Eclipse (horse)
- For the American thoroughbred racehorse born 1814 see American Eclipse (racehorse).
| Eclipse | |
|---|---|
 Eclipse (by George Stubbs) | |
| Sire | Marske |
| Grandsire | Squirt |
| Dam | Spilletta |
| Damsire | Regulus |
| Sex | Stallion |
| Foaled | 1 April 1764 |
| Country | Great Britain |
| Colour | Chestnut |
| Breeder | Duke of Cumberland |
| Owner | William Wildman Dennis O'Kelly |
| Trainer | Sullivan |
| Record | 18 starts, 18 wins (plus 7 heats)[1] |
| Earnings | 2,149 guineas |
| Major wins | |
| Winchester King's Plate (1769) Salisbury King's Plate (1769) Canterbury King's Plate (1769) Lewes King's Plate (1769) Lichfield King's Plate (1769) Match race against Bucephalus (1770) Newmarket First Spring King's Plate (1770) Guilford King's Plate (1770) Nottingham King's Plate (1770) York King's Plate (1770) 6yo+ Great Subscription Purse (1770) Lincoln Heath King's Plate (1770) Newmarket October King's Plate (1770) | |
| Honours | |
Eclipse Stakes at Sandown Park (GB) Prix Eclipse at Maisons-Laffitte (France) The Eclipse Awards (USA) | |
| Last updated on 29 October 2012 | |
Eclipse (1 April 1764 – 26 February 1789) was an undefeated 18th-century British Thoroughbred racehorse who won 18 races, including 11 King's Plates. After retiring from racing he became a very successful sire and today appears in the pedigree of most modern Thoroughbreds.
Contents
1 Breeding
2 Racing career
3 Race record
4 Stud record
4.1 Notable progeny
5 Death
6 Honours and analysis
7 Pedigree
8 See also
9 References
10 External links
Breeding
Eclipse was foaled during and named after the solar eclipse of 1 April 1764, at the Cranbourne Lodge stud of his breeder, Prince William Augustus, Duke of Cumberland.[2] It was at this stud that his sire, the Jockey Club Plate winner Marske (by Squirt from The Ruby Mare) stood. His dam, Spilletta (foaled 1749), was by Regulus, who was by the Godolphin Arabian. Eclipse's male-line great-grandsire was Bartlett's Childers, and his male-line great-great-grandsire was Darley Arabian. Eclipse was a brother to the successful broodmare Proserpine. They were inbred to Snake in the fourth generation (4m x 4f) of their pedigree. After the death of Prince William in 1765, Eclipse was sold for 75 guineas to a sheep dealer from Smithfield, William Wildman.
Eclipse was a bright chestnut with a narrow blaze running down his face. He had a white stocking on his right hind leg. Eclipse was a big horse for his time, just over 16 hands (64 inches, 163 cm), and was an inch higher at the rump than at the withers. He was strong, sound and fast. He was sometimes criticized for having a large, unattractive head. His difficult temperament was well documented, and might have led to him being gelded.[3] Instead he was turned over to a rough-rider, who worked him hard all day, and at night as well on poaching expeditions if the stories are to be believed. This treatment, rather than souring his disposition, settled Eclipse enough to allow him to be raced, although his jockeys never attempted to hold him.[4]
Racing career
Prior to Eclipse's first start at the age of five, a trial was arranged at Epsom (although the location has also been given as Mickleham[5]). Bookmakers, trying to verify if rumours about the horse were true, showed up but were too late — the trial had already been run. On their way home though, they encountered an old woman who told them she had seen a horse with a white leg being chased by another, whom she did not think would catch the horse with the white leg, even if he pursued him to the end of the world. Accordingly, when Eclipse started in his first race on May 3 1769, a £50 Plate for horses who had never won, he was 4/1 on favourite.[5] The race consisted of three heats of four miles each. Eclipse won easily.[6]
After his second victory in a race in May 1769, Dennis O'Kelly purchased Eclipse in two stages. (50 percent in June 1769 for 650 guineas, 50 percent in April 1770 for 1,100 guineas).[7] Supposedly, at this time O'Kelly used the famous phrase "Eclipse first and the rest nowhere," before making his bets for this race, although some sources[5] have him saying this for the second heat of the horse's debut. At that time, a horse that was more than 240 yards behind the lead was said to be nowhere. His jockey was John Oakley, supposedly the only jockey who could handle Eclipse's temperamental manner and running style of holding his nose very close to the ground. Eclipse won the race and covered O'Kelly's bet.[7]
His toughest challenge was a match race versus the highly regarded Bucephalus in April 1770. Bucephalus was game, but Eclipse was the easy winner.[6] In August, he took on top class horses Tortoise and Bellario in the Great Subscription Purse at York, but at odds of 20/1 on, routed both of them, being over a furlong in front after two miles, and winning in a canter.[5]
Eclipse won 18 races, including 11 King's Plates, supposedly without ever being fully extended and proving far superior to all competition.[7] During his racing career, Eclipse ran over 63 miles and walked 1,400 miles to race meetings across England.[1]
Eclipse is still remembered in the phrase "Eclipse first and the rest nowhere", snowcloned as "[name of competitor] first and the rest nowhere," referring to any dominating victory. This phrase is occasionally seen in American print media (most often in newspaper sport sections) but is more common in Britain.
