Palate
| Palate | |
|---|---|
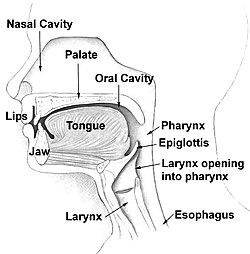 Head and neck. | |
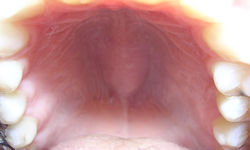 Palate exhibiting torus palatinus. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Palatum |
| MeSH | D010159 |
| TA | A05.1.01.102 |
| FMA | 54549 |
Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |
The palate /ˈpælɪt/ is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.[1] A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separate. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior bony hard palate and the posterior fleshy soft palate (or velum).[2][3]
Contents
1 Structure
1.1 Innervation
1.2 Development
1.3 Variation
2 Function
3 History
3.1 Etymology
4 See also
5 Bibliography
6 References
Structure
Innervation
The maxillary nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve supplies sensory innervation to the palate.
Development
The hard palate forms before birth.
Variation
If the fusion is incomplete, it is called a cleft palate.
Function
When functioning in conjunction with other parts of the mouth the palate produces certain sounds, particularly velar, palatal, palatalized, postalveolar, alveolo-palatal, and uvular consonants.[4]
History
Etymology
The English synonyms palate and palatum, and also the related adjective palatine (as in palatine bone), are all from the Latin palatum via Old French palat, words that, like their English derivatives, refer to the "roof of the mouth."[5]
The Latin word palatum and its derivatives mentioned above are all unrelated to a similar-sounding Latin word meaning palace, palatium, from which other senses of palatine and the English word palace itself derive.[6]
As the roof of the mouth was once considered the seat of the sense of taste, palate can also refer to this sense itself, as in the phrase "a discriminating palate". By further extension, the flavor of a food (particularly beer or wine) may be called its palate, as when a wine is said to have an oaky palate.
See also
- Language
- Vocal tract
Pallet, palette and pellet, objects whose names are homophonous with palate for many English-speakers- Palatability
Bibliography
Saladin, Kenneth (2010). Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. New York: McGraw Hill. p. 256..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
Thompson, Gale (2005–2006). World of Anatomy and Physiology. Thompson Corporation. pp. Palate (Hard and Soft Palate).
References
^
Wingerd, Bruce D. (1811). The Human Body Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology. Fort Worth: Saunders College Publishing. p. 166. ISBN 0-03-055507-8.
^ Wingerd, Bruce D. (1994). The Human Body Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology. Fort Worth: Saunders College Publishing. p. 478. ISBN 0-03-055507-8.
^
Goss, Charles Mayo (1966). Gray's Anatomy. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger. p. 1172.
^
Goss, Charles Mayo (1966). Gray's Anatomy. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger. p. 1201.
^ Harper, Douglas. "palate (the entry for)". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 10 September 2011.palate - late 14c., 'roof of the mouth,' from O.Fr. palat, from L. palatum 'roof of the mouth,' perhaps of Etruscan origin. Popularly considered the seat of taste, hence transferred meaning 'sense of taste' (1520s).
^ Harper, Douglas. "palatine (the entry for)". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 10 September 2011.palatine (adj.) - mid-15c., from M.Fr. palatin (15c.), from M.L. palatinus 'of the palace' (of the Caesars), from L. palatium (see palace). Used in English to mean 'quasi-royal authority.' Reference to the Rhineland state is from c.1580.