Left- and right-hand traffic

Countries by handedness of traffic, c. 2018
Left-hand traffic
Right-hand traffic

Change of traffic directions at the Thai–Lao Friendship Bridge

Right-hand traffic on the A2 in Germany

Left-hand traffic on the M25 motorway in the UK
Left-hand traffic (LHT) and right-hand traffic (RHT) are the practice, in bidirectional traffic, of keeping to the left side or to the right side of the road, respectively. A fundamental element to traffic flow, it is sometimes referred to as the rule of the road.[1]
RHT is used in 163 countries and territories, with the remaining 78 countries and territories using LHT. Countries that use LHT account for about a sixth of the world's area with about 35% of humanity and a quarter of its roads.[2] In 1919, 104 of the world's territories were LHT and an equal number were RHT. From 1919 to 1986, 34 of the LHT territories switched to RHT.[3]
Many of the countries with LHT were formerly part of the British Empire. In addition, Japan, Indonesia, Thailand, Suriname and other countries have retained the LHT tradition. Conversely, many of the countries with RHT were formerly part of the French colonial empire or, in Europe, were subject to French rule during the Napoleonic conquests.
For rail traffic, LHT predominates in Western Europe (except Germany, Austria, Spain and the Netherlands), Latin America, and in countries formerly in the British and French Empires, whereas North American and central and eastern European train services operate RHT.
According to the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea, water traffic is effectively RHT: a vessel proceeding along a narrow channel must keep to starboard (the right-hand side), and when two power-driven vessels are meeting head-on both must alter course to starboard also. For aircraft the US Federal Aviation Regulations suggest RHT principles, both in the air and on water.[4]
In healthy populations, traffic safety is thought to be the same regardless of handedness, although some researchers have speculated that LHT may be safer for ageing populations[5] since humans are more commonly right-eye dominant than left-eye dominant.[6]
Contents
1 History
2 Changing sides
2.1 Europe
2.2 Asia and the Pacific
2.3 Africa
3 Safety
4 Changing sides at borders
5 Road vehicle configurations
5.1 Driver seating position
5.2 Headlamps and other lighting equipment
5.2.1 Rear fog lamps
5.3 Crash testing differences
6 Worldwide distribution by country
7 Traffic rules
8 Rail traffic
9 Gallery
10 See also
11 References
12 External links
History
Ancient Greek, Egyptian, and Roman troops kept to the left when marching.[7] In 1998, archaeologists found a well-preserved double track leading to a Roman quarry near Swindon, in southern England. The grooves in the road on the left side (viewed facing down the track away from the quarry) were much deeper than those on the right side, suggesting LHT, at least at this location, since carts would exit the quarry heavily loaded, and enter it empty.[8]
The first reference in English law to an order for LHT was in 1756, with regard to London Bridge.[9]
Some historians, such as C. Northcote Parkinson, believed that ancient travellers on horseback or on foot generally kept to the left, since most people were right-handed. If two men riding on horseback were to start a fight, each would edge toward the left.[7] In the year 1300, Pope Boniface VIII directed pilgrims to keep left.[7]
In the late 1700s, traffic in the United States was RHT based on teamsters' use of large freight wagons pulled by several pairs of horses. The wagons had no driver's seat, so the (typically right-handed) postilion held his whip in his right hand and thus sat on the left rear horse. Seated on the left, the driver preferred that other wagons pass him on the left so that he could be sure to keep clear of the wheels of oncoming wagons.[10]
In France, traditionally foot traffic had kept right, while carriage traffic kept left. Following the French Revolution, all traffic kept right.[9] Following the Napoleonic Wars, the French imposed RHT on parts of Europe.[citation needed] During the colonial period, RHT was introduced by the French in New France, French West Africa, the Maghreb, French Indochina, the West Indies, French Guiana and the Réunion, among others.
Meanwhile, LHT was introduced by the British in parts of Canada (Atlantic Canada and British Columbia), Australia, New Zealand, the East Africa Protectorate (now Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda), British India, Rhodesia and the Cape Colony (now Zambia, Zimbabwe and South Africa), British Malaya (now Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore), British Guiana, and British Hong Kong. LHT was also introduced by the Portuguese Empire in Portuguese Macau, Colonial Brazil, Portuguese Timor, Portuguese Mozambique, and Portuguese Angola.
The first keep-right law for driving in the United States was passed in 1792 and applied to the Philadelphia and Lancaster Turnpike.[11]New York formalized RHT in 1804, New Jersey in 1813 and Massachusetts in 1821.[12]
In the early 1900s some countries including Canada, Spain, and Brazil had different rules in different parts of the country. During the 1900s many countries standardised within their jurisdictions, and changed from LHT to RHT, mostly to conform with regional custom. Currently nearly all countries use one side or the other throughout their entire territory. Most exceptions are due to historical considerations and/or involve islands with no road connection to the main part of a country. China is RHT except the Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and Macau. The United States is RHT except the United States Virgin Islands.[13] The United Kingdom is LHT, but its overseas territories of Gibraltar and British Indian Ocean Territory are RHT.
Changing sides