He is attested to have covered 83 feet per second at top speed, and covered 25 feet in a single stride.[4]
Race record
| Date | Race name[4] | Distance | Course | Prize | Odds | Runners | Place | Runner-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3 May 1769 | £50 Race | 4 mile heats | Epsom Downs | 050 £50 | 0.25 1/4 | 5 | 1 | Gower |
29 May 1769 | £50 Plate | 2 mile heats | Ascot | 050 £50 | 0.125 1/8 | 2 | 1 | Crême de Barbade |
13 June 1769 | King's Plate | 4 mile heats | Winchester | 105100 gns | 1.25 5/4 | 5 | 1 | Turner's Slouch |
15 June 1769 | 50 Guinea Plate | Winchester | 05350 gns | N/A | 1 | 1 | Walkover | |
28 June 1769 | King's Plate | Salisbury | 105100 gns | N/A | 1 | 1 | Walkover | |
29 June 1769 | City Silver Bowl | 4 mile heats | Salisbury | 03130 gns | 0.1 1/10 | 3 | 1 | Sulphur |
25 July 1769 | King's Plate | Canterbury | 105100 gns | N/A | 1 | 1 | Walkover | |
27 July 1769 | King's Plate | 4 miles | Lewes | 105100 gns | 0.1 1/10 | 2 | 1 | Kingston |
19 September 1769 | King's Plate | 3 miles | Lichfield | 0.05 1/20 | 2 | 1 | Tardy | |
17 April 1770 | Match race | Newmarket | 0.67 4/6 | 2 | 1 | Bucephalus | ||
19 April 1770 | King's Plate | 3.5 mile heats | Newmarket | 420400 gns | 0.1 1/10 | 4 | 1 | Diana |
5 June 1770 | King's Plate | Guildford | N/A | 1 | 1 | Walkover | ||
3 July 1770 | King's Plate | Nottingham | N/A | 1 | 1 | Walkover | ||
20 August 1770 | King's Plate | York | N/A | 1 | 1 | Walkover | ||
23 August 1770 | Subscription Purse | 4 | York | 319£319 | 0.05 1/20 | 3 | 1 | Tortoise |
3 September 1770 | King's Plate | Lincoln Heath | 105100 gns | N/A | 1 | 1 | Walkover | |
3 October 1770 | 150 Guineas Race | Newmarket | 157150 gns | 0.014 1/70 | 2 | 1 | Corsican | |
4 October 1770 | King's Plate | Newmarket | N/A | 1 | 1 | Walkover |
In ten of the King's Plates, Eclipse carried 12 st, or 168 pounds, the highest weight (by one pound) that was carried by a winner in England up to 1840.[4]
Stud record
In 1771, Eclipse was retired to stud after a racing career of about 17 months due to lack of competition as nobody was betting on rival horses. Initially he stood at O'Kelly's Clay Hill Stud, near Epsom (Surrey), for a fee of 10 guineas which rose rapidly to 25 and then to 50 guineas a mare. During 1788, he was relocated to Cannons Stud, Edgware (Middlesex).[7]
Overall, Eclipse sired 344 winners of more than ₤158,000[8] (although the number varies with different reports, ranging from 325 to 400).[7]
Notable progeny
s = stallion, m = mare
Foaled | Name | Sex | Major Wins |
| 1772 | Planet | s | Jockey Club Plate, Weights and Scales Plate, 1200 Guineas Stakes |
| 1773 | Potoooooooo (Pot-8-Os) | s | 1200 Guineas Stakes, Clermont Cup (x3), Jockey Club Plate (x3), Newmarket Whip (x2), Craven Stakes[9] |
| 1774 | Jupiter | s | 100 guineas sweep at Newmarket[10] |
| 1774 | Satellite | s | Guildford King's Plate, Winchester King's Plate[11] |
| 1775 | King Fergus | s | 500 guineas sweep at Bath[12] |
| 1778 | Joe Andrews | s | Stand Plate at York[2] |
| 1778 | Mercury | s | Lewes King's Plate[13] |
| 1778 | Young Eclipse | s | Epsom Derby[2] |
| 1780 | Dungannon | s | Craven Stakes[14] |
| 1780 | Saltram | s | Epsom Derby[2] |
| 1780 | Volunteer | s | 1200 Guineas Stakes, Cumberland Subscription Stakes[15] |
