Schools of Buddhism
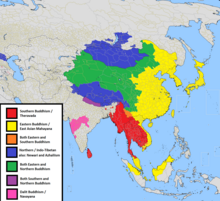
Map showing the three major Buddhist divisions
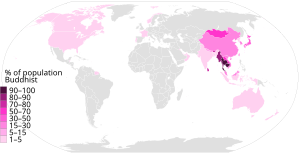
Percentage of Buddhists by country, according to the Pew Research Center.
| Part of a series on |
| Buddhism |
|---|
 |
History
|
|
Buddhist texts
|
Practices
|
Nirvāṇa
|
Traditions
|
Buddhism by country
|
|
The Schools of Buddhism are the various institutional and doctrinal divisions of Buddhism that have existed from ancient times up to the present. The classification and nature of various doctrinal, philosophical or cultural facets of the schools of Buddhism is vague and has been interpreted in many different ways, often due to the sheer number (perhaps thousands) of different sects, subsects, movements, etc. that have made up or currently make up the whole of Buddhist traditions. The sectarian and conceptual divisions of Buddhist thought are part of the modern framework of Buddhist studies, as well as comparative religion in Asia.
From a largely English-language standpoint, and to some extent in most of Western academia, Buddhism is separated into two groups at its foundation: Theravāda, literally "the Teaching of the Elders" or "the Ancient Teaching," and Mahāyāna, literally the "Great Vehicle." The most common classification among scholars is threefold, with Mahāyāna itself split between the traditional Mahāyāna teachings, and the Vajrayāna teachings which emphasize esotericism.
Contents
1 Classifications
2 Terminology
3 Early schools
3.1 Twenty sects
3.2 Influences on East Asian schools
4 Theravāda subschools
5 Mahāyāna schools
6 Esoteric schools
7 New Buddhist movements
8 See also
9 References
10 Further reading
11 External links
Classifications
The Macmillan Encyclopedia of Religion distinguishes three types of classification of Buddhism, separated into "Movements", "Nikāyas" and "Doctrinal schools":[clarification needed]
- Schools:
Theravada, primarily in South Asia and Southeast Asia.
Mahāyāna, primarily in East Asia.
Vajrayāna, primarily in Tibet, Bhutan, Mongolia and the Russian republic of Kalmykia.
Nikāyas, or monastic fraternities, three of which survive at the present day:
Theravāda, in Southeast Asia and South Asia
Dharmaguptaka, in China, Korea and Vietnam
Mūlasarvāstivāda, in the Tibetan tradition
- Doctrinal schools
- Svatantrika & Prasaṅgika
Terminology
The terminology for the major divisions of Buddhism can be confusing, as Buddhism is variously divided by scholars and practitioners according to geographic, historical, and philosophical criteria, with different terms often being used in different contexts. The following terms may be encountered in descriptions of the major Buddhist divisions:
- "Conservative Buddhism"
- an alternative name for the early Buddhist schools.
- "Early Buddhist schools"
- the schools into which Buddhism became divided in its first few centuries; only one of these survives as an independent school, Theravāda
- "East Asian Buddhism"
- a term used by scholars[1] to cover the Buddhist traditions of Japan, Korea, and most of China and Southeast Asia
- "Eastern Buddhism"
- an alternative name used by some scholars[2][page needed] for East Asian Buddhism; also sometimes used to refer to all traditional forms of Buddhism, as distinct from Western(ized) forms.
- "Ekayāna (one yana)
- Mahayana texts such as the Lotus Sutra and the Avatamsaka Sutra sought to unite all the different teachings into a single great way. These texts serve as the inspiration for using the term Ekayāna in the sense of "one vehicle". This "one vehicle" became a key aspect of the doctrines and practices of Tiantai and Tendai Buddhist sects, which subsequently influenced Chán and Zen doctrines and practices. In Japan, the one-vehicle teaching of the Lotus Sutra also inspired the formation of the Nichiren sect.
- "Esoteric Buddhism"
- usually considered synonymous with "Vajrayāna".[3] Some scholars have applied the term to certain practices found within the Theravāda, particularly in Cambodia.[4][page needed]
- "Hīnayāna"
- literally meaning "lesser vehicle." It is considered a controversial term when applied by the Mahāyāna to mistakenly refer to the Theravāda school, and as such is widely viewed as condescending and pejorative.[5] Moreover, Hīnayāna refers to the now non extant schools with limited set of views, practices and results, prior to the development of the Mahāyāna traditions. The term is currently most often used as a way of describing a stage on the path in Tibetan Buddhism, but is often mistakenly confused with the contemporary Theravāda tradition, which is far more complex, diversified and profound, than the literal and limiting definition attributed to Hīnayāna .[6] Its use in scholarly publications is now also considered controversial.[7]
- "Lamaism"
- an old term, still sometimes used, synonymous with Tibetan Buddhism; widely considered derogatory.
