Small Isles
| Small Isles National Scenic Area | |
|---|---|
 A distant view of Eigg, with the hills of Rùm behind. | |
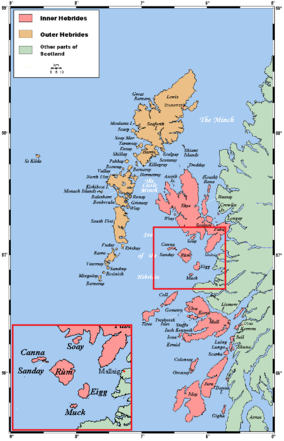 The location of the Small Isles within the Hebrides | |
| Location | Lochaber, Highland, Scotland |
| Coordinates | Coordinates: 56°58′N 6°16′W / 56.967°N 6.267°W / 56.967; -6.267 |
| Area | 472 km2 (182 sq mi)[1] |
| Established | 1981 |
| Governing body | Scottish Natural Heritage |

Blaeu's 1654 Atlas of Scotland - The Small Isles. Rùm is at centre, surrounded by "Kannay', 'Egg' and 'Muck'.

Ordnance Survey Map of 1896
The Small Isles (Scottish Gaelic: Na h-Eileanan Tarsainn)[2] are a small archipelago of islands in the Inner Hebrides, off the west coast of Scotland. They lie south of Skye and north of Mull and Ardnamurchan – the most westerly point of mainland Scotland. The islands are not particularly small (indeed Rùm is the 15th largest of Scotland's islands), but are named due to being within the civil parish of Small (or Sma) Isles.[3] The Gaelic name of Na h-Eileanan Tarsainn translates as "cross isles" referring to the islands position between Morar and the Uists.[2]
The islands form part of the Lochaber area of the Highland council area. Until 1891 Canna, Rùm and Muck were historically part of the shire of Argyll;[citation needed]Eigg was historically part of Inverness-shire. All of the Small Isles were in Inverness-shire between 1891 and 1975, and remain part of the registration county of Inverness for land registration and statistical purposes. A single community council covers the islands.[4]
The islands and surrounding sea area together form the Small Isles National Scenic Area, one of the forty such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development.[5] The designated area covers 47,235 ha in total, of which 16,271 ha is on land, with a further 30,964 ha being marine (i.e. below low tide level).[1]
Contents
1 Geography
2 Demographics
3 Transport
4 Nature and conservation
5 Footnotes
6 External links
Geography
The four main islands are Canna, Rùm, Eigg and Muck. The largest is Rùm with an area of 104.6 square kilometres (40.4 sq mi).[6]
Smaller islands surrounding the main four include:
Sanday, separated from Canna by a narrow tidal channel;[7]
Eilean Chathastail, near Eigg and- Eilean nan Each (Horse Island), near the north coast of Muck (NM3981)
There are also a number of skerries:
Hyskeir or Òigh-sgeir, (not to be confused with Heisker or the Monach Islands in the Outer Hebrides)
Garbh Sgeir,- Eagamol, near Eilean nan Each
- Humla, and
- two places called Dubh Sgeir
Demographics
According to the 2011 census, the total population of the Small Isles was 153. Five of the islands are inhabited: Eigg (83), Muck (27), Rùm (22), Canna (12) and Sanday (9).[8]
The inhabited islands are in contrasting forms of ownership: Canna (along with the tidally linked Sanday) is owned by a national conservation charity, the National Trust for Scotland;[9][10] Eigg has been owned by a local community trust since 1997;[11] Muck remains in private ownership;[12] and Rùm is largely in the hands of the state (via Scottish Natural Heritage), although some land in and around the only village (Kinloch) is owned by a community trust.[13][14]
Transport
A Caledonian MacBrayne ferry, MV Lochnevis, links the Small Isles to each other and to the mainland port of Mallaig. The ferry runs a daily service, calling at different islands depending on the day of the week; there are two calls at certain islands on each day to allow for day visits to and from each island.[15] The Lochnevis has a landing craft-style stern ramp allowing vehicles to be driven onto and off the vessel at a new slipway constructed in 2001,[16] however visitors are not normally permitted to bring vehicles to the Small Isles.[17] During the summer months the islands are also served by Arisaig Marine's passenger ferry MV Sheerwater from Arisaig, 10 miles (16 km) south of Mallaig. Timetables are also arranged to allow time onshore on different islands depending on the day of the week.[18]
Nature and conservation
The Small Isles are all important for their wildlife,[19] with Rùm being designated as both a national nature reserve and a Special Area of Conservation (SAC).[20][21] Rùm is home to one of the world’s largest colony of Manx shearwater,[20] and was the location for the first stage of the reintroduction of white-tailed sea-eagles into Scotland, with 82 birds being released between 1975 and 1985.[22] Rùm, and Canna and Sanday (jointly), are designated as Special Protection Areas (SPA) due their birdlife, with all three islands hosting important breeding populations of guillemots and kittiwakes.[23][24] The Canna and Sanday SPA is also designated due to its importance to breeding Atlantic puffins and shags,[23] whilst the Rùm SPA designation notes the presence of golden eagles, Manx shearwaters, and red-throated divers.[24]
Around 800 km2 of the waters around Rùm, Canna and the low-lying rocky islet of Oigh-sgeir have been designated as the Small Isles Nature Conservation Marine Protected Area (NCMPA). Of particular note is that this area holds the UK's only known colony of fan mussels.[25] The seas surrounding all of the Small Isles have also been identified as a candidate area for designation as a Special Area of Conservation, due to their importance for harbour porpoises.[26]
Footnotes
^ ab "National Scenic Areas - Maps". SNH. 2010-12-20. Retrieved 2018-06-05..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab Iain Mac an Tàilleir. "Placenames" (PDF). Pàrlamaid na h-Alba. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-05-29. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
^ Haswell-Smith, Hamish (2004). The Scottish Islands. Edinburgh: Canongate.
ISBN 1-84195-454-3. p. 130
^ "Small Isles Community Council - Boundary Map". The Highland Council. April 2011. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ "National Scenic Areas". Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved 2018-01-17.
^ Haswell-Smith, Hamish (2004). The Scottish Islands. Edinburgh: Canongate.
ISBN 1-84195-454-3. p. 138
^ "History of Canna". Retrieved 2007-06-11.
^ "2011 Census: First Results on Population and Household Estimates for Scotland - Release 1C, Part Two, Appendix 2" (PDF). National Records of Scotland. 2013-07-23. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ "Canna". National Trust for Scotland. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ "Property Page - Canna". Who Owns Scotland. 2010-09-21. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ "About the Isle of Eigg Heritage Trust". Isle of Eigg Heritage Trust. Retrieved 2018-06-04.
^ "Property Page - Muck". Who Owns Scotland. 2002-12-31. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ "Rum NNR". Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ "Welcome to the Isle of Rum". Isle of Rum Community Trust. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ "Small Isles Ferry Timetable Summer 2018". Caledonian MacBrayne. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ Caledonian MacBrayne: Ferries of the Clyde, Highlands and Islands. Ships Illustrated. Special Issue No. 11.
ISBN 978-1-910554-17-3. p. 74.
^ "Small Isles Vehicle Permit Scheme". Highland Council. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ "MV Sheerwater Timetable 2018" (PDF). Arisaig Marine. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
^ "The special qualities of the National Scenic Areas" (PDF). Scottish Natural Heritage. 2010. p. 225. Retrieved 2018-05-15.
^ ab "Rum National Nature Reserve". Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved 2018-06-07.
^ "Site Details for Rum SAC". Scottish Natural Heritage. 2018-06-06. Retrieved 2018-06-26.
^ "Return of a Native: reintroduction". Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved 2018-06-07.
^ ab "Site Details for Canna and Sanday SPA". Scottish Natural Heritage. 2018-05-02. Retrieved 2018-05-07.
^ ab "Site Details for Rum SPA". Scottish Natural Heritage. 2018-05-02. Retrieved 2018-05-07.
^ "Small Isles NCMPA". Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved 2018-05-07.
^ "Site Details for Inner Hebrides and the Minches Candidate SAC". Scottish Natural Heritage. 2018-05-02. Retrieved 2018-06-07.
External links
- Visit Small Isles
- Gazetteer for Scotland: Parish of Small Isles
- Gazetteer for Scotland: Parish of Small Isles (History)
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Small Isles. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Small Isles. |
![]() Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Small Isles". Encyclopædia Britannica. 25 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 246–247.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Small Isles". Encyclopædia Britannica. 25 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 246–247.

