Cloxacillin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cloxapen, others |
AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | by mouth, IM |
| ATC code |
|
Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 37 to 90% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Elimination half-life | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Excretion | kidney and biliary |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.468 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
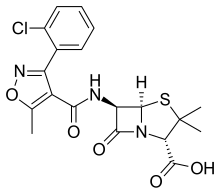
| Formula | C19H18ClN3O5S |
| Molar mass | 435.88 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
.mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} (verify) | |
Cloxacillin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.[1] This includes impetigo, cellulitis, pneumonia, septic arthritis, and otitis externa.[1] It is not effective for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).[2] It is used by mouth and by injection.[1]
Side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis.[1]Clostridium difficile diarrhea may also occur.[2] It is not recommended in people who have previously had a penicillin allergy.[1] Use during pregnancy appears to be relatively safe.[1] Cloxacillin is in the penicillin family of medications.[2]
Cloxacillin was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1965.[3] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[4] The wholesale cost in the developing world is about US$0.16 per day for the pills.[5] It is not commercially available in the United States.[2]
Contents
1 Mechanism of action
2 Society and culture
3 See also
4 References
Mechanism of action
It is semisynthetic and in the same class as penicillin. Cloxacillin is used against staphylococci that produce beta-lactamase, due to its large R chain, which does not allow the beta-lactamases to bind. This drug has a weaker antibacterial activity than benzylpenicillin, and is devoid of serious toxicity except for allergic reactions.
Society and culture
Cloxacillin was discovered and developed by Beecham.[6]
It is sold under a number of trade names, including Cloxapen, Cloxacap, Tegopen and Orbenin.
See also
- Dicloxacillin
- Flucloxacillin
- Nafcillin
- Oxacillin
References
^ abcdef WHO Model Formulary 2008 (PDF). World Health Organization. 2009. pp. 110, 586. ISBN 9789241547659. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcd "Cloxacillin (Professional Patient Advice)". www.drugs.com. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 10 December 2016.
^ Fischer, Janos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 490. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2016-12-20.
^ "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
^ "Cloxacillin Sodium". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
^ David Greenwood (2008). Antimicrobial drugs: chronicle of a twentieth century medical triumph. Oxford University Press US. pp. 124–. ISBN 978-0-19-953484-5. Archived from the original on 6 June 2013. Retrieved 18 November 2010.
This systemic antibiotic-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |