Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a layer inside a planetary body bounded below by a core and above by a crust. Mantles are either made of rock or ices, and are generally the largest and most massive layer of the planetary body. Mantles are characteristic of planetary bodies that have undergone differentiation by density. The mantle is bounded on the bottom by the planetary core and on top by the crust. In addition to the Earth, the other terrestrial planets, a number of asteroids, and moons have mantles.
Contents
1 Earth's mantle
1.1 Structure
1.1.1 Rheological structure
1.1.2 Seismic structure
1.1.3 Mineralogical structure
1.2 Characteristics
1.3 Temperature
1.4 Movement
1.5 Exploration
2 Other planetary mantles
3 See also
4 References
5 Further reading
6 External links
Earth's mantle
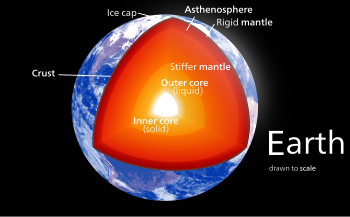
The internal structure of Earth
The interior of Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is divided into layers of different composition. The mantle is a layer between the crust and the outer core. Earth's mantle is a silicate rocky shell with an average thickness of 2,886 kilometres (1,793 mi).[1] The mantle makes up about 84% of Earth's volume.[2] It is predominantly solid but in geological time it behaves as a viscous fluid. The mantle encloses the hot core rich in iron and nickel, which makes up about 15% of Earth's volume.[2] Past episodes of melting and volcanism at the shallower levels of the mantle have produced a thin crust of crystallized melt products near the surface.[3] Information about the structure and composition of the mantle has been obtained from geophysical investigation and from direct geoscientific analyses of Earth mantle-derived xenoliths and mantle that has been exposed by mid-oceanic ridge spreading.
Two main zones are distinguished in the upper mantle: the inner asthenosphere composed of plastic flowing rock of varying thickness, on average about 200 km (120 mi) thick,[4] and the lowermost part of the lithosphere composed of rigid rock about 50 to 120 km (31 to 75 mi) thick.[5] A thin crust, the upper part of the lithosphere, surrounds the mantle and is about 5 to 75 km (3.1 to 46.6 mi) thick.[6] Recent analysis of hydrous ringwoodite from the mantle suggests that there is between one[7] and three[8] times as much water in the transition zone between the lower and upper mantle than in all the world's oceans combined.[9]
In some places under the ocean the mantle is actually exposed on the surface of Earth.[10] There are also a few places on land where mantle rock has been pushed to the surface by tectonic activity, most notably the Tablelands region of Gros Morne National Park in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador and Zabargad Island (St. John's Island) in the Red Sea. (Also Macquarie Island, Saint Peter and Saint Paul Archipelago, Troodos Ophiolite, Lizard Complex, Semail Ophiolite, and other ophiolites)
Structure
Rheological structure
The Earth's mantle is divided into two major rheological layers: the rigid lithosphere comprising the uppermost mantle, and the less viscous asthenosphere, separated by the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. The lithosphere and overlying crust make up tectonic plates, which move over the asthenosphere.
Seismic structure
The Earth's mantle is divided into three major layers defined by sudden changes in seismic velocity:
- the upper mantle (starting at the Moho, or base of the crust around 7 to 35 km (4.3 to 21.7 mi) downward to 410 km (250 mi))[11]
- the transition zone (approximately 410–660 km or 250–410 mi)
- the lower mantle (approximately 660–2,891 km or 410–1,796 mi)
The lower ~200 km of the lower mantle constitutes the D" (D-double-prime) layer, a region with anomalous seismic properties. This region also contains LLSVPs and ULVZs.
Mineralogical structure
The top of the mantle is defined by a sudden increase in seismic velocity, which was first noted by Andrija Mohorovičić in 1909; this boundary is now referred to as the Mohorovičić discontinuity or "Moho".[12][13]
The upper mantle is dominantly peridotite, comprised primarily of variable proportions of the minerals olivine, clinopyroxene, orthopyroxene, and an aluminous phase. The aluminous phase is plagioclase in the uppermost mantle, then spinel, and then garnet below ~100 km. Gradually through the upper mantle, pyroxenes become less stable and transform into majoritic garnet.
At the top of the transition zone, olivine undergoes isochemical phase transitions to wadsleyite and ringwoodite. Unlike nominally anhydrous olivine, these high-pressure olivine polymorphs have a large capacity to store water in their crystal structure. This has led to the hypothesis that the transition zone may host a large quantity of water[14]. At the base of the transition zone, ringwoodite decomposes into bridgmanite (formerly called magnesium silicate perovskite), and ferropericlase. Garnet also becomes unstable at or slightly below the base of the transition zone.
