Museo del Prado
 | |
 Exterior of the Prado Museum | |
| Established | 1819 |
|---|---|
| Location | Paseo del Prado, Madrid, Spain |
| Coordinates | 40°24′49″N 3°41′33″W / 40.413722°N 3.692412°W / 40.413722; -3.692412 |
| Type | Art museum, Historic site |
| Visitors | 2.892.937 (2018)[1] Ranked 18th globally (2013)[1] |
| Director | Miguel Falomir[2] |
| Public transit access |
|
| Website | www.museodelprado.es |
| Museo Nacional del Prado | |
|---|---|
Native name Spanish: Museo Nacional del Prado | |
 Museo del Prado (Main wing) | |
| Location | Madrid, Spain |
| Architect | Juan de Villanueva |
Spanish Property of Cultural Interest | |
| Official name: Museo Nacional del Prado | |
| Type | Non-movable |
| Criteria | Monument |
| Designated | 1962 |
| Reference no. | RI-51-0001374 |
 Location of Museo Nacional del Prado in Spain | |
The Prado Museum (Spanish: Museo del Prado; Spanish pronunciation: [muˈseo ðel ˈpɾaðo]) is the main Spanish national art museum, located in central Madrid. It is widely considered to have one of the world's finest collections of European art, dating from the 12th century to the early 20th century, based on the former Spanish Royal Collection, and the single best collection of Spanish art. Founded as a museum of paintings and sculpture in 1819, it also contains important collections of other types of works. El Prado is one of the most visited sites in the world, and it is considered one of the greatest art museums in the world. The numerous works by Francisco Goya, the single most extensively represented artist, as well as by Hieronymus Bosch, El Greco, Peter Paul Rubens, Titian, and Diego Velázquez, are some of the highlights of the collection.
The collection currently comprises around 8,200 drawings, 7,600 paintings, 4,800 prints, and 1,000 sculptures, in addition to a large number of other works of art and historic documents. As of 2012, the museum displayed about 1,300 works in the main buildings, while around 3,100 works were on temporary loan to various museums and official institutions. The remainder were in storage.[3] The museum received 2.8 million visitors in 2012.[4] It is one of the largest museums in Spain.
The best-known work on display at the museum is Las Meninas by Velázquez. Velázquez and his keen eye and sensibility were also responsible for bringing much of the museum's fine collection of Italian masters to Spain, now the largest outside Italy.
The museum is planning a 16% extension in the nearby Salón de Reinos, to be opened in 2019.[5]
Contents
1 History
2 Historic structure
3 Special exhibitions
4 Nearby museums
5 Management
5.1 Funding
5.2 Directors
6 Collection highlights
6.1 Selected works
7 In Google Earth
8 Further reading
9 References
10 External links
History
The building that is now the home of the Museo Nacional del Prado was designed in 1785 by architect of the Enlightenment in Spain Juan de Villanueva on the orders of Charles III to house the Natural History Cabinet. Nonetheless, the building's final function was not decided until the monarch's grandson, Ferdinand VII, encouraged by his wife, Queen María Isabel de Braganza, decided to use it as a new Royal Museum of Paintings and Sculptures. The Royal Museum, which would soon become known as the National Museum of Painting and Sculpture, and subsequently the Museo Nacional del Prado, opened to the public for the first time in November 1819. It was created with the double aim of showing the works of art belonging to the Spanish Crown and to demonstrate to the rest of Europe that Spanish art was of equal merit to any other national school.

In the main exhibition hall, first floor
The first catalogue of the Museum, published in 1819 and solely devoted to Spanish painting, included 311 paintings, although at that time the Museum housed 1,510 from the various royal residences, the Reales Sitios, including works from other schools. The exceptionally important royal collection, which forms the nucleus of the present-day Museo del Prado, started to increase significantly in the 16th century during the time of Charles V and continued under the succeeding Habsburg and Bourbon monarchs. Their efforts and determination led to the Royal Collection being enriched by some of the masterpieces now to be seen in the Prado. These include The Descent from the Cross by Rogier van der Weyden, The Garden of Earthly Delights by Hieronymous Bosch, Knight with his Hand on his Breast by El Greco, The Death of the Virgin by Mantegna, The Holy Family, known as "La Perla", by Raphael, Charles V at Mülhberg by Titian, Christ Washing the Disciples’ Feet by Tintoretto, Dürer's Self-portrait, Las Meninas by Velázquez, The Three Graces by Rubens, and The Family of Charles IV by Goya.
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinner{width:100%!important;max-width:none!important}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center}}