- "Mahāyāna"
- a movement that emerged from early Buddhist schools, together with its later descendants, East Asian and Tibetan Buddhism. Vajrayāna traditions are sometimes listed separately. The main use of the term in East Asian and Tibetan traditions is in reference to spiritual levels,[8][page needed] regardless of school.
- "Mainstream Buddhism"
- a term used by some scholars for the early Buddhist schools.
- "Mantrayāna"
- usually considered synonymous with "Vajrayāna".[9] The Tendai school in Japan has been described as influenced by Mantrayana.[8][page needed]
- "Newar Buddhism"
- a non-monastic, caste based Buddhism with patrilineal descent and Sanskrit texts.
- "Nikāya Buddhism" or "schools"
- an alternative term for the early Buddhist schools.
- "Non-Mahāyāna"
- an alternative term for the early Buddhist schools.
- "Northern Buddhism"
- an alternative term used by some scholars[2][page needed] for Tibetan Buddhism. Also, an older term still sometimes used to encompass both East Asian and Tibetan traditions. It has even been used to refer to East Asian Buddhism alone, without Tibetan Buddhism.
- "Secret Mantra"
- an alternative rendering of Mantrayāna, a more literal translation of the term used by schools in Tibetan Buddhism when referring to themselves.[10]
- "Sectarian Buddhism"
- an alternative name for the early Buddhist schools.
- "Southeast Asian Buddhism"
- an alternative name used by some scholars[11][page needed] for Theravāda.
- "Southern Buddhism"
- an alternative name used by some scholars[2][page needed] for Theravāda.
- "Śravakayāna"
- an alternative term sometimes used for the early Buddhist schools.
- "Tantrayāna" or "Tantric Buddhism"
- usually considered synonymous with "Vajrayāna".[9] However, one scholar describes the tantra divisions of some editions of the Tibetan scriptures as including Śravakayāna, Mahāyāna and Vajrayāna texts[12] (see Buddhist texts). Some scholars[13][page needed], particularly François Bizot,[14] have used the term "Tantric Theravada" to refer to certain practices found particularly in Cambodia.
- "Theravāda"
- the Buddhism of Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Burma, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia and parts of Vietnam, China, India, and Malaysia. It is the only surviving representative of the historical early Buddhist schools. The term "Theravāda" is also sometimes used to refer to all the early Buddhist schools.[15]
- "Tibetan Buddhism"
- usually understood as including the Buddhism of Tibet, Mongolia, Bhutan and parts of China, India and Russia, which follow the Tibetan tradition.
- "Vajrayāna"
- a movement that developed out of Indian Mahāyāna, together with its later descendants. There is some disagreement on exactly which traditions fall into this category. Tibetan Buddhism is universally recognized as falling under this heading; many also include the Japanese Shingon school. Some scholars[16][page needed] also apply the term to the Korean milgyo tradition, which is not a separate school. One scholar says, "Despite the efforts of generations of Buddhist thinkers, it remains exceedingly difficult to identify precisely what it is that sets the Vajrayana apart."[17]
Early schools

Map of the major geographical centers of Sectarian Buddhist schools in India. Sarvāstivāda (red), Theravāda (orange), Mahāsāṃghika (yellow), Pudgalavāda (green), and Dharmaguptaka (gray).

An image of Gautama Buddha with a swastika, a traditional Buddhist symbol of infinity, on his chest. Ananda, the Buddha's disciple, appears in the background. This statue is from Hsi Lai Temple.