Traffic moves from left to right in Stockholm, Sweden, on 3 September 1967
Europe
Influential in Europe was the 1920 Paris Convention, which advised driving on the right-hand side of the road, in order to harmonise traffic across a continent with many borders. This was despite the fact that left-hand traffic was still widespread: in 1915 for example, LHT was introduced everywhere in the Austro-Hungarian Empire; however, three years later the Empire was split up into several countries, and they all changed eventually to RHT, notably including when Nazi Germany introduced RHT with almost immediate effect in Czechoslovakia in 1938–39.[14][15]
Sweden was LHT from about 1734 to 1967,[16] despite having land borders with RHT countries, and approximately 90 percent of cars being left-hand drive (LHD) vehicles.[17] A referendum was held in 1955, with an overwhelming majority voting against a change to RHT. Nevertheless, some years later the government ordered a conversion, which took place at 5 am on Sunday, 3 September 1967. The accident rate dropped sharply after the change,[18] but soon rose back to near its original level.[19] The day was known as Dagen H ("H-Day"), the 'H' being for Högertrafik ("right traffic"). When Iceland switched the following year, it was known as H-dagurinn, again meaning "H-Day".[20]
In the late 1960s, the UK Department for Transport considered switching to RHT, but declared it unsafe and too costly for such a built-up nation.[21] Road building standards, for motorways in particular, allow asymmetrically designed road junctions, where merge and diverge lanes differ in length.[22]
Today, four countries in Europe continue to use left-hand traffic, all island nations: the UK, Cyprus, Ireland, and Malta.
Asia and the Pacific
Nationalist China adopted RHT in 1946. This convention was preserved when the CCP took the mainland and the KMT retreated to Taiwan. Hong Kong and Macau continue to be LHT.
Both North Korea and South Korea switched to RHT in 1945 after liberation from Japanese colonial power.
Myanmar switched to RHT in 1970.[23]
Samoa, a former German colony, had been RHT for more than a century. It switched to LHT in 2009,[24] being the first territory in almost 30 years to switch.[25] The move was legislated in 2008 to allow Samoans to use cheaper right-hand drive (RHD) vehicles—which are better suited for left-hand traffic—imported from Australia, New Zealand or Japan, and to harmonise with other South Pacific nations. A political party, The People's Party, was formed to try to protest against the change, a protest group which launched a legal challenge,[26] and an estimated 18,000 people attending demonstrations against it.[27] The motor industry was also opposed, as 14,000 of Samoa's 18,000 vehicles are designed for RHT and the government has refused to meet the cost of conversion.[25] After months of preparation, the switch from right to left happened in an atmosphere of national celebration. There were no reported incidents.[2] At 05:50 local time, Monday 7 September, a radio announcement halted traffic, and an announcement at 6:00 ordered traffic to switch to LHT.[24] The change coincided with more restrictive enforcement of speeding and seat-belt laws.[28] That day and the following day were declared public holidays, to reduce traffic.[29] The change included a three-day ban on alcohol sales, while police mounted dozens of checkpoints, warning drivers to drive slowly.[2]
The Philippines was mostly LHT during its Spanish[30] and American colonial periods,[31][32] as well as during the Commonwealth era.[33] During the Japanese occupation the Philippines remained LHT,[34] also because LHT had been required by the Japanese;[35] but during the Battle of Manila the liberating American forces drove their tanks to the right for easier facilitation of movement. RHT was formally finalised by Executive Order No. 34 signed by President Sergio Osmeña on 10 March 1945.[36]
Africa
A number of non-contiguous former British colonies in West Africa originally drove LHT and switched to RHT in the early 1970s to match the surrounding countries. Sierra Leone switched to RHT in 1971, Nigeria in 1972 and Ghana in 1974. Before this period The Gambia, a country entirely contained within RHT Senegal, had officially switched to RHT in 1965.[37]
Rwanda, a former Belgian colony in central Africa, is RHT but is considering switching to LHT, to bring the country in line with other members of the East African Community (EAC).[38] A survey, carried out in 2009, indicated that 54% of Rwandans were in favour of the switch. Reasons cited were the perceived lower costs of RHD vehicles as opposed to LHD versions of the same model, easier maintenance and the political benefit of harmonisation of traffic regulations with other EAC countries. The same survey also indicated that RHD cars are 16 to 49 per cent cheaper than their LHD equivalents.[39] In 2014 an internal report from consultants to the Ministry of Infrastructure recommended a switch to LHT.[40] In 2015, the ban on RHD vehicles was lifted; RHD trucks from neighbouring countries cost $1000 less than LHD models imported from Europe.[41][42]
Safety
In one study, researchers concluded that left-hand traffic may be safer for elderly drivers,[43] since humans are more commonly right-eye dominant than left-eye dominant.[44] Comparing accident statistics between countries operating either LHT or RHT, Leeming concluded that LHT is superior.[45] However, Watson has criticised the small sample size and dismisses the notion.[3]
Changing sides at borders

A road sign in the British county of Kent placed on the right-hand side of the road.

Border between Sweden and Norway in 1934
Although many LHT jurisdictions are on islands, there are cases where vehicles may be driven from LHT across a border into a RHT area. Such borders are mostly located in Africa and southern Asia. The Vienna Convention on Road Traffic regulates the use of foreign registered vehicles in the 74 countries that have ratified it.
LHT Thailand has three RHT neighbors: Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar. Most of its borders use a simple traffic light to do the switch, but there are also interchanges which enable the switch while keeping up a continuous flow of traffic.[46]
There are four road border crossing points between Hong Kong and Mainland China. In 2006, the daily average number of vehicle trips recorded at Lok Ma Chau was 31,100.[47] The next largest is Man Kam To, where there is no changeover system and the border roads on the mainland side Wenjindu intersect as one-way streets with a main road.
The Takutu River Bridge (which links LHT Guyana and RHT Brazil[48]) is the only border in the Americas where traffic changes sides.
Although the United Kingdom is separated from Continental Europe by the English Channel, the level of cross-Channel traffic is very high; the Channel Tunnel alone carries 3.5 million vehicles per year, by rail, between the UK and France.
Road vehicle configurations
Driver seating position

Bolivia is RHT, with the exception of Yungas Road which is LHT to help drivers see their outer wheel.
In RHT jurisdictions, vehicles are configured with LHD, with the driver sitting on the left side. In LHT jurisdictions, the reverse is true. The driver's side, the side closest to the centre of the road, is sometimes called the offside, while the passenger side, the side closest to the side of the road, is sometimes called the nearside.[49]
Historically there was less consistency in the relationship of the position of the driver to the handedness of traffic. Most American cars produced before 1910 were RHD.[11] In 1908 Henry Ford standardised the Model T as LHD in RHT America,[11] arguing that with RHD and RHT, the passenger was obliged to "get out on the street side and walk around the car" and that with steering from the left, the driver "is able to see even the wheels of the other car and easily avoids danger."[50] By 1915 other manufacturers followed Ford's lead, due to the popularity of the Model T.[11]
In specialised cases, the driver will sit on the nearside, or kerbside. Examples include:
- Where the driver needs a good view of the nearside, e.g. street sweepers, or vehicles driven along unstable road edges.[51]
- Where it is more convenient for the driver to be on the nearside, e.g. delivery vehicles. The Grumman LLV postal delivery truck is widely used with RHD configurations in RHT North America. Some Unimogs are designed to switch between LHD and RHD to permit operators to work on the more convenient side of the truck.
Generally, the convention is to mount a motorcycle on the left,[52] and kickstands are usually on the left[53] which makes it more convenient to mount on the safer kerbside[53] as is the case in LHT. Some jurisdictions prohibit fitting a sidecar to a motorcycle's offside.[54][55]
Headlamps and other lighting equipment

