Greater London.
Suburban expansion
By 1653, Ilford was a compact village of 50 houses, mostly sited north and south of the current Broadway[2] and the area was distinctly rural. In 1801 the population of Ilford was 1,724 and by 1841 it had grown to 3,742.[2] It had a population of 41,244 in 1901 and occupied an area of 8,496 acres (34 km2). 2,500 houses of the vast Becontree Estate, built by the London County Council from 1921, were within the boundaries of Ilford; the addition caused a rise in population of 11,600 by 1926.[2] The Central line service of the London Underground to new and former main-line stations in the area began in 1947[11] and the population of the Municipal Borough of Ilford peaked in 1951 at 184,706, declining to 178,024 in 1961 before being absorbed into Redbridge and Greater London in 1965. At the 2001 Census the combined populations of the Ilford North and Ilford South constituencies was 196,414.[12][13]
Notable events
John Logie Baird, who invented the television, moved to Ilford in the mid to late 1920s to work on his new invention. He worked in a workshop on the roof of the Plessey premises in Ley Street, which has long since been demolished to make way for new housing.
Olympics
Its proximity to the Olympic Park in Stratford meant that in 2011, Ilford was the fastest-growing tourist destination in Europe due to the London 2012 Summer Olympics.[14]
Governance
Ilford is divided between the UK Parliament constituencies of Ilford North and Ilford South. Ilford North consists of the Redbridge wards of Aldborough, Barkingside, Redbridge, Clayhall, Fairlop, Fullwell, Hainault and Roding. The MP is Wes Streeting of the Labour Party, who succeeded the previous MP Lee Scott of the Conservative Party in the 2015 general election. Ilford South corresponds to the Redbridge wards of Chadwell, Clementswood, Cranbrook, Goodmayes, Loxford, Mayfield, Newbury, Seven Kings, and Valentines.[15] The MP is Mike Gapes of the Labour Party.[15] Ilford forms part of the Havering and Redbridge London Assembly constituency and the London European Parliament constituency.
Geography
Ilford is bounded in the west by the North Circular Road and the River Roding and is contiguous with Barking to the south, Gants Hill to the north and Seven Kings to the east. Climate data for Ilford is taken from the nearest weather station at Greenwich, around 6 miles (9.7 km) south south west of the railway station:
| Climate data for Greenwich Park, elevation: 47 m or 154 ft, 1981–2010 normals | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.4 (57.9) | 19.7 (67.5) | 21.7 (71.1) | 25.6 (78.1) | 30.0 (86.0) | 32.8 (91.0) | 35.3 (95.5) | 37.5 (99.5) | 30.0 (86.0) | 25.6 (78.1) | 18.9 (66.0) | 15.0 (59.0) | 37.5 (99.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.1 (46.6) | 8.6 (47.5) | 11.6 (52.9) | 14.6 (58.3) | 18.1 (64.6) | 21.0 (69.8) | 23.4 (74.1) | 23.1 (73.6) | 20.0 (68.0) | 15.5 (59.9) | 11.3 (52.3) | 8.4 (47.1) | 15.3 (59.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.6 (42.1) | 5.7 (42.3) | 8.1 (46.6) | 10.3 (50.5) | 13.5 (56.3) | 16.4 (61.5) | 18.6 (65.5) | 18.5 (65.3) | 15.7 (60.3) | 12.2 (54.0) | 8.6 (47.5) | 5.9 (42.6) | 11.6 (52.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) | 2.7 (36.9) | 4.6 (40.3) | 5.9 (42.6) | 8.9 (48.0) | 11.8 (53.2) | 13.7 (56.7) | 13.8 (56.8) | 11.4 (52.5) | 8.8 (47.8) | 5.8 (42.4) | 3.4 (38.1) | 7.8 (46.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.4 (15.1) | −9.4 (15.1) | −7.8 (18.0) | −2.2 (28.0) | −1.1 (30.0) | 5.0 (41.0) | 7.2 (45.0) | 6.1 (43.0) | 2.8 (37.0) | −3.3 (26.1) | −5.0 (23.0) | −7.2 (19.0) | −9.4 (15.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 41.6 (1.64) | 36.3 (1.43) | 40.3 (1.59) | 40.1 (1.58) | 44.9 (1.77) | 47.4 (1.87) | 34.6 (1.36) | 54.3 (2.14) | 51.0 (2.01) | 61.1 (2.41) | 57.5 (2.26) | 48.4 (1.91) | 557.4 (21.94) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 11.4 | 8.5 | 9.8 | 9.0 | 9.2 | 7.4 | 6.3 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 9.5 | 109.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 44.7 | 65.4 | 101.7 | 148.3 | 170.9 | 171.4 | 176.7 | 186.1 | 133.9 | 105.4 | 59.6 | 45.8 | 1,410 |