Sthaviravāda
Sarvāstivāda
Kāśyapīya (after 232 BCE)
Mūlasarvāstivāda (third and fourth centuries)
Sautrāntika (between 50 BCE and c. 100 CE)
Vibhajyavāda (prior to 240 BCE; during Aśoka)
Theravāda (c. 240 BCE)
- Theravāda subschools (see below)
Mahīśāsaka (after 232 BCE)
Dharmaguptaka (after 232 BCE)
Pudgalavāda ('Personalist') (c. 280 BCE)
Vatsīputrīya (under Aśoka) later name: Saṃmitīya
- Dharmottarīya
- Bhadrayānīya
- Sannāgarika
Mahāsāṃghika ('Majority', c. 380 BCE)
Ekavyahārikas (under Aśoka)
- Lokottaravāda
Golulika (during Aśoka)
Bahuśrutīya (late third century BCE)
Prajñaptivāda (late third century BCE)
- Cetiyavāda
Caitika (mid-first century BCE)
- Apara Śaila
- Uttara Śaila
Twenty sects
Sthaviravāda split into 11 sects:
- Sarvāstivādin
- Haimavata
- Vatsīputrīya
- Dharmottara
- Bhadrayānīya
- Sammitiya
- Channagirika
- Mahīśāsaka
- Dharmaguptaka
- Kāśyapīya
- Sautrāntika
Sthaviravāda─┬─ Haimavata────────────────────────────────────────────
└─ Sarvāstivādin─┬───────────────────────────────────
├ Vatsīputrīya ─┬────────────────────
│ ├ Dharmottara───────
│ ├ Bhadrayānīya─────
│ ├ Sammitiya────────
│ └ Channagirika─────
├ Mahīśāsaka─┬─────────────────────
│ └ Dharmaguptaka──────
├ Kāśyapīya────────────────────────
└ Sautrāntika──────────────────────
Mahāsāṃghika split into 9 sects:
- Ekavyahārika
- Lokottaravādin
- Kaukkutika
- Bahuśrutīya
- Prajñaptivāda
- Caitika
- Aparaśaila
- Uttaraśaila
Mahasanghika─┬──────────────────────┬─────
├ Ekavyahārika ├ Caitika
├ Lokottaravādin ├ Aparaśaila
├ Kaukkutika └ Uttaraśaila
├ Bahuśrutīya
└ Prajñaptivāda
Influences on East Asian schools
The following later schools used the vinaya of the Dharmaguptaka:
- Chinese Buddhism, especially the Vinaya School
- Korean Buddhism, especially Gyeyul
- Vietnamese Buddhism
- Japanese Ritsu
The following involve philosophical influence:
- The Japanese Jojitsu is considered by some an offshoot of Sautrāntika; others consider it to be derived from Bahuśrutīya.
- The Chinese/Japanese Kusha school is considered an offshoot of Sarvāstivāda, influenced by Vasubandhu.
Theravāda subschools
The different schools in Theravāda often emphasize different aspects (or parts) of the Pāli canon and the later commentaries, or differ in the focus on and recommended way of practice. There are also significant differences in strictness or interpretation of the vinaya.
Bangladesh:
- Sangharaj Nikaya
- Mahasthabir Nikaya
Burma:
Thudhamma Nikaya
Vipassanā tradition of Mahasi Sayadaw and disciples
- Shwegyin Nikaya
Dvaya Nikaya or Dvara Nikaya (see Mendelson, Sangha and State in Burma, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York, 1975)- Hngettwin Nikaya
Sri Lanka:
Siam Nikaya
Waturawila (or Mahavihara Vamshika Shyamopali Vanavasa Nikaya)
Amarapura Nikaya
Kanduboda (or Swejin Nikaya)
Tapovana (or Kalyanavamsa)
Ramañña Nikaya
Sri Kalyani Yogasrama Samstha (or ‘Galduwa Tradition’)- Delduwa
- forest nikaya
Thailand
Maha Nikaya
- Dhammakaya Movement
Mahasati meditation (mindfulness meditation)
Thammayut Nikaya
Thai Forest Tradition
- Tradition of Ajahn Chah
- Tradition of Ajahn Chah
- Vipassana movement
- Tantric Theravada
Mahāyāna schools

Thousand-armed Avalokiteśvara Bodhisattva. Guanyin Nunnery, Anhui, China
Indian Buddhism
Mādhyamaka
- Prāsangika
- Svātantrika
- Yogācāra
Chinese Buddhism
Vinaya school[18]
Jingtu (Pure Land)
Satyasiddhi (Historical)
Abhidharmakośa (Historical)
Daśabhūmikā (absorbed into Huayan)- Tiantai
Huayan (Avataṃsaka)
Chan (Zen)
Tangmi (Esoteric)
Sanlun (Mādhyamaka)
Weishi (Yogācāra)
Korean Buddhism
Tongbulgyo (Interpenetrated Buddhism - including Jeongto, or Pure Land)
Gyeyul (Vinaya school)
Cheontae (Tiantai)
Hwaeom (Avataṃsaka)
Seon (Zen)
Jingak (Esoteric)
Samnon (Mādhyamaka)
Beopsang (Yogācāra)
Yeolban (Nirvana school)
Wonbulgyo (Korean Reformed Buddhism)
Vietnamese Buddhism
Tịnh Độ (Pure Land)
Thiền (Zen)
Trúc Lâm (Syncretic)
Unified Buddhist Church (Engaged Buddhism)
Hòa Hảo (Reformist)
Japanese Buddhism
Pure Land
- Jōdo-shū
- Jōdo Shinshū
- Ji-shū