Bird's-eye view of low beam light pattern for RH traffic, with long seeing range on the right and short cutoff on the left so oncoming drivers are not dazzled.
Most low-beam headlamps produce an asymmetrical light suitable for use on only one side of the road. Low beam headlamps in LHT jurisdictions throw most of their light forward-leftward; those for RHT throw most of their light forward-rightward, thus illuminating obstacles and road signs while minimising glare for oncoming traffic.
In Europe, headlamps approved for use on one side of the road must be adaptable to produce adequate illumination with controlled glare for temporarily driving on the other side of the road,[56]:p.13 ¶5.8. This may be achieved by affixing masking strips or prismatic lenses to a part of the lens or by moving all or part of the headlamp optic so all or part of the beam is shifted or the asymmetrical portion is occluded.[56]:p.13 ¶5.8.1 Some varieties of the projector-type headlamp can be fully adjusted to produce a proper LHT or RHT beam by shifting a lever or other movable element in or on the lamp assembly.[56]:p.12 ¶5.4 Some vehicles adjust the headlamps automatically when the car's GPS detects that the vehicle has moved from LHT to RHT and vice versa.[citation needed]
Because blackout strips and adhesive prismatic lenses reduce the safety performance of the headlamps, most countries require all vehicles registered or used on a permanent or semi-permanent basis within the country to be equipped with headlamps designed for the correct traffic-handedness.[citation needed]
Without sidecars attached, motorcycles, motor scooters, mopeds, and bicycles are almost symmetric with their handlebars in the centre. However, motorcycles are often equipped with automotive-type asymmetrical-beam headlamps that likewise require adjustments or replacement when brought into a country with opposite traffic-handedness.[citation needed]
Rear fog lamps
In the European Union, vehicles must be equipped with one or two red rear fog lamps. A single rear fog lamp must be located between the vehicle's longitudinal centreline and the outer extent of the driver's side of the vehicle.[57] Rear fog lamps are also being found on vehicles produced for Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Crash testing differences
An Australian news source reports that some RHD cars imported to that country did not perform as well on crash tests as the LHD versions, although the cause is unknown, and may be due to differences in testing methodology.[58]
Worldwide distribution by country
Of the 194 countries currently recognised by the United Nations (and the unrecognised Palestine and Kosovo), 140 use RHT and 54 use LHT. A country and its territories and dependencies is counted once.
| Country | Road traffic | Road switched sides | Multi-track rail traffic generally | Notes, exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Afghanistan | RHT | RHT/LHT | Was LHT until the 1950s, in line with neighbouring British India and later Pakistan.[59] | |
Albania | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Algeria | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Andorra | RHT[60] | |||
Angola | RHT[60] | 1928 | Originally LHT, like its colonial power Portugal. Switched to RHT with Portugal in 1928. | |
Antigua and Barbuda | LHT[60] | Former British colony. | ||
Argentina | RHT | 10 June 1945 | LHT | The anniversary on 10 June is still observed each year as Día de la Seguridad Vial (road safety day).[61] The Premetro and Metrotranvía Mendoza use RHT. |
Armenia | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Australia | LHT | LHT | ||
Austria | RHT | 1921–38 | RHT[62] | Originally LHT, like most of former Austria-Hungary. Switched sides in 1921 in Vorarlberg, 1930 in North Tyrol, 1935 in Carinthia and East Tyrol, and in 1938 in the rest of the country. The Semmering Railway uses LHT. |
Azerbaijan | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Bahamas | LHT[60] | In Bahamas LHD vehicles are common due to the import of used cars from the United States.[63][64] | ||
Bahrain | RHT | 1967 | Former British protectorate. Switched to same side as neighbours.[65] | |
Bangladesh | LHT[60] | LHT | ||
Barbados | LHT | |||
Belgium | RHT[60] | 1899 | LHT | The Brussels Metro is nominally RHT, with LHT on the circle line west of Halle Gate. This was done to enable unidirectional vehicles to use island platforms. |
Belarus | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Belize | RHT | 1961[1] | Former British colony. Switched to same side as neighbours. | |
Benin | RHT[60] | |||
Bhutan | LHT[60] | Under British protection before 1949. | ||
Bolivia | RHT[60] | |||
Bosnia and Herzegovina | RHT[60] | 1918 | RHT[66] | Switched sides after the collapse of Austria-Hungary. |
Botswana | LHT[60] | |||
Brazil | RHT | 1928[60] | RHT | A Portuguese colony until the early 19th century as LHT and retained it at least partially following independence, switched some states still on LHT to RHT in 1928, the same year as Portugal.[67][68] While some areas in present-day Brazil formerly belonged to Bolivia were already in RHT. |
Brunei | LHT[60] | |||
Bulgaria | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Burkina Faso | RHT[60] | |||
Burundi | RHT | Former Belgian colony. Considering switching to LHT[69] in line with neighbours Tanzania, Kenya and Uganda. | ||
Cambodia | RHT | LHT | RHT implemented while part of French Indochina. RHD cars, many of which were smuggled from Thailand, were banned from 2001, even though they accounted for 80% of vehicles in the country.[70] | |
Cameroon | RHT[60] | 1961 | ||
Canada | RHT | 1920–24 | RHT | Territories now in Canada have always been RHT, except British Columbia, which changed to RHT in stages from 1920 to 1923,[71][72] and New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island which changed in 1922, 1923, and 1924 respectively.[73]Newfoundland and Labrador changed to RHT in 1947 while still a dominion of the British Empire, two years before joining Canada.[74] |
Cape Verde | RHT[60] | 1928 | Originally LHT, like its colonial power Portugal. Switched to RHT with Portugal in 1928. | |
Central African Republic | RHT[60] | |||
Chad | RHT[60] | |||
Chile | RHT[60] | 1918 | LHT | The Santiago Metro uses RHT. |
China | RHT (Mainland China) LHT (Hong Kong and Macau)[60] | 1946 | RHT/LHT | At one time, northern provinces were RHT due to American influence, while southern provinces were LHT due to British influence. LHT was uniform in the 1930s. Hong Kong and Macau are all on LHT due to their colonial heritage. Most metro systems use RHT include Ma On Shan line, except for the Hong Kong MTR and the Macau LRT. |
Colombia | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Comoros | RHT[60] | |||
Congo | RHT[60] | |||
Democratic Republic of Congo | RHT[60] | |||
Costa Rica | RHT[60] | |||
Côte d'Ivoire | RHT[60] | |||
Croatia | RHT[60] | RHT | Istria and Dalmatia were RHT, while Croatia-Slavonia was LHT when Croatia was part of Austria-Hungary[75]. The LHT regions switched to RHT on joining the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. | |
Cuba | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Cyprus | LHT[60] | Former British colony. | ||
Czech Republic | RHT[60] | 1939 | RHT | Was LHT, like most of former Austria-Hungary, switched during the German occupation of Czechoslovakia. |
Denmark | RHT | RHT[76] | Includes Faroe Islands and Greenland | |
Djibouti | RHT[60] | |||
Dominica | LHT[60] | Former British colony. | ||
Dominican Republic | RHT[60] | |||
East Timor | LHT | 1976 | Originally LHT, like its colonial power Portugal. Switched to RHT with Portugal in 1928.[1] Under the Indonesian occupation of East Timor, changed back to LHT in 1976. | |
Ecuador | RHT[60] | LHT | The Quito Metro and Cuenca tram system will use RHT. | |
Egypt | RHT[60] | LHT | Road vehicles are RHT due to French influence, but railway system was built by British companies. | |
El Salvador | RHT[60] | |||
Equatorial Guinea | RHT[60] | |||
Eritrea | RHT[60] | 1964 | ||
Estonia | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Ethiopia | RHT[60] | 1964 | LHT | The Addis Ababa Light Rail uses RHT. |
Fiji | LHT | LHT | ||
Finland | RHT | 1858 | RHT/LHT | Formerly ruled as part of LHT Sweden, switched to RHT as the Grand Duchy of Finland by Russian decree.[77] Most of the Helsinki commuter rail lines use LHT, but the Helsinki Metro uses RHT. |
France | RHT | 1792 | LHT[78]/RHT | Includes French Polynesia, New Caledonia, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Wallis and Futuna, French Guiana, Réunion, Saint Barthélemy, Collectivity of Saint Martin, Guadeloupe, Mayotte. Railroads in Alsace and Moselle use RHT as a former part of German Empire. CDGVAL uses RHT. Most metro systems use RHT, except for the Lyon Metro. |
Gabon | RHT[60] | |||
Gambia | RHT | 1965[37] | ||
Georgia | RHT[60] | RHT | About 40% vehicles in Georgia are RHD due to the low cost of used cars imported from Japan[79]. The Batumi Ropeway uses LHT. | |
Germany | RHT[80] | RHT | ||
Ghana | RHT | 1974[81] | Former British colony. Ghana changed to driving on the right on 4 August 1974, the last former British colony in the region to do so, the military National Redemption Council having passed the Right Hand Traffic Act by decree in 1973.[82] When changing to RHT, a Twi language slogan was "Nifa, Nifa Enan" or "Right, Right, Fourth".[83]Ghana has also banned RHD vehicles. Ghana prohibited new registrations of RHD vehicles after 1 August 1974, three days before the traffic change on 4 August 1974. RHD vehicles may be imported only temporarily into Sierra Leone, for example for humanitarian programmes, but must be exported at the end of the operation. | |
Greece | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Grenada | LHT[60] | |||
Guatemala | RHT[60] | |||
Guinea | RHT[60] | |||
Guinea-Bissau | RHT[60] | 1928 | Originally LHT, like its colonial power Portugal. Switched to RHT with Portugal in 1928. | |
Guyana | LHT[60] | |||
Haiti | RHT[60] | |||
Honduras | RHT[60] | |||
Hungary | RHT[60] | 1941 | RHT | Originally LHT, like most of Austria-Hungary. Most of the Suburban trains in Budapest use LHT, but the Budapest Metro uses RHT. |
Iceland | RHT | 1968 | LHT | The day of the switch was known as H-dagurinn. Most passenger cars were already LHD. |
Iran | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Iraq | RHT[60] | LHT | ||
India | LHT[60] | LHT | Former British colony. | |
Indonesia | LHT[84] | RHT[85] | Roads were built by the British, but railways are RHT due to Dutch influence. The Jakarta MRT will also use RHT. | |
Ireland | LHT[60] | LHT | Part of the United Kingdom until 1922. | |
Israel | RHT[60] | LHT | Under British rule till 1948; The Jerusalem Light Rail uses RHT. | |
Italy | RHT | 1924–26 | LHT | Until 1927 the countryside was RHT while cities were LHT.[86] Rome changed to RHT in 1924 and Milan in 1926. Alfa Romeo and Lancia did produce LHD cars until as late as 1950 and 1953 respectively only to special order, as many drivers favoured the RHD layout even in RHT as this offered the driver a clearer view of the edge of the road in mountainous regions at a time when many such roads lacked barriers or walls.[87] The metro systems in Brescia, Genoa, Milan, and Turin use RHT, as well as all tram systems. |
Jamaica | LHT[60] | |||
Japan | LHT[88] | LHT | Post-World War II Okinawa was ruled by the United States Civil Administration of the Ryukyu Islands and was RHT. It was returned to Japan in 1972 but did not convert back to LHT until 1978.[89] The conversion operation was known as 730 (Nana-San-Maru, which refers to the date of the changeover, 30 July). Okinawa is one of few places to have changed from RHT to LHT in the late 20th century. The Hakone Ropeway uses RHT. | |
Jordan | RHT[60] | RHT, despite the Mandate for Palestine and the Transjordan memorandum being under British rule till 1946. | ||
Kazakhstan | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Kenya | LHT[90] | British colony until 1963. | ||
Kiribati | LHT[60] | |||
North Korea | RHT | 1946 | LHT/RHT | Korea had been LHT because of the influence of Japan in the 1900s. Switched to RHT under Soviet and American occupation after 1945. The metro system in Pyongyang uses a mixture of RHT and LHT. |
South Korea | RHT | 1946 | LHT/RHT | Korea had been LHT because of the influence of Japan in the 1900s. Switched to RHT under Soviet and American occupation after 1945. Most metro systems in South Korea use RHT (exceptions include lines 1 and 4 of the Seoul Metropolitan Subway, the Bundang Line, and the Shinbundang Line). |
Kosovo | RHT | RHT | ||
Kuwait | RHT[60] | |||
Kyrgyzstan | RHT | RHT | Former part of RHT Soviet Union. In 2012, over 20,000 cheaper used RHD cars were imported from Japan.[91] | |
Laos | RHT[60] | LHT | RHT implemented while part of French Indochina. | |
Latvia | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Lebanon | RHT[60] | Former French mandate. | ||
Lesotho | LHT[60] | |||
Liberia | RHT[60] | |||
Libya | RHT[60] | |||
Liechtenstein | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Lithuania | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Luxembourg | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Macedonia | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Madagascar | RHT[60] | |||
Malawi | LHT[60] | Former British colony. | ||
Malaysia | LHT[60] | LHT | Former British colony. | |
Maldives | LHT[60] | Former British colony. | ||
Mali | RHT[60] | |||
Malta | LHT[60] | British colony until 1964. | ||
Marshall Islands | RHT[60] | Was being under American rule. | ||
Mauritania | RHT | Mining roads between Fderîck and Zouérat are LHT.[92] | ||
Mauritius | LHT[60] | Former British colony. Island nation. | ||
Mexico | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Micronesia | RHT[60] | Was being under American rule. Nearly 80% vehicles are RHD due to the import of used cars from Japan. | ||
Moldova | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Monaco | RHT[60] | LHT | ||
Mongolia | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Montenegro | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Morocco | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Mozambique | LHT[93] | LHT | ||
Myanmar | RHT | 1970 | LHT | Much of infrastructure still geared to LHT, most cars are used RHD vehicles, imported from Japan.[94] |
Netherlands | RHT | 1906[95] | RHT | Rotterdam was LHT until 1917.[96] Includes Curaçao, Sint Maarten, and Aruba |
Namibia | LHT | 1918 | RHT as a German colony. After South Africa occupied German South-West Africa during World War I, switched to LHT.[1]South-West Africa was made a South African mandate by the League of Nations, and the new rule of the road was established in law.[97] | |
Nauru | LHT[60] | 1918 | ||
Nepal | LHT[98] | Former British protectorate. | ||
New Zealand | LHT[84] | LHT | Includes territories Niue and Cook Islands | |
Nicaragua | RHT[60] | |||
Niger | RHT[60] | |||
Nigeria | RHT | 1972[99] | LHT | Former British colony. Switched to RHT as it is surrounded by former French RHT colonies. Federal Road Safety Commission (FRSC) warned operators of RHD vehicles that they would face prosecution[100] under Section 71 of the National Road Traffic Regulation (2004), which states that no RHD vehicle shall be registered or driven on public roads.[101] |
Norway | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Oman | RHT | Not a party to the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic and bans all foreign-registered RHD vehicles.[102] | ||
Pakistan | LHT[60] | LHT | Was part of undivided India | |
Palau | RHT[60] | Most cars are used RHD vehicles, imported from Japan because it's a second Japanese-speaking country. | ||
