Grand Ducal Police
| Grand Ducal Police Police Grand-Ducale | |
|---|---|
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | January 1, 2000 |
| Preceding agency |
|
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| National agency | Luxembourg |
| Operations jurisdiction | Luxembourg |
 | |
| Policing for the Grand Ducal Police is organised under six primary intervention centres, under which further secondary intervention centres operate | |
| General nature |
|
| Agency executive |
|
| Website | |
| Official Site | |

Grand Ducal Police vehicle in Stolzembourg

TM-170, Grand Ducal Police armoured vehicle
The Grand Ducal Police (Luxembourgish: Groussherzoglech Police; French: Police Grand-Ducale; German: Großherzogliche Polizei) is the national law enforcement agency in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The police is under the control of the Minister for the Interior of Luxembourg, although they operate in the name, and under the ultimate control, of the Grand Duke. Day-to-day executive control is exercised by the Director-General. The Grand Ducal Police has existed in its current form since January 1, 2000, when the Grand Ducal Gendarmerie was merged with the police.[1]
The Grand Ducal Police is responsible for ensuring Luxembourg's internal security, maintaining law and order, border control and enforcing all laws and Grand Ducal decrees. It is also responsible for assisting the military in its internal operations, as prescribed by the Grand Duke.[1]
Contents
1 Organisation
2 Director-General
3 Emergencies
4 Footnotes
5 External links
Organisation
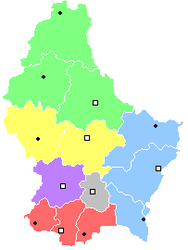
The Grand Ducal Police's operations are divided into six regions (circonscriptions régionales), which are under the command of a regional director. The director is responsible for primary intervention centres, secondary intervention centres, local police stations, and region-wide services. The region headquarters are in Capellen, Diekirch, Esch-sur-Alzette, Grevenmacher, Luxembourg City, and Mersch.
The primary intervention centres (Centre d'Intervention Primaire, abbreviated 'CIP') are the most capable and best equipped police stations to address emergencies. The CIPs also serve as the headquarters for the region, providing administrative support for the region's other operation centres. The CIPs' jurisdictions cover their respective regions (illustrated in different colours on the map, right).
Under the six CIPs are thirteen 'secondary intervention centre' (Centre d'Intervention Secondaire, abbreviated 'CIS'). As the CIPs perform the role of the CISs, as well as their own functions, there are seven dedicated CISs, located in Differdange, Dudelange, Echternach, Redange, Remich, Troisvierges, and Wiltz.
Local police stations (Commissariat de Proximité, abbreviated 'CP') operate separately from the CISs and CIPs, but are under the control of the regional director. In addition to the thirteen CIPs and CISs, which perform the role of CPs, there are thirty-eight dedictated local stations, distributed across the main towns and cities of Luxembourg. Eight of these dedicated CPs are in Luxembourg City, in addition to the CIP.
A special police division at Luxembourg – Findel Airport is directly responsible for border control.[2]
The regional police forces are also directly responsible for policing the roads, criminal investigation, and providing aid to victims of crime.
| CIP | CIS | Communes | Population (As of 2005[update]) | Area (km²) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Capellen | |||||
Capellen | Bertrange, Clemency, Dippach, Garnich, Habscht, Kehlen, Koerich, Kopstal, Mamer, Steinfort, Strassen | 43,134 | 208.17 | ||
Diekirch | |||||
Diekirch | Bettendorf, Bourscheid, Colmar-Berg, Consthum, Diekirch, Ermsdorf, Erpeldange, Ettelbruck, Feulen, Hoscheid, Medernach, Mertzig, Putscheid, Reisdorf, Schieren, Tandel, Vianden | 33,090 | 320.71 | ||
Troisvierges | Clervaux, Heinerscheid, Hosingen, Munshausen, Troisvierges, Weiswampach, Wincrange | 12,625 | 316.80 | ||
Wiltz | Boulaide, Esch-sur-Sûre, Goesdorf, Heiderscheid, Kiischpelt, Lac de la Haute-Sûre, Neunhausen, Wiltz, Winseler | 12,460 | 264.55 | ||
Esch-sur-Alzette | |||||
Differdange | Bascharage, Differdange, Pétange, Sanem | 54,459 | 77.67 | ||
Dudelange | Bettembourg, Dudelange, Frisange, Roeser, Weiler-la-Tour | 36,104 | 102.17 | ||
Esch-sur-Alzette | Esch-sur-Alzette, Kayl, Leudelange, Mondercange, Reckange-sur-Mess, Rumelange, Schifflange | 57,824 | 99.14 | ||
Grevenmacher | |||||
Echternach | Beaufort, Bech, Berdorf, Consdorf, Echternach, Junglinster, Rosport-Mompach, Waldbillig | 20,499 | 240.92 | ||
Grevenmacher | Betzdorf, Biwer, Flaxweiler, Grevenmacher, Lenningen, Manternach, Mertert, Niederanven, Schuttrange, Stadtbredimus, Wormeldange | 28,287 | 243.97 | ||
Remich | Bous, Burmerange, Contern, Dalheim, Mondorf-les-Bains, Remerschen, Remich, Sandweiler, Waldbredimus, Wellenstein | 20,605 | 125.63 | ||
Luxembourg City | |||||
Luxembourg City | Hesperange, Luxembourg, Walferdange | 94,552 | 85.74 | ||
Mersch | |||||
Mersch | Bissen, Fischbach, Heffingen, Helperknapp, Larochette, Lintgen, Lorentzweiler, Mersch, Nommern, Steinsel | 26,886 | 233.40 | ||
Redange | Beckerich, Ell, Grosbous, Préizerdaul, Rambrouch, Redange, Saeul, Useldange, Vichten, Wahl | 14,499 | 267.49 | ||
| Total | 455,024 | 2,586 | |||
Important: On June 22nd 2015, the government of Luxembourg announced a complete overhaul of that organization structure. As a consequence, this chapter has to be revised, once the new structure will be in place.
Director-General
The head of the Grand Ducal Police is the Director-General. There have been four Directors-General since the creation of the Grand Ducal Police in 2000.
| Name | Start | End |
|---|---|---|
| Charles Bourg | 2000 | 2001 |
| Pierre Reuland | 2001 | 2008 |
| Romain Nettgen | 2008 | 2015 |
| Philippe Schrantz | 2015 | Present day |
Emergencies
It is either the CISs or the CIPs that one contacts in the event of an emergency, as they are the only police stations that are open 24/7. The emergency telephone number for the police is 113, as opposed to 112 for all other emergency services.
Footnotes
^ ab "Mémorial A, 1999, No. 87" (PDF) (in French). Service central de législation. Retrieved 2006-08-28..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ List of national services responsible for border control
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Police grand-ducale. |
- Grand Ducal Police official website
- Musée International d'Effets de Gendarmerie et Police Luxembourg website