- Yūzū-nembutsu-shū
Risshū school (Vinaya school)
Jojitsu (Satyasiddhi - historical)
Kusha (Abhidharmakośa - historical)
Sanron (Mādhyamaka - historical)
Hossō (Yogācāra)
Kegon (Avatamsaka)
Japanese esoteric Buddhism
Tendai (Tiantai)
Shingon
- Shinnyo-en
Shugendo (Syncretic)
Zen
- Rinzai
- Sōtō
- Ōbaku
Fuke-shū (Historical)
Nichiren Buddhism
- Nichiren Shū
- Honmon Butsuryū-shū
- Kempon Hokke
- Nichiren Shōshū
Esoteric schools
Subcategorised according to predecessors
Tibetan Buddhism
- Nyingma
New Bön (synthesis of Yungdrung Bön and Nyingmapa)
Kadam (Historical)
Gelug
- New Kadampa Tradition
Sakya
- Ngor-pa
- Tsar-pa
- Jonang
Kagyu:
- Shangpa Kagyu
Marpa Kagyu:
- Rechung Kagyu
Dagpo Kagyu:
Karma Kagyu (or Kamtshang Kagyu)- Tsalpa Kagyu
- Baram Kagyu
Pagtru Kagyu (or Phagmo Drugpa Kagyu):
- Taklung Kagyu
- Trophu Kagyu
- Drukpa Kagyu
- Martsang Kagyu
- Yerpa Kagyu
- Yazang Kagyu
- Shugseb Kagyu
- Drikung Kagyu
Rime movement (ecumenical movement)
- Newar Buddhism
Tangmi Buddhism
- Japanese Mikkyo
Shingon
- Shinnyo-en
Tendai (derived from Tiantai but added tantric practices)
Shugendo (Syncretized with Shinto, Taoism, and shamanism)
- Japanese Mikkyo
New Buddhist movements
- Bodhi Shrawan Dharma Shangha Nepal
- Dalit Buddhist movement
- Dhammakaya Movement
- Diamond Way
- Engaged Buddhism
- Kenshōkai
- New Kadampa Tradition
- Nipponzan Myōhōji
- Reiyūkai
- Risshō Kōsei Kai
- Shambhala Buddhism
- Share International
- Shōshinkai
- Sōka Gakkai
- Triratna Buddhist Community
- True Buddha School
- Vipassana movement
- Won Buddhism
See also
- Navayana
- Early Buddhist schools
- Gandhāran Buddhist Texts
- Humanistic Buddhism
- Southern, Eastern and Northern Buddhism
- Perfection of Wisdom School
References
^ B & G, Gethin, R & J, P & K
^ abc Penguin, Harvey
^ Encyclopedia of Religion, Macmillan, New York, volume 2, page 440
^ Indian Insights, Luzac, London, 1997
^ "Hinayana (literally, 'inferior way') is a polemical term, which self-described Mahāyāna (literally, 'great way') Buddhist literature uses to denigrate its opponents", p. 840, MacMillan Library Reference Encyclopedia of Buddhism, 2004
^ Ray, Reginald A (2000) Indestructible Truth: The Living Spirituality of Tibetan Buddhism, p.240
^ "The supposed Mahayana-Hinayana dichotomy is so prevalent in Buddhist literature that it has yet fully to loosen its hold over scholarly representations of the religion", p. 840, MacMillan Library Reference Encyclopedia of Buddhism, 2004
^ ab '
^ ab Harvey, pages 153ff
^ Hopkins, Jeffrey (1985) The Ultimate Deity in Action Tantra and Jung's Warning against Identifying with the Deity Buddhist-Christian Studies, Vol. 5, (1985), pp. 159–172
^ R & J, P & K
^ Skilling, Mahasutras, volume II, Parts I & II, 1997, Pali Text Society, Lancaster, page 78
^ Indian Insights, loc. cit.
^ Crosby, Kate( 2000)Tantric Theravada: A bibliographic essay on the writings of François Bizot and others on the yogvacara Tradition. In Contemporary Buddhism, 1:2, 141–198[1]
^ Encyclopedia of Religion, volume 2, Macmillan, New York, 1987, pages 440f; Cambridge Dictionary of Philosophy, sv Buddhism
^ Harvey
^ Lopez, Buddhism in Practice, Princeton University Press, 1995, page 6
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-05-28. Retrieved 2013-07-29.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link) .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}.
Further reading
- Bhikkhu Sujato (2007). Sects and sectarianism: the origins of Buddhist schools, Taipei, Taiwan: Buddha Educational Foundation; revised edidion: Santipada 2012
- Dutt, N. (1998). Buddhist Sects in India. New Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass.
- Coleman, Graham, ed. (1993). A Handbook of Tibetan Culture. Boston: Shambhala Publications, Inc..
ISBN 1-57062-002-4.
Warder, A.K. (1970). Indian Buddhism. Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass.
External links
The Sects of the Buddhists by T. W. Rhys Davids, in the Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, 1891. pp. 409–422