Palestine | RHT[60] | |||
Panama | RHT | 1943[103] | RHT | |
Papua New Guinea | LHT[60] | After Australia occupied German New Guinea during World War I, switched to LHT. | ||
Paraguay | RHT | 1945[104] | ||
Peru | RHT[60] | LHT | ||
Philippines | RHT | 1946[36] | RHT | Was LHT during the Spanish and American colonial periods. Switched to RHT during Battle of Manila in 1945. |
Poland | RHT | RHT | Partitions of Poland belonging to the German Empire and the Russian Empire were RHT. Partitions that were part of Austria-Hungary were LHT and changed to RHT in the 1920s.[105] | |
Portugal | RHT[84] | 1928 | LHT | Colonies Goa, Macau and Mozambique, which had land borders with LHT countries, did not switch and continue to drive on the left.[93] The Porto Metro uses RHT. |
Qatar | RHT[60] | |||
Romania | RHT[60] | RHT | Transylvania, the Banat and Bukovina were until 1919 LHT like most of former Austria-Hungary, while Wallachia and Moldavia were already RHT. | |
Russia | RHT[60] | RHT | In the Russian Far East RHD vehicles are common due to the import of used cars from nearby Japan.[106] Railway between Moscow and Ryazan is LHT. Sormovskaya line in Nizhny Novgorod Metro also uses LHT. | |
Rwanda | RHT[69] | Former Belgian mandate. Considering switching to LHT[69][107] like its neighbours Tanzania, Kenya and Uganda. | ||
Saint Kitts and Nevis | LHT | Former British colony. | ||
Saint Lucia | LHT | Former British colony. | ||
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | LHT | Former British colony. | ||
Samoa | LHT | 2009 | Switched to LHT to allow for cheaper importation of cars from Australia, New Zealand and Japan.[84] | |
San Marino | RHT[60] | |||
São Tomé and Príncipe | RHT[60] | 1928 | Originally LHT, like its colonial power Portugal. Switched to RHT with Portugal in 1928. | |
Saudi Arabia | RHT[60] | LHT/RHT | The Makkah Metro and the Riyadh Metro use RHT. | |
Senegal | RHT[60] | |||
Serbia | RHT[60] | RHT | Vojvodina was LHT while part of Austria-Hungary. | |
Seychelles | LHT[60] | Former British colony. Island nation. | ||
Sierra Leone | RHT | 1971[108] | Importation of RHD vehicles was banned in 2013.[109] | |
Singapore | LHT[60] | LHT | Former British colony. | |
Slovakia | RHT[60] | 1939–41 | RHT | Was LHT like most of former Austria-Hungary. Switched to RHT when it became a client state of Nazi Germany. |
Slovenia | RHT[60] | LHT | Was LHT like most of Austria-Hungary. Switched to RHT to unite with Croatia-Slavonia, Dalmatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia and Montenegro to form with Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. | |
Solomon Islands | LHT[60] | |||
Somalia | RHT | 1968[110] | ||
South Africa | LHT[111][112] | LHT | Former British colony. | |
South Sudan | RHT | 1973 | Was LHT during the period of British colonial rule. Split from Sudan in 2011 after the majority of the population voted for independence. | |
Spain | RHT | 1924 | RHT | Up to the 1920s Barcelona was RHT, and Madrid was LHT until 1924. The Madrid and Bilbao metro systems use LHT.[113] |
Sri Lanka | LHT[60] | LHT | Former British colony. | |
Sudan | RHT[60] | 1973 | Former British colony. | |
Suriname | LHT[60] | 1920s | ||
Swaziland | LHT[60] | |||
Sweden | RHT[60] | 3 September 1967 | LHT | The day of the switch was known as Dagen H. Most passenger cars were already LHD. The tram systems in Gothenburg (except for a short part), Norrköping and Stockholm are RHT.[114] The railroads in Malmö use RHT due to the connection to Denmark. |
Switzerland | RHT[60] | LHT | The tram system in Zurich and the Lausanne Metro use RHT. | |
Syria | RHT[60] | |||
Taiwan | RHT | 1946 | LHT | Was LHT during the period of Japanese rule. The government of the Republic of China changed Taiwan to RHT in 1946 along with the rest of China.[115] Most metro systems use RHT. |
Tajikistan | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Tanzania | LHT[60] | |||
Thailand | LHT[84] | LHT | One of the few LHT countries not a former British colony. Shares long land border with RHT Laos and Cambodia. | |
Togo | RHT[60] | |||
Tonga | LHT[60] | |||
Trinidad and Tobago | LHT[116] | Former British colony. | ||
Tunisia | RHT[60] | LHT | French RHT was enforced in the French protectorate of Tunisia from 1881. | |
Turkey | RHT[60] | RHT | The Istanbul Metrobus uses LHT. | |
Turkmenistan | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Tuvalu | LHT[60] | Former British colony. | ||
Uganda | LHT[60] | |||
Ukraine | RHT | 1922[105] | RHT | West Ukraine was LHT, like most of former Austria-Hungary. Carpathian Ruthenia remained LHT as part of Czechoslovakia before switching in 1941 as part of Hungary. The rest of Ukraine, having been part of the Russian Empire, already drove on the right. Some sections of Kryvyi Rih Metrotram use LHT due to tramcars have doors only on right side, which makes it impossible to use RHT at stations with island platforms.[117] |
United Arab Emirates | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
United Kingdom | LHT (Mainland UK) RHT (Gibraltar, British Indian Ocean Territory) | 1929 (in Gibraltar) | LHT | Includes Crown Dependencies and Overseas Territories Isle of Man, Guernsey, Jersey, Anguilla, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Falkland Islands, Montserrat, Pitcairn Islands (unregistered), Turks and Caicos Islands, Saint Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha are all LHT. Gibraltar has been RHT since 1929 because of its land border with Spain.[118] The British Indian Ocean Territory is the only other overseas territory driving on the right. The Channel Islands (Jersey and Guernsey) drove on the right under German occupation until their liberation in 1945.[119] The Falkland Islands similarly drove on the right during their occupation by Argentina in 1982.[120] Virtually all passenger vehicles in British Virgin Islands as well as in Cayman Islands are LHD due to grey imports of used cars from the US and South Korea. |
United States | RHT LHT (U.S. Virgin Islands) | RHT/LHT[121] | American Samoa, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico is RHT. U.S. Virgin Islands, like much of the Caribbean, is LHT and is the only American jurisdiction that still has LHT, because the islands drove on the left when the US purchased the former Danish West Indies from Denmark in 1917 (known as the Treaty of the Danish West Indies.) However, virtually all passenger vehicles are LHD due to imports of US vehicles. | |
Uruguay | RHT | 1945[122] | LHT | Became LHT in 1918, but as in some other countries in South America, changed to RHT on 2 September 1945.[122] A speed limit of 30 km/h (19 mph) was observed until 30 September for safety. |
Uzbekistan | RHT[60] | RHT | ||
Vanuatu | RHT[123] | |||
Venezuela | RHT[60] | LHT | The Caracas Metro uses RHT. | |
Vietnam | RHT[60] | LHT | Became RHT as French Indochina. | |
Yemen | RHT | 1977[1] | South Yemen, formerly the British colony of Aden, changed to RHT in 1977. A series of postage stamps commemorating the event was issued.[124]North Yemen was already RHT. | |
Zambia | LHT[60] | |||
Zimbabwe | LHT | LHT | Former British colony. In 2010, the government attempted to ban LHD vehicles.[125] |
Traffic rules
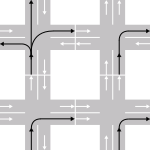
LHT
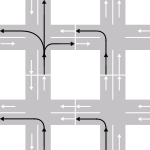
RHT
| Manoeuvre | LHT | RHT |
|---|---|---|
| Unless overtaking, stay on the | left | right |
| In roundabouts, traffic rotates | clockwise | anti-clockwise |
| Oncoming traffic is seen coming from the | right | left |
| Traffic must cross oncoming traffic when turning | right | left |
| Most traffic signs are on the | left | right |
Pedestrians crossing a two-way road look first for traffic from their | right | left |
Dual carriageway ramps are on the | left | right |
| After stopping at a red light, it may be legal to turn | left | right |
| On most vehicles, the driver sits on the | right | left |
Rail traffic