| 1781 | Serjeant | s | Epsom Derby,[2]1200 Guineas Stakes |
| 1782 | Alexander | s | Ran at Newmarket in the late 1780s[16] |
| 1784 | Annette | m | Epsom Oaks[2] |
| 1784 | Don Quixote | s | |
| 1784 | Pegasus | s | Macaroni Stakes[17] |
Eclipse's daughters include Horatia, one of only twelve mares to produce two Derby winners: Archduke and Paris.[6] She also produced two-time Doncaster Cup winner Stamford. Other daughters of Eclipse produced Derby winners John Bull and Skyscraper, and St. Leger winners Tartar, Remembrancer and Phoenomenon. Chanticleer, Haphazard, and Weasel are also noted as important runners out of Eclipse mares.[3][18]
Eclipse was never the leading sire in Great Britain and Ireland, although he finished in second place 11 times, usually behind Herod. A book published in 1970 stated that the Royal Veterinary College had determined that nearly 80% of Thoroughbred racehorses had Eclipse in their pedigree.[1] That percentage has naturally increased with time and the inevitable inbreeding in the Thoroughbred population. More recently it has been estimated that Eclipse is not only somewhere in the pedigree, but a tail-male ancestor of "95pc of contemporary thoroughbreds"[19] or of "nearly every living thoroughbred."[2]
This modern dominance comes mainly through a sire line established by Potoooooooo, although King Fergus would also found another successful branch leading to Ribot.[20] Potoooooooo's grandson Waxy would lead the sire list in 1811, and Waxy's grandson Birdcatcher in turn led the sire list in 1852 and 1856. Birdcatcher's grandson Stockwell outdid them both, becoming leading sire seven times. Stockwell's grandson Bend Or founded a line that led four generations later to Phalaris[21] The Phalaris line has several branches, notably through Nearco and Native Dancer.
In Great Britain and Ireland, the Eclipse sire line includes modern leading sires such as Sadler's Wells, Danehill and Galileo. In North America, leading sires in his line include Bold Ruler (sire of Secretariat), Mr. Prospector (ancestor of American Pharoah), Danzig, Storm Cat, A.P. Indy, Giant's Causeway and Tapit. In Japan, Eclipse's sire line includes leading sires Sunday Silence, King Kamehameha and Deep Impact, while in Australia leading sires from his line include Redoute's Choice, Encosta De Lago and Fastnet Rock.
Death
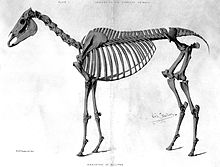
Skeleton of Eclipse
Eclipse died due to an attack of colic on 27 February 1789, at the age of 24. His skeleton is now housed at the Royal Veterinary College, Hertfordshire, in the Learning Resource Centre named after him, although it cannot be said for certain whether all the bones displayed are really from Eclipse.[22] His hooves were made into inkstands, although the fact that there are at least five Eclipse-hoof inkstands casts some doubt on the authenticity of some. Hairs from his tail have also been used for decorations.[23]
A necropsy on Eclipse found that he had an abnormally large heart (weighing 14 pounds (6.4 kg). This trait has been referred to in the context of thoroughbreds as the "X-Factor" Theory.[24] While the theory has yet to be proven, it has gained popularity due to the large hearts seen occasionally in his descendants, including Secretariat and Phar Lap.