In addition to works from the Spanish royal collection, other holdings increased and enriched the Museum with further masterpieces, such as the two Majas by Goya. Among the now closed museums whose collections have been added to that of the Prado were the Museo de la Trinidad in 1872, and the Museo de Arte Moderno in 1971. In addition, numerous legacies, donations and purchases have been of crucial importance for the growth of the collection. Various works entered the Prado from the Museo de la Trinidad, including The Fountain of Grace by the School of Van Eyck, the Santo Domingo and San Pedro Martír altarpieces painted for the monastery of Santo Tomás in Ávila by Pedro Berruguete, and the five canvases by El Greco executed for the Colegio de doña María de Aragón. Most of the Museum's 19th-century paintings come from the former Museo de Arte Moderno, including works by the Madrazos, José de Madrazo y Agudo and Federico de Madrazo, Vicente López, Carlos de Haes, Eduardo Rosales and Sorolla.
Upon the deposition of Isabella II in 1868, the museum was nationalized and acquired the new name of "Museo del Prado". The building housed the royal collection of arts, and it rapidly proved too small. The first enlargement to the museum took place in 1918. Since the creation of the Museo del Prado more than 2,300 paintings have been incorporated into its collection, as well as a large number of sculptures, prints, drawings and works of art through bequests, donations and purchases, which account for most of the New Acquisitions. Numerous bequests have enriched the Museum's holdings, such as the outstanding collection of medals left to the Museum by Pablo Bosch; the drawings and items of decorative art left by Pedro Fernández Durán as well as Van der Weyden's masterpiece, The Virgin and Child; and the Ramón de Errazu bequest of 19th-century paintings. Particularly important donations include Barón Emile d'Erlanger's gift of Goya's Black Paintings in 1881. Among the numerous works that have entered the collection through purchase are some outstanding ones acquired in recent years including two works by El Greco, The Fable and The Flight into Egypt acquired in 1993 and 2001, Goya's Countess of Chinchón bought in 2000, Velázquez's portrait of The Pope's Barber, acquired in 2003 and Fra Angelico's Madonna of the Pomegranate purchased in 2016.
Between 1873 and 1900, the Prado helped decorate city halls, new universities, and churches. During the Second Spanish Republic from 1931 to 1936, the focus was on building up provincial museums. During the Spanish Civil War, upon the recommendation of the League of Nations, the museum staff removed 353 paintings, 168 drawings and the Dauphin's Treasure and sent the art to Valencia, then later to Girona, and finally to Geneva. The art had to be returned across French territory in night trains to the museum upon the commencement of World War II. During the early years of the dictatorship of Francisco Franco, many paintings were sent to embassies.[6]

A main promenade entrance is dominated by this 1899 bronze statue of Diego Velázquez, by Aniceto Marinas
The main building was enlarged with short pavilions in the rear between 1900 and 1960. The next enlargement was the incorporation of two buildings (nearby but not adjacent) into the institutional structure of the museum: the Casón del Buen Retiro, which is equipped to display up to 400 paintings and which housed the bulk of the 20th-century art from 1971 to 1997, and the Salón de Reinos (Throne building), formerly the Army Museum.
In 1993, an extension proposed by the Prado's director at the time, Felipe Garin, was quickly abandoned after a wave of criticism.[7] In the late 1990s, a $14 million roof work forced the Velázquez masterpiece Las Meninas to change galleries twice.[8] In 1998, the Prado annex in the nearby Casón del Buen Retiro closed for a $10 million two-year overhaul that included three new underground levels. In 2007, the museum finally executed Rafael Moneo's project to expand its exposition room to 16,000 square meters, hoping to increase the yearly number of visitors from 1.8 million to 2.5 million.