Trains use right-hand track
Trains use left-hand track
Several states in Europe have RHT for roads but LHT for trains: Belgium, Italy, Monaco, Portugal, Slovenia, Sweden and Switzerland. France has mainly LHT for trains, except in Alsace-Lorraine, an eastern French territory which belonged to Germany for much of its history. UK and Ireland have LHT for both road and rail.
Gallery

Hong Kong drives on the left.

Mainland China drives on the right.

Left-hand traffic in Vienna, Austria circa 1930.

Gibraltar has been RHT since 1929.

A sign reminding motorists to keep left in Australia.

Vehicles entering and leaving Macau cross over each other at the Lotus Bridge.

Sign reminding motorists to drive on the left in Ireland.
See also
- Bidirectional traffic
- Hook turn
- Traffic-light signalling and operation
- World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations
References
^ abcde Kincaid, Peter (December 1986). The Rule of the Road: An International Guide to History and Practice. Greenwood Press. pp. 50, 86–88, 99–100, 121–122, 198–202. ISBN 0-313-25249-1..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abc Barta, Patrick. "Shifting the Right of Way to the Left Leaves Some Samoans Feeling Wronged". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 4 December 2016.
(subscription required)
^ ab Watson, Ian. "The rule of the road, 1919-1986: A case study of standards change" (PDF). Retrieved 30 November 2016.
^ FAR Sec. 91.115(c): "When aircraft, or an aircraft and a vessel, are approaching head-on, or nearly so, each shall alter its course to the right to keep well clear."
^ Foerch, C; Steinmetz, H (2009). "Left-sided traffic directionality may be the safer "rule of the road" for ageing populations". Med Hypotheses. 73 (1): 20–3. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.01.044. PMID 19327893.
^ "Your Dominant Eye and Why it Matters". Retrieved 11 December 2016.
^ abc Anderson, Charles (2003). Puzzles and Essays from the Exchange Essays. Haworth Information Press. pp. 2–3.|access-date=requires|url=(help)
^ Walters, Bryn. "Huge Roman Quarry found in North Wiltshire" (PDF). ARA The Bulletin of The Association for Roman Archaeology. Autumn 1998 (Six): 8–9. ISSN 1363-7967. Retrieved 7 October 2016.
^ ab Hamer, Mike. "Left is right on the road". New Scientist (20 December 1986/1 January 1987): 16–18. Retrieved 7 October 2016.
^ Why We Drive on the Right of the Road, ''Popular Science Monthly'', Vol.126, No.1, (January 1935), p.37. Books.google.com.au. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
^ abcd Weingroff, Richard. "On The Right Side of the Road". United States Department of Transportation. Retrieved 10 January 2014.
^ "An Act Establishing the Law of the Road". Massachusetts General Court. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
^ "Travel Tips | US Virgin Islands". Usvitourism.vi. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
^ Vasold, Manfred (2010). "Obacht! Linksverkehr" (PDF). Kultur & Technik. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
^ "Seventy-five years of driving on the right". Radio Prague. 18 March 2014.
^ "Högertrafik" (in Swedish). vardo.aland.fi. Archived from the original on 3 December 2007. Retrieved 11 August 2006.
^ Réalités, Issues 200-205, Société d'études et publications économiques, 1967, page 95
^ TIME (15 September 1967). "Sweden: Switch to the Right". TIME. Archived from the original on 18 October 2012. Retrieved 31 October 2012.
^ Mieszkowski, Katharine (14 August 2009). "Salon News: Whose side of the road are you on?". Salon.com. Retrieved 12 December 2010.
^ 45 ár frá hægri umferð, Morgunblaðið, 26 May 2013 English translation
^ Tom Geoghegan (7 September 2009). "Could the UK drive on the right?". BBC News Magazine. British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
^
"Layout of Grade Separated Junctions" (PDF). The Highways Agency. 2006: 4.9ff.
^ "The Unique World of Burmese Driving". a minor diversion. 2012-03-14. Retrieved 2015-09-28.
^ ab Bryant, Nick (7 September 2009). "Samoan cars ready to switch sides". BBC News. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
^ ab Askin, Pauline (7 September 2009). "Outcry as Samoa motorists prepare to drive on left". Reuters. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
^ Dyer, Gwynne (1 September 2009). "Right-to-life plea fails to sway Samoan court in road appeal". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 5 November 2011.
^ Dobie, Michael (6 September 2009). "Samoa drivers brace for left turn". BBC News. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
^ "Samoan drivers change from right-hand side of the road to the left". Heraldsun.com.au. Retrieved 31 October 2012.
^ Jackson, Cherelle (25 July 2008). "Samoa announces driving switch date". Nzherald.co.nz. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
^ Plaza Mayor de Manila, by José Honorato Lozano (1815/21(?)-1885), in the album Vistas de las islas Filipinas y trajes de sus habitantes, published 1847. Collection of the Biblioteca Nacional de España.
^ "ESCOLTA MANILA PHILIPPINES- YEAR 1903". YouTube. March 6, 2010. Retrieved March 14, 2017.
^ "Manila - Castillian Memoirs 1930s". YouTube. April 19, 2008. Retrieved March 14, 2017.
^ "Manila, Queen of the Pacific 1938". YouTube. May 6, 2008. Retrieved March 14, 2017.
^ Goupal, Lou (June 26, 2013). "Manila Nostalgia: Dewey Boulevard during the Japanese occupation". YouTube. Manila Nostalgia. Retrieved March 14, 2017.Original video clips from a Japanese propaganda film shot in early 1942.
^ Tadeo, Patrick Everett (March 10, 2015). "How the Philippines became a left-hand-drive country". Top Gear Philippines. Retrieved March 14, 2017.
^ ab "Executive Order No. 34, s. 1945". www.officialgazzete.gov.ph.
^ ab Tourist and Business Directory - The Gambia, 1969, page 19