Honours and analysis
The Eclipse Awards are American Thoroughbred horse-racing awards named after Eclipse. They honour the champions of the sport, and are sponsored by the National Thoroughbred Racing Association (NTRA), Daily Racing Form and the National Turf Writers Association, who select all finalists at the end of the year. The most prestigious of these Awards is the Eclipse Award for Horse of the Year title.
The Eclipse Stakes is a Group 1 flat race in the United Kingdom for three-year-olds and older run over a distance of 1¼ miles and 7 yards (2,018 metres) at Sandown Park.
Eclipse Press is the book-publishing division of Blood-Horse Publications, an international publishing house for top Thoroughbred and general equine magazines, books, videos, CD-ROMs and annual references.
Sheffield-based Eclipse tools, now part of Spear & Jackson, took their name and their Eclipse first... slogan in 1909 from the horse.
The life story of Eclipse inspired the novel O'Kelly's Eclipse by screenwriter Arthur Weiss.
Nicholas Clee's Eclipse: The Story of the Rogue, the Madam and the Horse That Changed Racing[19] is a biography of Eclipse and of the people connected to him, among them the gambler Dennis O'Kelly and the brothel madam Charlotte Hayes. Other biographies of Eclipse include Michael Church's Eclipse: The Horse, The Race, The Awards (2000), and Theodore Cook's 1907 book Eclipse and O'Kelly.
Contrary to popular belief, the Mitsubishi Eclipse was named for the racehorse, and not for the natural phenomenon.[25]
Pedigree
At the time of Eclipse's birth, stud records were maintained by the individual breeder with no central authority. Record-keeping was somewhat haphazard, compounded by spelling and transcription errors, and the fact that the names of mares were often not recorded. In 1791, James Weatherby and William Sydney Towers pieced together the General Stud Book, which is the source of the pedigree shown below. However, there are still several debated entries of interest to pedigree experts. Details of the issues can be found in Appendix 2 of Nicholas Clee's book on Eclipse. The most notable issues are summarized below.[26]
According to all official records, Eclipse's sire was Marske (written as 'Mask' in a 1764 entry in the Royal Stud Book). Marske was a moderately successful racehorse who had little early success in the breeding shed. His stud fee at the time of Eclipse's conception was only half a guinea, though it subsequently grew to 30 guineas. During Eclipse's lifetime however, it was rumoured that his real sire was Shakespeare, who was a somewhat better racehorse than Marske and was said to resemble Eclipse more closely. According to a contemporary source, Eclipse's dam was covered in 1763 first by Shakespeare and later by Marske, and paternity was based on Eclipse's foaling date corresponding to the date of the second breeding session. Since both Marske and Shakespeare were great-grandsons of the Darley Arabian, Eclipse would still descend from that stallion.[26]
Eclipse's dam was Spilletta, who is shown as a bay in the General Stud Book but recorded as a chestnut in the personal records of her second owner, the Duke of Ancaster. There is again confusion over her breeding: The General Stud Book shows her sire as the undefeated Regulus (by the Godolphin Arabian) but a 1754 racing calendar shows her sire as Sedbury (by the Byerley Turk). Spilletta's dam was Mother Western, whose paternity is subject to similar confusion between Scarborough Colt and Easby Snake.[26] Spilletta raced only once, finishing last in a field of three. In her first eight years as a broodmare, Spilletta produced only one live foal. In 1760, she was bred to Markse for the first time with no issue. Three years later, they were mated again: Eclipse was the result.[27]
| Sire Marske (GB) br. 1750 | Squirt ch. 1732 | Bartlett's Childers b. 1716 | Darley Arabian b. c1700 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Betty Leedes | |||
Sister to Old Country Wench | Snake* | ||
| Grey Wilkes | |||
| The Ruby Mare | Blacklegs | Hutton's Bay Turk | |
Coneyskins mare | |||
Bay Bolton mare | Bay Bolton | ||
Fox Cub mare | |||
| Dam Spilletta (GB) b. 1749 | Regulus ch. 1739 | Godolphin Arabian b. c.1724 | (unknown) |
(unknown) | |||
| Grey Robinson | Bald Galloway | ||
Sister to Old Country Wench | |||
| Mother Western | Easby Snake | Snake* | |
Akaster Turk mare | |||
Old Montagu mare | Old Montagu | ||
Hautboy mare (Family: 12)[28] |
Note: b. = Bay, ch. = Chestnut, br. = Brown
* Eclipse was inbred 4 × 4 to Snake. This means that the stallion appears twice in the fourth generation of his pedigree.