The cafeteria in the underground extension by Rafael Moneo
A glass-roofed and wedge-shaped foyer now contains the museum's shops and cafeteria, removing them from the main building to make more room for galleries.[8] The 16th-century Cloister of Jerónimo has been removed stone by stone to make foundations for increased stability of surrounding buildings and will be re-assembled in the new museum's extension. Hydraulic jacks had to be used to prevent the basement walls from falling during construction.
[9] The enlargement is an underground building which connects the main building to another one entirely reconstructed.
In November 2016, it was announced that British architect Norman Foster, in a joint project with Carlos Rubio Carvajal, is to renovate the Hall of Realms, which once formed part of the Buen Retiro palace and transform it into a $32 million extension of the Prado. The museum announced the selection of Foster and Rubio after a jury reviewed the proposals of the eight competition finalists – including David Chipperfield, Rem Koolhaas and Eduardo Souto de Moura –,[10] who had already been shortlisted from an initial list of 47 international teams of architects.[11] The building was acquired by the Prado in 2015, after having served as an army museum until 2005. The project is designed to give the Prado about 61,500 square feet of additional available space, of which about 27,000 square feet will be used to exhibit works.[11]
Historic structure

The Goya Gate in the north façade of the museum.
The Museo del Prado is one of the buildings constructed during the reign of Charles III (Carlos III) as part of a grandiose building scheme designed to bestow upon Madrid a monumental urban space. The building that lodges the Museum of the Prado was initially conceived by José Moñino y Redondo, count of Floridablanca and was commissioned in 1785 by Charles III for the reurbanización of the Paseo del Prado. To this end, Charles III called on one of his favorite architects, Juan de Villanueva, author also of the nearby Botanical Garden and the City Hall of Madrid.[12]
The prado ("meadow") that was where the museum now stands gave its name to the area, the Salón del Prado (later Paseo del Prado), and to the museum itself upon nationalisation. Work on the building stopped at the conclusion of Charles III's reign and throughout the Peninsular War and was only initiated again during the reign of Charles III's grandson, Ferdinand VII. The premises had been used as headquarters for the cavalry and a gunpowder-store for the Napoleonic troops based in Madrid during the war.
Special exhibitions
Between 8 November 2011 and 25 March 2012, a group of 179 works of art were brought to the Museo del Prado from the Hermitage Museum in St. Petersburg.[13] Notable works included:
A Scholar (1631), by Rembrandt
The Lute Player (c. 1596), by Caravaggio
Ecstasy of Saint Teresa (1647), by Bernini
Game of Bowls (1908), by Henri Matisse
Bouquet of Cornflowers with Stems of Oats in a Vase (c. 1900), by House of Fabergé
Pond at Montgeron (1876), by Claude Monet
Belt buckle with a monster attacking a horse, (4th–3rd century BC), (gold ornament from Peter I’s Siberian Collection)
Moonrise, Two Men on the Shore (c. 1900), by Caspar David Friedrich
Composition VI (1913), by Wassily Kandinsky
Metaphysical Still life (1918), by Giorgio Morandi
Conversely, for the first time in its 200-year history, the Museo del Prado has toured an exhibition of its renowned collection of Italian masterpieces at the National Gallery of Victoria in Melbourne, Australia, from 16 May 2014 until 31 August 2014. Many of the works have never before left Spain.
Nearby museums
The Prado, with the nearby Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum and the Museo Reina Sofía, forms Madrid's Golden Triangle of Art.
Nearby is the Real Academia de Bellas Artes de San Fernando. The Museo Arqueológico houses some art of Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Greece, and Rome formerly in the collection of the Prado.
The Naval Museum, managed by the Ministry of Defence, is also nearby.
Management
Funding
Until the early 2000s, the Prado's annual income was approximately $18 million, $15 million of which came from the government and the remainder from private contributions, publications, and admissions.[14] In 2001, the conservative government of José María Aznar decided to change the museum's financing platform, ushering in a public-private partnership. Under its new bylaws, which the Cortes Generales approved in 2003, the Prado must gradually reduce its level of state support to 50 percent from 80 percent. In exchange, the museum gained control of the budget — now roughly €35 million — and the power to raise money from corporate donations and merchandising. However, its recent €150 million expansion was paid for by the Spanish state.[15]
In 1991, Manuel Villaescusa bequeathed his fortune of nearly $40 million in Madrid real estate to the Prado, to be used solely for the acquisition of paintings. The museum subsequently sold Villaescusa's buildings to realize income from them. The bequest suddenly made the Prado one of the most formidable bidders for paintings in the world.[14]
Directors
The first four directors were drawn from nobility. From 1838 to 1960, the directors were mostly artists. Since then, most of them have been art historians.
José Gabriel de Silva-Bazán y Waldstein, 1817–1820
Pedro de Alcántara Téllez-Girón y Pimentel, 1820–1823
José Idiáquez Carvajal, 1823–1826
José Rafael de Silva Fernández de Híjar, 1826–1838
José de Madrazo, 1838–1857
Juan Antonio de Ribera, 1857–1860
Federico de Madrazo, 1860–1868
Antonio Gisbert, 1868–1873
Francisco Sans Cabot, 1873–1881
Federico de Madrazo, 1881–1894
Vicente Palmaroli, 1894–1896
Francisco Pradilla, 1896–1898
Luis Álvarez Catalá, 1898–1901
José Villegas Cordero, 1901–1918
Aureliano de Beruete y Moret, 1918–1922
Fernando Álvarez de Sotomayor, 1922–1931
Ramón Pérez de Ayala, 1931–1936
Pablo Ruiz Picasso, 1936–1939
Fernando Álvarez de Sotomayor, 1939–1960
Francisco Javier Sánchez Cantón, 1960–1968
Diego Angulo Íñiguez, 1968–1971
Xavier de Salas Bosch, 1971–1978
José Manuel Pita Andrade, 1978–1981
Federico Sopeña, 1981–1983
Alfonso Pérez Sánchez, 1983–1991
Felipe Garín Llombart, 1991–1993
Francisco Calvo Serraller, 1993–1994
José María Luzón Nogué, 1994–1996
Fernando Checa Cremades, 1996–2002
Miguel Zugaza Miranda, 2002–2017
Miguel Falomir, 2017–Present
Collection highlights