^ "Rwanda wants to drive on the left". Independent.co.ug. 3 June 2012. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
^ "East Africa: Rwanda Looks to the Left". allAfrica.com. 27 September 2010. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
^ Bari, Dr Mahabubul (29 July 2014). "The study of the possibility of switching driving side in Rwanda". European Transport Research Review. 6 (4): 439–453. doi:10.1007/s12544-014-0144-2. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
^ Right-hand-drive vehicles return on Rwandan roads, The East African, March 13, 2015
^ Tumwebaze, Peterson (9 September 2014). "Govt okays importation of RHD trucks, to decide on other vehicle categories in October". The New Times. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
^ Foerch, C; Steinmetz, H (2009). "Left-sided traffic directionality may be the safer „rule of the road" for ageing populations". Med Hypotheses. 73 (1): 20–3. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.01.044. PMID 19327893.
^ "Your Dominant Eye and Why it Matters". Retrieved 2016-12-11.
^ Leeming, J. J. 1969. Road accidents: prevent or punish? London: Cassell
^ Jennings, Ken. "What Happens When Left-Hand Roads Meet Right-Hand Roads". Conde Nast Traveler. Retrieved 18 November 2016.
^ "Hong Kong 2006 – Transport – Cross-Boundary Traffic". Yearbook.gov.hk. 15 August 2007. Retrieved 12 December 2010.
^ "Takutu bridge opens to traffic". Stabroeknews.com. 27 April 2009. Retrieved 12 December 2010.
^ "Nearside (dictionary definition)". Dictionary.reverso.net. Retrieved 12 December 2010.
^ Miller, Wayne (2015). Car Crazy: The Battle for Supremacy between Ford and Olds and the Dawn of the Automobile Age. PublicAffairs. p. 279. ISBN 9781610395526. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
^ LHD Specialist: Location of the Steering Wheel Archived 21 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Hinchliffe, Mark. "How to mount your motorbike". Retrieved 11 December 2016.
^ ab "MOUNTING AND DISMOUNTING A MOTORCYCLE". Motorcycle Test Tips. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
^ "S.I. No. 5/2003 - Road Traffic (Construction and Use of Vehicles) Regulations 2003". Irish Statute Book. 42. (1). Retrieved 6 November 2017.where a side–car is attached to a mechanically propelled bicycle, the side–car shall be ... fitted on the left side of the vehicle
; "Motorcycle Sidecar & Trailer legislation". MAG Ireland. Irish Motorcyclists Association. 9 Feb 2014. Retrieved 6 November 2017.
^ "The Road Vehicles (Construction and Use) Regulations 1986 - Section 93". UK Government. 25 June 1986. Retrieved 9 December 2012.
^ abc "UN Regulation 112, "Motor vehicle headlamps emitting an asymmetrical passing beam or a driving beam or both and equipped with filament lamps"" (PDF).
^ "UN Regulation 48" (PDF).
^ "Popular family SUV Hyundai Tucson slammed for 'four-star' Australian crash test result". Retrieved 5 November 2017.
^ L. R. Reddy (2002). Inside Afghanistan: End of the Taliban Era?. APH. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
^ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzaaabacadaeafagahaiajakalamanaoapaqarasatauavawaxayazbabbbcbdbebfbgbhbibjbkblbmbnbobpbqbrbsbtbubvbwbxbybzcacbcccdcecfcgchcicjckclcmcncocpcqcrcsctcucvcwcxcyczdadbdcdddedfdgdhdidjdkdldmdndodpdqdrdsdtdudvdwdxdydzeaebecedee "Worldwide Driving Orientation by Country". Retrieved 13 December 2016.
^ "10 de Junio: Día Mundial de la Seguridad Vial". Retrieved 13 December 2016.
^ New Scientist, Volume 112, IPC Magazines, 1986, page 18
^ IIWINC. "Driving in the Bahamas - Caribya!". caribya.com. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
^ "Safety and security - Bahamas travel advice". Retrieved 26 June 2018.
^ Bahrain Government Annual Reports, Times of India Press, 1968, page 158
^ Uwe Hilgemann (15 November 2015). "Zillertal Railway Narrow Gauge in Bosnian Gauge". Retrieved 26 June 2018 – via YouTube.
^ "História". Touring Club do Brasil (in Portuguese). Retrieved 8 January 2017."Já na década de 1920 (...) Em um país onde os documentos veiculares só tinham validade municipal e alguns estados adotavam a mão-inglesa" (Translation: In the 1920s (...) In a country where vehicular documents were valid only citywide and some states adopted left-hand traffic.)
^ "Decreto 18.323/1928" (in Portuguese). Retrieved 17 January 2017."Art. 31. São obrigações communs a todos os conductores de vehiculos: a) conservar sua direita, trafegando o mais proximo possivel da beira da estrada, e sempre deixando a seu lado esquerdo espaço livre para passagem dos vehiculos que tiverem de passar á frente ou que transitarem em senttido contrario." (Translation: article 31: The common obligations to vehicle drivers are; a) Keep to the right, driving the closest as possible to the roadside, letting their left side free for vehicles overtaking or for oncoming traffic.)
, the first nationwide traffic legislation, cited unambiguously RHT as the standard for the country.
^ abc Nkwame, Marc (27 July 2013). "Burundi, Rwanda to start driving on the left". DailyNews Online. Retrieved 28 May 2016.
^ "Cambodia bans right-hand drive cars". BBC News. 1 January 2001. Retrieved 12 January 2007.
^ "Change of Rule of Road in British Columbia 1920" (PDF). The British Columbia Road Runner. March 1966. Retrieved 27 August 2017.
^ Griffin, Kevin (1 January 2016). "Week In History: Switching from the left was the right thing to do". Vancouver Sun. Retrieved 26 August 2017.
^ Smith, Ivan. "Highway Driving Rule Changes Sides". History of Automobiles - The Early Days in Nova Scotia, 1899-1949. Retrieved 27 August 2017.
^ Dyer, Gwynne (30 August 2009). "A triumph for left over right". Winnipeg Free Press. Retrieved 27 August 2017.