The lower mantle is comprised primarily of bridgmanite and ferropericlase, with minor amounts of calcium perovskite, calcium-ferrite structured oxide, and stishovite. In the lowermost ~200 km of the mantle, bridgmanite isochemically transforms into post-perovskite.
Characteristics
The mantle differs substantially from the crust in its mechanical properties as the direct consequence of the difference in composition (expressed as different mineralogy). The distinction between crust and mantle is based on chemistry, rock types, rheology and seismic characteristics. The crust is a solidification product of mantle derived melts, expressed as various degrees of partial melting products during geologic time. Partial melting of mantle material is believed to cause incompatible elements to separate from the mantle, with less dense material floating upward through pore spaces, cracks, or fissures, that would subsequently cool and solidify at the surface. Typical mantle rocks have a higher magnesium to iron ratio and a smaller proportion of silicon and aluminium than the crust. This behavior is also predicted by experiments that partly melt rocks thought to be representative of Earth's mantle.

Mapping the interior of the Earth with earthquake waves.
Mantle rocks shallower than about 410 km (250 mi) depth consist mostly of olivine, pyroxenes, spinel-structure minerals, and garnet;[15] typical rock types are thought to be peridotite,[15]dunite (olivine-rich peridotite), and eclogite. Between about 400 km (250 mi) and 650 km (400 mi) depth, olivine is not stable and is replaced by high pressure polymorphs with approximately the same composition: one polymorph is wadsleyite (also called beta-spinel type), and the other is ringwoodite (a mineral with the gamma-spinel structure). Below about 650 km (400 mi), all of the minerals of the upper mantle begin to become unstable. The most abundant minerals present, the silicate perovskites, have structures (but not compositions) like that of the mineral perovskite followed by the magnesium/iron oxide ferropericlase.[16] The changes in mineralogy at about 400 and 650 km (250 and 400 mi) yield distinctive signatures in seismic records of the Earth's interior, and like the moho, are readily detected using seismic waves. These changes in mineralogy may influence mantle convection, as they result in density changes and they may absorb or release latent heat as well as depress or elevate the depth of the polymorphic phase transitions for regions of different temperatures. The changes in mineralogy with depth have been investigated by laboratory experiments that duplicate high mantle pressures, such as those using the diamond anvil.[17]
| Element | Amount | | Compound | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
O | 44.8 | | | |
Mg | 22.8 | SiO2 | 46 | |
Si | 21.5 | MgO | 37.8 | |
Fe | 5.8 | FeO | 7.5 | |
Ca | 2.3 | Al2O3 | 4.2 | |
Al | 2.2 | CaO | 3.2 | |
Na | 0.3 | Na2O | 0.4 | |
K | 0.03 | K2O | 0.04 | |
| Sum | 99.7 | Sum | 99.1 |
The inner core is solid, the outer core is liquid, and the mantle solid/plastic. This is because of the relative melting points of the different layers (nickel–iron core, silicate crust and mantle) and the increase in temperature and pressure as depth increases. At the surface both nickel–iron alloys and silicates are sufficiently cool to be solid. In the upper mantle, the silicates are generally solid (localised regions with small amounts of melt exist); however, as the upper mantle is both hot and under relatively little pressure, the rock in the upper mantle has a relatively low viscosity. In contrast, the lower mantle is under tremendous pressure and therefore has a higher viscosity than the upper mantle. The metallic nickel–iron outer core is liquid because of the high temperature, despite the high pressure. As the pressure increases, the nickel–iron inner core becomes solid because the melting point of iron increases dramatically at these high pressures.[20]
Temperature
In the mantle, temperatures range between 500 to 900 °C (932 to 1,652 °F) at the upper boundary with the crust to over 4,000 °C (7,230 °F) at the boundary with the core.[20] The geothermal gradient of the mantle increases rapidly in the thermal boundary layers at the top and bottom of the mantle, and increases gradually through the interior of the mantle.[21] Although the higher temperatures far exceed the melting points of the mantle rocks at the surface (about 1200 °C for representative peridotite), the mantle is almost exclusively solid.[20] The enormous lithostatic pressure exerted on the mantle prevents melting, because the temperature at which melting begins (the solidus) increases with pressure.
Movement

This figure is a snapshot of one time-step in a model of mantle convection. Colors closer to red are hot areas and colors closer to blue are cold areas. In this figure, heat received at the core–mantle boundary results in thermal expansion of the material at the bottom of the model, reducing its density and causing it to send plumes of hot material upwards. Likewise, cooling of material at the surface results in its sinking.