See also
- List of leading Thoroughbred racehorses
References
^ abc Ahnert, Rainer L. (editor in chief), “Thoroughbred Breeding of the World”, Pozdun Publishing, Germany, 1970
^ abcdefg Thoroughbred Bloodlines: Eclipse Retrieved on 2011-08-21
^ ab Peters, Anne. "Eclipse". www.tbheritage.com. Retrieved 18 June 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcd Whyte, James Christie (1840). History of the British turf, from the earliest period to the present day, Volume I. London: H. Colburn. p. 130. Retrieved 1 May 2013.
^ abcd Barrett, Norman, ed. (1995). The Daily Telegraph Chronicle of Horse Racing. Enfield, Middlesex: Guinness Publishing. p. 8.
^ abc Byles, Tony (14 January 2015). 101 Interesting Facts on the History of Horse Racing (Kindle ed.). Apex Publishing. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
^ abcde Montgomery, E.S, “The Thoroughbred”, Arco, New York, 1973
ISBN 0-668-02824-6
^ Barrie, Douglas M., The Australian Bloodhorse, Angus & Robertson, Sydney, 1956
^ "Pot8os". www.bloodlines.net. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "Jupiter". www.bloodlines.net. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "Satellite". www.bloodlines.net. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "King Fergus". www.bloodlines.net. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "Thoroughbred Foundation Sires – Mercury". www.tbheritage.com. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "Dungannon". www.bloodlines.net. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "Volunteer". www.bloodlines.net. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "Thoroughbred Foundation Sires – Alexander". www.tbheritage.com. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ "Thoroughbred Foundation Sires – P". www.tbheritage.com. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ Morris, Simon; Tesio Power 2000 – Stallions of the World, Syntax Software
^ ab Clee, Nicholas (2010). Eclipse: The Story of the Rogue, the Madam and the Horse That Changed Racing. London: Black Swan. ISBN 978-0-552-77442-0.
^ "St. Simon Sire Line". www.bloodlines.net.
^ "Phalaris Sire Line". www.bloodlines.net. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
^ Bower, M. A.; Campana, M. G.; Nisbet, R. E. R.; Weller, R.; Whitten, M.; Edwards, C. J.; Stock, F.; Barrett, E.; O'connell, T. C. (2012-10-01). "Truth in the Bones: Resolving the Identity of the Founding Elite Thoroughbred Racehorses". Archaeometry. 54 (5): 916–925. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4754.2012.00666.x. ISSN 1475-4754.
^ TB Heritage: Eclipse Retrieved on 2009-8-7
^ "The X-Factor: Heart of the Matter". Retrieved 3 May 2013.
^ "MITSUBISHI Eclipse (1990–1994)". autoevolution. Retrieved 18 June 2016.
^ abc Clee, Nicholas (2012). "Appendix 2". Eclipse. New York: Overlook Pr. pp. 298–307. ISBN 978-1-4683-0333-9.
^ Clee, Nicholas (2012). Eclipse. New York: Overlook Pr. pp. 48–9. ISBN 978-1-4683-0333-9.
^ Thoroughbred Bloodlines: Lister's Turk Retrieved 2011-08-21
External links
- Science News – Why Was The Racehorse Eclipse So Good?
- BBC: DNA study of 'greatest racehorse'
- BBC: 'Averageness' key to great racehorses
Mayor Jefe de Raza : Eclipse (in Spanish)