| Source #1: Met Office[16][17][18] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: BBC Weather[19] | |||||||||||||
Demography
Ilford has a very large ethnic-minority population, with Ilford North having the fourth-highest Jewish proportion of residents in the 2001 census.[12] The Hindu, Muslim and Sikh population number some 30,000.[20] The large South Asian community in Ilford speak a variety of languages, including Tamil, Gujarati, Hindi, Bengali, Punjabi and Urdu.[21]
According to the 2001 census, Ilford North and Ilford South consisted of the following demographs:
| Ilford North | Ilford South | |
|---|---|---|
| Total Population | 89,806 | 106,608 |
| White | 75.6% | 45.1% |
| Black | 5.2% | 11.4% |
| Asian | 15.5% | 39.3% |
| Mixed | 2.2% | 2.8% |
| Other | 1.5% | 1.4% |
| Ilford North | Ilford South | |
|---|---|---|
| Christian | 55.1% | 42.5% |
| Hindu | 6.7% | 10.5% |
| Jewish | 10.3% | 7.9% |
| Muslim | 6.4% | 19.6% |
| Sikh | 2.7% | 9.4% |
[12][13]
At the 2011 census, the Clementswood and Loxford wards were ranked the 10th and 12th in Greater London with the least white British population. The Valentines ward is ranked lower but still quite high. The other wards around Ilford are also very ethnically diverse, especially Goodmayes where only
16.9% of residents are White British. In Clementswood, only 9.4% of the population was White British and 66.3% were Asian.[22][citation needed]
Transport

Ilford railway station
The town is served by Ilford railway station on the Great Eastern Main Line in Travelcard Zone 4.[23] All trains calling at the station are the high-frequency Liverpool Street-Shenfield. This service was taken over by TfL Rail on 31 May 2015 for the new Crossrail project set to run through Ilford in 2017.[24]Gants Hill tube station is located in the north of Ilford and is served by the Central line of the London Underground.[23] It is planned that the Liverpool Street-Shenfield service will be replaced by Crossrail in 2018.[25] The first stage of the East London Transit begins at Ilford.[26]
Buses
Ilford is a hub of the London Buses network with services to central London and various suburbs.[27]
Culture

Ilford Kenneth More Theatre
Art, theatre and media
Ilford is the location of the Kenneth More Theatre. The local newspaper, covering the town and the borough, is the Ilford Recorder.
- Kenneth More Theatre
The theatre was officially opened in January 1975. It places emphasis on serving the local community, and stages a mix of professional and amateur productions. Its programme is varied, and runs throughout the year with productions generally changing on a weekly basis. It is well known within the local area for its annual pantomime, which normally runs from mid-December to mid-January.[28]
- St.Alban’s Singers
St. Alban’s Singers is a mixed voice choir for men and women based in St. Alban’s Church in Albert Road, Ilford. The choir meets to rehearse at the church each Tuesday evening during term-time and aims to give three concerts per year. [29]
Sport
An unspecified venue in Ilford was used for a cricket match in August 1737 between Essex and London. It is the earliest known organised match definitely played in Essex.[30]
Ilford Cricket Club plays home games at Valentines Park. This ground was opened in 1897.[31] It was used regularly by Essex County Cricket Club, but inadequate maintenance meant that the county stopped playing there after 2001.[32]
Ilford has two Non-League football clubs Ilford F.C. and Waltham Forest F.C. who both play at the Cricklefield Stadium.