Because of the temperature difference between the Earth's surface and outer core and the ability of the crystalline rocks at high pressure and temperature to undergo slow, creeping, viscous-like deformation over millions of years, there is a convective material circulation in the mantle.[22] Hot material upwells, while cooler (and heavier) material sinks downward. Downward motion of material occurs at convergent plate boundaries called subduction zones. Locations on the surface that lie over plumes are predicted to have high elevation (because of the buoyancy of the hotter, less-dense plume beneath) and to exhibit hot spot volcanism. The volcanism often attributed to deep mantle plumes is alternatively explained by passive extension of the crust, permitting magma to leak to the surface (the "Plate" hypothesis).[23]
The convection of the Earth's mantle is a chaotic process (in the sense of fluid dynamics), which is thought to be an integral part of the motion of plates. Plate motion should not be confused with continental drift which applies purely to the movement of the crustal components of the continents. The movements of the lithosphere and the underlying mantle are coupled since descending lithosphere is an essential component of convection in the mantle. The observed continental drift is a complicated relationship between the forces causing oceanic lithosphere to sink and the movements within Earth's mantle.
Although there is a tendency to larger viscosity at greater depth, this relation is far from linear and shows layers with dramatically decreased viscosity, in particular in the upper mantle and at the boundary with the core.[24] The mantle within about 200 km (120 mi) above the core–mantle boundary appears to have distinctly different seismic properties than the mantle at slightly shallower depths; this unusual mantle region just above the core is called D″ ("D double-prime"), a nomenclature introduced over 50 years ago by the geophysicist Keith Bullen.[25]D″ may consist of material from subducted slabs that descended and came to rest at the core–mantle boundary and/or from a new mineral polymorph discovered in perovskite called post-perovskite.
Earthquakes at shallow depths are a result of stick-slip faulting; however, below about 50 km (31 mi) the hot, high pressure conditions ought to inhibit further seismicity. The mantle is considered to be viscous and incapable of brittle faulting. However, in subduction zones, earthquakes are observed down to 670 km (420 mi). A number of mechanisms have been proposed to explain this phenomenon, including dehydration, thermal runaway, and phase change.
The geothermal gradient can be lowered where cool material from the surface sinks downward, increasing the strength of the surrounding mantle, and allowing earthquakes to occur down to a depth of 400 km (250 mi) and 670 km (420 mi).
The pressure at the bottom of the mantle is ~136 GPa (1.4 million atm).[15] Pressure increases as depth increases, since the material beneath has to support the weight of all the material above it. The entire mantle, however, is thought to deform like a fluid on long timescales, with permanent plastic deformation accommodated by the movement of point, line, and/or planar defects through the solid crystals comprising the mantle. Estimates for the viscosity of the upper mantle range between 1019 and 1024Pa·s, depending on depth,[24] temperature, composition, state of stress, and numerous other factors. Thus, the upper mantle can only flow very slowly. However, when large forces are applied to the uppermost mantle it can become weaker, and this effect is thought to be important in allowing the formation of tectonic plate boundaries.
Exploration
Exploration of the mantle is generally conducted at the seabed rather than on land because of the relative thinness of the oceanic crust as compared to the significantly thicker continental crust.
The first attempt at mantle exploration, known as Project Mohole, was abandoned in 1966 after repeated failures and cost over-runs. The deepest penetration was approximately 180 m (590 ft). In 2005 an oceanic borehole reached 1,416 metres (4,646 ft) below the sea floor from the ocean drilling vessel JOIDES Resolution.
On 5 March 2007, a team of scientists on board the RRS James Cook embarked on a voyage to an area of the Atlantic seafloor where the mantle lies exposed without any crust covering, midway between the Cape Verde Islands and the Caribbean Sea. The exposed site lies approximately three kilometres beneath the ocean surface and covers thousands of square kilometres.[26][27]
A relatively difficult attempt to retrieve samples from the Earth's mantle was scheduled for later in 2007.[28] The Chikyu Hakken mission attempted to use the Japanese vessel Chikyū to drill up to 7,000 m (23,000 ft) below the seabed. This is nearly three times as deep as preceding oceanic drillings.
A novel method of exploring the uppermost few hundred kilometres of the Earth was proposed in 2005, consisting of a small, dense, heat-generating probe which melts its way down through the crust and mantle while its position and progress are tracked by acoustic signals generated in the rocks.[29] The probe consists of an outer sphere of tungsten about one metre in diameter with a cobalt-60 interior acting as a radioactive heat source. It was calculated that such a probe will reach the oceanic Moho in less than 6 months and attain minimum depths of well over 100 km (62 mi) in a few decades beneath both oceanic and continental lithosphere.[30]
Exploration can also be aided through computer simulations of the evolution of the mantle. In 2009, a supercomputer application provided new insight into the distribution of mineral deposits, especially isotopes of iron, from when the mantle developed 4.5 billion years ago.[31]
Other planetary mantles
The terrestrial planets (Earth, Venus, Mars and Mercury), the Moon, two of Jupiter's moons (Io and Europa) and the asteroid Vesta each has a mantle made of silicate rock.[32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39] Interpretation of spacecraft data suggests that at least two other moons of Jupiter (Ganymede and Callisto), as well as Titan and Triton, each have a mantle made of ice or other solid volatile substances[40][41][42][43].
See also
- Core–mantle boundary
- Earth's internal heat budget
- Lehmann discontinuity
- Mantle xenoliths
- Mantle convection
- Mesosphere (mantle)
- Mohorovičić discontinuity
- Numerical modeling (geology)
- Post-perovskite phase transition
- Primitive mantle
References
^ Sorokhtin, O.G.; Chilingarian, G.V.; Sorokhtin, N.O. (2011). Evolution of Earth and its climate birth, life and death of Earth. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Ltd. p. 137. ISBN 9780444537584. Retrieved 29 May 2015..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab
Robertson, Eugene (2007). "The interior of the earth". USGS. Retrieved 2009-01-06.
^
"The structure of the Earth". Moorland School. 2005. Archived from the original on 2007-10-13. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
^ Thompson, Graham R.; Turk, Jonathan (2007). Earth science and the environment (4th ed., International student ed.). Australia: Thomson Brooks/Cole. pp. 133–134. ISBN 9780495112877. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
^ Lithosphere: Schlumberger Oilfield Glossary. Glossary.oilfield.slb.com. Retrieved on 2013-05-11.
^ Crust: Schlumberger Oilfield Glossary. Glossary.oilfield.slb.com. Retrieved on 2013-05-11.
^ "Rare Diamond confirms that Earth's mantle holds an ocean's worth of water". Scientific American. March 12, 2014. Retrieved March 13, 2014.
^ Schmandt, Brandon; Jacobsen, Steven D.; Becker, Thorsten W.; Liu, Zhenxian; Dueker, Kenneth G. (13 June 2014). "Dehydration melting at the top of the lower mantle". Science. 344 (6189): 1265–1268. Bibcode:2014Sci...344.1265S. doi:10.1126/science.1253358. Retrieved 13 June 2014.
^ Bob Yirka (June 8, 2017). "Study suggests mid-mantle holds as much water as Earth's oceans". Phys.org. Retrieved June 8, 2017.
^ Mission to Study Earth's Gaping 'Open Wound'. LiveScience. Retrieved on 2013-05-11.
^ The location of the base of the crust varies from approximately 10 to 70 kilometers. Oceanic crust is generally less than 10 kilometers thick. "Standard" continental crust is around 35 kilometers thick, and the large crustal root under the Tibetan Plateau is approximately 70 kilometers thick.
^ Alden, Andrew (2007). "Today's Mantle: a guided tour". About.com. Retrieved 2007-12-25.
^ "Istria on the Internet – Prominent Istrians – Andrija Mohorovicic". 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-25.
^ Bercovici, David; Karato, Shun-ichiro (2003-09). "Whole-mantle convection and the transition-zone water filter". Nature. 425 (6953): 39–44. doi:10.1038/nature01918. ISSN 0028-0836. Check date values in:|date=(help)
^ abc
Burns, Roger George (1993). Mineralogical Applications of Crystal Field Theory. Cambridge University Press. p. 354. ISBN 0-521-43077-1. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
^ Anderson, Don L. (2007) New Theory of the Earth. Cambridge University Press.
ISBN 978-0-521-84959-3,
ISBN 0-521-84959-4
^
Alden, Andrew. "The Big Squeeze: Into the Mantle". About.com. Retrieved 2007-12-25.
^
mantle@Everything2.com. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
^
Jackson, Ian (1998). The Earth's Mantle - Composition, Structure, and Evolution. Cambridge University Press. pp. 311–378. ISBN 0-521-78566-9.
^ abc
Louie, J. (1996). "Earth's Interior". University of Nevada, Reno. Retrieved 2007-12-24.
^ Turcotte, DL; Schubert, G (2002). "4". Geodynamics (2nd ed.). Cambridge, England, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 136–7. ISBN 978-0-521-66624-4.