^ Baedeker, Karl (1900). "Austria, including Hungary, Transylvania, Dalmatia and Bosnia". p. xiii-xiv. Retrieved 28 July 2017.In Styria, Upper and Lower Austria, Salzburg, Carniola, Croatia, and Hungary we keep to the left, and pass to the right in overtaking; in Carinthia, Tyrol, and the Austrian Littoral (Adriatic coast: Trieste, Gorizia and Gradisca, Istria and Dalmatia) we keep to the right and overtake to the left. Troops on the march always keep to the right side of the road, so in whatever part of the Empire you meet them, keep to the left.
^ ";Hvorfor kører nogle lande i højre side? (Why do some countries drive on the right side?)". videnskab.dk. Retrieved 31 Aug 2014.
^ "Högertrafik i Sverige och Finland". aland.net.
^ 'Left is right on the road', Mick Hamer New Scientist, 25 December 1986 – 1 January 1987 No 1540/1541, p.16.
^ Sputnik. ""Выживут" ли праворульные машины в Грузии". sputnik-georgia.ru. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
^ Hillger, Don; Toth, Garry. "Right-Hand/Left-Hand Driving Customs". Colorado State University. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
^ Daily Graphic, Issue 7526, December 21 1974, page 9
^ "Right-Hand Traffic Act". Ghanalegal.com. Retrieved 2014-05-14.
^ Phil Bartle. "Studies Among the Akan People of West Africa Community, Society, History, Culture; With Special Focus on the Kwawu by Phil Bartle, PhD". Cec.vcn.bc.ca. Retrieved 2014-05-14.
^ abcde "Right-Hand Traffic versus Left-Hand Traffic". The Basement Geographer. Retrieved 20 November 2016.
^ hadi anto (26 July 2016). "indonesia train compilation" – via YouTube.
^ "Sight for sure eyes, Honest John's Agony Column". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 28 March 2008.
^ Nick Georgano, ed. (2000). "Lancia". The Beaulieu Encyclopedia of the Automobile (Vol. 2: G-O ed.). Taylor & Francis. p. 867. ISBN 1-57958-293-1.
^ "Why Does Japan Drive On The Left". 2pass.co.uk. Retrieved 11 August 2006.
^ Andrew H. Malcolm (5 July 1978). "U-Turn for Okinawa: From Right-Hand Driving to Left; Extra Policemen Assigned". The New York Times. p. A2.
^ "Customs Services Department – Frequently Asked Questions". KRA. Retrieved 12 December 2010.
^ "Over 20,000 Right Hand Drive Cars Imported in Kyrgyzstan in 2012". The Gazette of Central Asia. Satrapia. 8 May 2013.
^ "Photo of All Change. Swop Over Point for the Traffic !". Panoramio. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
^ ab Mozambique: memoirs of a revolution, John Paul, Penguin, 1975, page 41
^ Myanmar’s car market set to take new direction, Motokazu Matsui and Takemi Nakagawa, Financial Times, 2 January 2017
^ Peter van Ammelrooy. "De Claim links rijden" (in Dutch). Volkskrant.nl. Retrieved 2014-05-14.
^ "De geschiedenis van het linksrijden". Engelfriet.net. Retrieved 2014-05-14.
^ The Laws of South West Africa, Volume 2, J. Meibert, 1961
^ "2.1 "Keeping Left" – Land Transport (Road User) Rule 2004 – New Zealand Legislation". New Zealand Government. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
^ Africa, Issues 6-10, Africa Journal, Limited, 1972, page 32
^ Famutimi, Temitayo (19 March 2012). "FRSC warns owners of right-hand drive vehicles". Punch.
^ Ibileke, Jethro (2 July 2012). "FRSC To Prosecute Operators Of Right-Hand Vehicles". PM News.
^ "Travel advice by country, Oman". Foreign & Commonwealth Office (fco.gov.uk). Archived from the original on 8 April 2008. Retrieved 8 August 2006.
^ Panama Shifts To Right Handed Driving Of Cars, Chicago Tribune, April 25, 1943
^ De izquierda a derecha, ABC Color, 2 March 2014
^ ab "Krakowska Komunikacja Miejska – autobusy, tramwaje i krakowskie inwestycje drogowe – History of the Cracow tram network". Komunikacja.krakow.eurocity.pl. 28 November 1982. Retrieved 11 May 2009.
^ "Russian Far East is still attached to Japanese cars". Russia behind the headlines. 31 August 2016. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
^ Peter. "Rwanda to adopt EAC driving standards". Rwanda Transport. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
^ The Rising Sun: A History of the All People's Congress Party of Sierra Leone, A.P.C. Secretariat, 1982, page 396
^ Sierra Leone Bans Right-Hand Vehicles as Hazards, Voice of America, Nina de Vries, 17 September 2013
^ "Somalia – Visa service and travel information". Travcour. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
^ "Road Rules". SACarRental.com. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
^ "Driving in South Africa Information". drivesouthafrica.co.za. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
^ Moya, Aurora. "Metro de Madrid, 1919–1989. Setenta años de historia", Chapter 1
^ Taplin, Michael (1995). Light Rail in Europe. Capital Transport. pp. 126, 128. ISBN 1-85414-180-5.
^ Passed by the Legislative Yuan (1946). "違警罰法 (Act Governing the Punishment of Police Offences)". Archived from the original on 10 December 2013. Retrieved 14 August 2012.
^ Trinidad and Tobago Adventure Guide, Kathleen O'Donnell, Stassi Pefkaros, Hunter Publishing, Inc, 2000, page 53
^ Vril (13 October 2013). "Криворожский скоростной трамвай". Retrieved 26 June 2018 – via YouTube.
^ Colonial Reports, Annual, Volumes 1480-1499, 1930, page 76
^ The Channel Islands War: 1940-1945, Peter King, Hale, 1991, page 31
^ Tobar, Hector (1 April 2002). "'82 Falklands Conflict Left a Legacy of Tragedy, Hope". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 1 March 2010.
^ "Which side of the road do they drive on?". brianlucas.ca.
^ ab El día en que el Río de la Plata dejó de manejar por la izquierda, Autoblog, 25 August 2015
^ "RHD/LHD Country Guide". toyota-gib.com. Retrieved 22 September 2017.
^ "South Yemen – Postage stamps – 1977". stampworld.com.
^ Left-hand vehicles to stay, NewsDay, 30 January 2014
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Left- and right-hand traffic. |
Google Maps placemarks of border crossings where traffic changes sides (browser-based), also available as a Google Earth placemarks file (requires Google Earth)- The Extraordinary Street Railways of Asunción, Paraguay