See also
- List of people from Redbridge
- List of schools in Redbridge
References
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 9 June 2014.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link) .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcdefgh Powell, W.R. (Edr.) (1966). The borough of Ilford, A History of the County of Essex: Volume 5. Victoria County History. British History Online. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ Great Britain Historical GIS / University of Portsmouth, Ilford parish population. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ ab Mills, A.D. (2001). Dictionary of London Place Names. Oxford.
^ ab Powell, W.R. (Edr.) (1966). The ancient parish of Barking: Introduction, A History of the County of Essex: Volume 5. Victoria County History. British History Online. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ ab "Redbridge Museum". Redbridge.gov.uk. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
^ "Ilford History and Chronology". Retrieved 27 July 2007.
^ "BAL-AMi Jukeboxes".
^ Robson, William (1939). The Government and Mis-government of London. London: Allen & Unwin.
^ Great Britain Historical GIS / University of Portsmouth, Ilford UD/MB (historic map). Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ Rose, D (1999). The London Underground: A diagrammatic history.
^ abc "UKPollingReport Election Guide 2010 » Ilford North". Retrieved 2 March 2014.
^ ab "UKPollingReport Election Guide 2010 » Ilford South". Retrieved 2 March 2014.
^ The Daily Telegraph (December 2011). "TripAdvisor: Ilford is Europe's fastest growing tourist destination". The Daily Telegraph.
^ ab Mike Gapes. "Ilford South - a profile". Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ "Greenwich 1981–2010 averages". Met Office. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
^ "Hot Spell - August 2003". Met Office. Retrieved 17 December 2018.
^ "Record Breaking Heat and Sunshine - July 2006". Met Office. Retrieved 17 December 2018.
^ "London Forecast". Met Office. Retrieved 17 December 2018.
^ "South Asian Development Partnership - Research,". Southasian.org.uk. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
^ "Setting up your business in London" (PDF). Thinklondon.com. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
^ "Clementswood - UK Census Data 2011". Ukcensusdata.com. 2012. Retrieved 2017-04-09.
^ ab Transport for London (March 2009). "High frequency services" (PDF). Greater London Authority. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ National Express East Anglia (May 2009). "Table 6" (PDF). National Express. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ "Crossrail maps: Route map". Crossrail. Archived from the original on 23 August 2009. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ Transport for London. "East London Transit". Greater London Authority. Archived from the original on 8 March 2010. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ Transport for London (September 2007). "Buses from Ilford" (PDF). Greater London Authority. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
^ "About us | Kenneth More Theatre". Kmtheatre.co.uk. 3 January 1975. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
^ "St. Alban's Singers - Choir in Ilford". stalbansingers.simdif.com.
^ Buckley, p. 14.
^ "Valentine's Park | England | Cricket Grounds". ESPN Cricinfo. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
^ Steen, Rob (8 September 2001). "Cricket Focus : Essex heartbreak at Valentines Park". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
Bibliography
Buckley, G. B. (1935). Fresh Light on 18th Century Cricket. Cotterell.
- Ian Dowling Valentines Park, Ilford: A Century of History (1999)
OCLC 43337735
- J E Oxley Barking and Ilford: An Extract from the Victoria History of the County of Essex vol 5 (1987)
James Thorne (1876), "Great Ilford", Handbook to the Environs of London, London: John Murray
Edward Walford (1883), "Ilford", Greater London, London: Cassell & Co., OCLC 3009761
External links
 Media related to Ilford at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ilford at Wikimedia Commons