Hieronymus Bosch, The Garden of Earthly Delights, between 1480 and 1505.

Diego Velázquez, Las Meninas, between 1656 and 1657.

Diego Velázquez, The Triumph of Bacchus, 1628–29

Fra Angelico, Annunciation, 1430–32

Raphael, Christ Falling on the Way to Calvary, 1517

Pieter Brueghel the Elder, The Triumph of Death, c. 1562

Peter Paul Rubens, The Adoration of the Magi, 1609/1628-1629

Peter Paul Rubens, The Three Graces, c.1635
Selected works
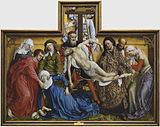
Rogier van der Weyden, The Descent from the Cross, c. 1435

Andrea Mantegna, Death of the Virgin, c. 1461

Antonello da Messina, The Dead Christ Supported by an Angel, c. 1475

Albrecht Dürer Adam and Eve, 1507

Raphael, Portrait of a Cardinal, c. 1510–11

Tintoretto, Christ Washing the Disciples' Feet, c. 1518

Correggio, Noli me tangere, c. 1525

Titian, Bacchanal of the Andrians, c. 1523–1526

Titian, Equestrian Portrait of Charles V, c. 1548

Titian, The Fall of Man, c. 1570

El Greco, The Holy Trinity, 1577–1579

El Greco, The Knight with His Hand on His Breast, c. 1580

Paolo Veronese, Venus and Adonis, c. 1580

Caravaggio, David and Goliath, 1600

Georges de La Tour, Ciego tocando la zanfonía, 1610–1630

Guido Reni, Hipómenes y Atalanta, 1618–19

Nicolas Poussin, Parnassus, c. 1630–31

Rembrandt, Artemisia, c. 1634

Anthony van Dyck, c. 1635

Diego Velázquez, The Surrender of Breda, 1634–35

Diego Velázquez, Mars Resting, 1639–1641

José de Ribera, Jacob's dream, 1639

Peter Paul Rubens, The Judgement of Paris, 1638–39

Claude Lorrain El embarque de santa Paula, 1639–40

Francisco de Zurbarán, Agnus Dei, 1635–1640

Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, La Inmaculada de Soult, 1678

Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, The Immaculate Conception, 1767

Francisco Goya, Third of May 1808, 1814

Francisco Goya, The Dog, 1819–1823

Francisco Goya, Saturn Devouring His Son, 1819–1823
In Google Earth
In 2009, the Prado Museum selected 14 of its most important paintings to be displayed in Google Earth and Google Maps at extremely high resolution, with the largest displayed at 14,000 megapixels. The images' zoom capability allows for close-up views of paint texture and fine detail.[16][17]
Further reading
- Alcolea Blanch, Santiago. The Prado, translated by Richard-Lewis Rees and Angela Patricia Hall. Madrid: Ediciones Polígrafa 1991.
- Araujo Sánchez, Ceferino. Los museos de España. Madrid 1875.
- Blanco, Antonio. Museo del Prado. Catálago de la Escultura. I Esculturas clásicas. II. Escultura, copia e imitaciones de las antiguas) (siglos XVI–XVIII). Madrid 1957.
- Luca de Tena, Consuelo and Mena, Manuela. Guía actualizada del Prado. Madrid: Alfiz 1985.
- Rumeu de Armas, Antonio. Origen y fundación del Museo del Prado. Madrid: Instituto de España 1980.
References
^ ab Top 100 Art Museum Attendance, The Art Newspaper, 2014. Retrieved on 15 July 2014.
^ Barrigós, Concha (21 March 2017). "Miguel Falomir, nuevo director del Prado: "Nunca, nunca pediré el traslado del 'Guernica'"". 20 minutos. Retrieved 1 April 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "The Collection: origins". Museo Nacional del Prado. Retrieved 15 November 2012.See also Museo del Prado, Catálogo de las pinturas, 1996, Ministerio de Educación y Cultura, Madrid, No ISBN, which lists about 7,800 paintings. Many works have been passed to the Museo Reina Sofia and other museums over the years; others are on loan or in storage. On the new displays, see El Prado se reordena y agranda. europapress.es here (in Spanish)
^ (in Spanish) "El Prado perderá un cuarto de sus visitantes" El País. Retrieved 28 June 2013.
^ "Prado Hall of Realms Redesign Competition - artnet News". artnet.com. 21 March 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
^ Alan Riding (1 August 1990). "The Prado Finds Out What It Has and Where". The New York Times. NYTimes.com. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
^ Alan Riding (1 May 1995). "The Prado Embarks On Plans to Expand Into a Complex". New York Times. NYTimes.com. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
^ ab Al Goodman (19 November 1998). "At Long Last, Expanding Spain's Treasure Chest". The New York Times. NYTimes.com. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
^ "Chronology of the extension". Museo Nacional del Prado. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
^ Hannah McGivern (November 25, 2016), Norman Foster to design Prado extension in historic palace Archived 27 November 2016 at the Wayback Machine The Art Newspaper.
^ ab Raphael Minder (November 25, 2016), Norman Foster to Remodel Palace for Prado Extension New York Times.
^ "Chronology of Museo del Prado, 1785" (in Spanish). Museo Nacional del Prado. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
^ "The Hermitage in the Prado". Museo Nacional del Prado. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
^ ab Michael Kimmelman (21 November 1993). "New Brooms Sweep Madrid's Museums". The New York Times. NYTimes.com. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
^ Dale Fuchs (24 December 2004). "The art of financing the Prado". New York Times. NYTimes.com. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
^ Tremlett, Giles (14 January 2009). "Online gallery zooms in on Prado's masterpieces (even the smutty bits)". The Guardian. London: Guardian News & Media Limited. Retrieved 5 March 2019.
^ "The Prado in Google Earth". Google.com. Archived from the original on 17 January 2009. Retrieved 24 January 2009.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Museo del Prado (category) |
Official website
- Masterworks in the collection
- Prado in Google Earth, extra high resolution
Coordinates: 40°24′50″N 3°41′33″W / 40.41389°N 3.69250°W / 40.41389; -3.69250





