^
Alden, Andrew (2007). "Today's Mantle: a guided tour". About.com. Retrieved 2007-12-25.
^ Foulger, G.R. (2010). Plates vs. Plumes: A Geological Controversy. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-6148-0.
^ ab Walzer, Uwe; Hendel, Roland and Baumgardner, John. Mantle Viscosity and the Thickness of the Convective Downwellings. igw.uni-jena.de
^
Alden, Andrew. "The End of D-Double-Prime Time?". About.com. Retrieved 2007-12-25.
^ Than, Ker (2007-03-01). "Scientists to study gash on Atlantic seafloor". Msnbc.com. Retrieved 2008-03-16.A team of scientists will embark on a voyage next week to study an “open wound” on the Atlantic seafloor where the Earth’s deep interior lies exposed without any crust covering.
^ "Earth's Crust Missing In Mid-Atlantic". Science Daily. 2007-03-02. Retrieved 2008-03-16.Cardiff University scientists will shortly set sail (March 5) to investigate a startling discovery in the depths of the Atlantic.
^ "Japan hopes to predict 'Big One' with journey to center of Earth". PhysOrg.com. 2005-12-15. Archived from the original on 2005-12-19. Retrieved 2008-03-16.An ambitious Japanese-led project to dig deeper into the Earth's surface than ever before will be a breakthrough in detecting earthquakes including Tokyo's dreaded "Big One," officials said Thursday.
^ Ojovan M.I., Gibb F.G.F., Poluektov P.P., Emets E.P. 2005. Probing of the interior layers of the Earth with self-sinking capsules. Atomic Energy, 99, 556–562
^ Ojovan M.I., Gibb F.G.F. "Exploring the Earth’s Crust and Mantle Using Self-Descending, Radiation-Heated, Probes and Acoustic Emission Monitoring". Chapter 7. In: Nuclear Waste Research: Siting, Technology and Treatment,
ISBN 978-1-60456-184-5, Editor: Arnold P. Lattefer, Nova Science Publishers, Inc. 2008
^ University of California – Davis (2009-06-15). Super-computer Provides First Glimpse Of Earth's Early Magma Interior. ScienceDaily. Retrieved on 2009-06-16.
^ "Earth Structure". Trinity University, Texas. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
^ Zharkov, V. N. & Zasurskii, I. Ia. (1981). "Distribution of the shearing stresses in the silicate mantle of Venus". Astronomicheskii Vestnik. 15: 11–16. Bibcode:1981AVest..15...11Z.
^ Longhi, John; et al. (1992). "The bulk composition, mineralogy and internal structure of Mars". Mars (A93-27852 09-91). University of Arizona Press, Tucson. pp. 184–208. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
^ "MESSENGER Provides New Look at Mercury's surprising core and landscape curiosities". NASA. 21 March 2012. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
^ "Moon ABCs Fact Sheet" (PDF). NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 September 2015. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
^ NASA (6 October 2000). "Scientists Show Jovian Moon Io's Mantle is Similar to Earth". NASA. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
^ "Frequently Asked Questions about Europa". NASA. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
^ Neumann, W.; et al. (2014). "Differentiation of Vesta: Implications for a shallow magma ocean". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 395: 267–280. arXiv:1402.3103. Bibcode:2014E&PSL.395..267N. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2014.03.033.
^ "Ganymede: In Depth". NASA. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
^ "Callisto: In Depth". NASA. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
^ "Layers of Titan". NASA. 23 February 2012. Retrieved 7 October 2015.
^ "Triton: In Depth". NASA. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
Further reading
Don L. Anderson, Theory of the Earth, Blackwell (1989), is a textbook dealing with the Earth's interior and is now available on the web. Retrieved 2007-12-23.
Jeanloz, Raymond (2000). "Mantle of the Earth". In Haraldur Sigurdsson; Bruce Houghton; Hazel Rymer; John Stix; Steve McNutt. Encyclopedia of Volcanoes. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 41–54. ISBN 978-0-12-643140-7.
- Nixon, Peter H. (1987). Mantle xenoliths: J. Wiley & Sons, 844p., (
ISBN 0-471-91209-3).
Donald L. Turcotte and Gerald Schubert, Geodynamics, Cambridge University Press, Third Edition (2014),
ISBN 978-1-107-00653-9 (Hardback)
ISBN 978-0-521-18623-0 (Paperback)
External links
| The Wikibook Historical Geology has a page on the topic of: Structure of the Earth |
The Biggest Dig: Japan builds a ship to drill to the earth's mantle – Scientific American (September 2005)- Information on the Mohole Project