Jersey City, New Jersey
| Jersey City, New Jersey | |||
|---|---|---|---|
City | |||
City of Jersey City | |||
| |||
Nickname(s): Wall Street West,[1]J.C., Chilltown,[2]Sixth Borough,[3]America's Golden Door[4][5][6][7][8] | |||
Motto(s): "Let Jersey Prosper"[9] "Jersey City, Make It Yours"[10] | |||
 Location in Hudson County and the state of New Jersey | |||
Interactive map of Jersey City | |||
 Jersey City Location in Hudson County Show map of Hudson County, New Jersey  Jersey City Location in New Jersey Show map of New Jersey  Jersey City Location in the United States Show map of the US  Jersey City Location in North America Show map of North America  Jersey City Location on Earth Show map of Earth | |||
Coordinates: 40°42′50″N 74°04′16″W / 40.714°N 74.071°W / 40.714; -74.071Coordinates: 40°42′50″N 74°04′16″W / 40.714°N 74.071°W / 40.714; -74.071[11][12] | |||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| County | |||
| Incorporated | February 22, 1838 | ||
| Government[17] | |||
| • Type | Faulkner Act (Mayor-Council) | ||
| • Body | City Council | ||
| • Mayor | Steven Fulop (term ends December 31, 2021)[13][14] | ||
| • Deputy Mayor | Vacant | ||
| • Business Administrator | Brian Platt[15] | ||
| • Municipal clerk | Robert Byrne[16] | ||
| Area[11] | |||
| • Total | 21.080 sq mi (54.596 km2) | ||
| • Land | 14.794 sq mi (38.316 km2) | ||
| • Water | 6.286 sq mi (16.281 km2) 29.82% | ||
| Area rank | 133rd of 566 in state 1st of 12 in county[11] | ||
| Elevation[18] | 20 ft (6 m) | ||
| Population (2010 Census)[19][20][21] | |||
| • Total | 247,597 | ||
| • Estimate (2017)[22] | 270,753 | ||
| • Rank | 75th in country (as of 2017)[23] 2nd of 566 in state 1st of 12 in county | ||
| • Density | 16,736.6/sq mi (6,462.0/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 10th of 566 in state 6th of 12 in county | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (Eastern (EDT)) | ||
| ZIP codes | 07097, 07302-07308, 07310-07311[24] | ||
| Area code(s) | 201[25] | ||
| FIPS code | 3401736000[11][26][27] | ||
GNIS feature ID | 0885264[11][28] | ||
| Website | www.jerseycitynj.gov | ||
Jersey City is the second-most-populous city in the U.S. state of New Jersey, after Newark.[29] It is the seat of Hudson County as well as the county's largest city.[30] As of 2017, the Census Bureau's Population Estimates Program calculated that Jersey City's population was 270,753,[22] with the largest population increase of any municipality in New Jersey since 2010,[31] an increase of about 9.4% from the 2010 United States Census, when the city's population was at 247,597.[21][32] ranking the city the 75th-most-populous in the nation.[33]
Part of the New York metropolitan area, Jersey City is bounded on the east by the Hudson River and Upper New York Bay and on the west by the Hackensack River and Newark Bay. A port of entry, with 30.7 miles (49.4 km) of waterfront[34] and extensive rail infrastructure and connectivity, the city is an important transportation terminus and distribution and manufacturing center for the Port of New York and New Jersey. Jersey City shares significant mass transit connections with Manhattan.[35][36] Redevelopment of the Jersey City waterfront has made the city one of the largest centers of banking and finance in the United States and has led to the district being nicknamed Wall Street West.[37]
After a peak population of 316,715 measured in the 1930 Census, the city's population saw a half-century-long decline to a low of 223,532 in the 1980 Census. Since then, the city's population has grown, with the 2010 population reflecting an increase of 7,542 (+3.1%) from the 240,055 counted in the 2000 Census, which had in turn increased by 11,518 (+5.0%) from the 228,537 counted in the 1990 Census.[38][39]
Contents
1 History
1.1 Lenape and New Netherland
1.2 19th century
1.3 20th and 21st centuries
2 Geography
2.1 Neighborhoods
2.1.1 Downtown Jersey City
2.1.2 Bergen-Lafayette
2.1.3 The Heights
2.1.4 Journal Square
2.1.5 McGinley Square
2.1.6 Hamilton Park
2.1.7 Greenville
2.2 Climate
3 Demographics
3.1 2010 Census
3.2 2000 Census
3.3 Community diversity
3.3.1 Latin American
3.3.1.1 Puerto Rican
3.3.2 Asian American
3.3.2.1 Indian American
3.3.2.2 Filipino American
3.3.2.3 Chinese American
3.3.2.4 Vietnamese American
3.3.3 European American
3.3.4 African American
3.3.5 Arab American
3.3.6 Muslim American
3.3.7 Same-sex couples
3.3.8 Artists-in-residence
4 Economy
4.1 Wall Street West
4.2 Retail
4.3 Port Jersey
4.4 Other
5 Art and culture
5.1 Notable landmarks
5.2 Museums and libraries
5.3 Hudson County Shakespeare Festival
5.4 In literature
6 Government
6.1 Local government
6.2 Federal, state and county representation
6.3 Politics
6.4 Emergency services
7 Education
7.1 Colleges and universities
7.2 Public schools
7.3 Private schools
7.3.1 Catholic schools
7.3.2 Other private schools
8 Media
9 Transportation
9.1 Air
9.2 Mass transit
9.2.1 Rail
9.2.2 Water
9.2.3 Bus
9.3 Road
9.4 Bike
9.5 Modal characteristics
10 Notable people
11 Sister cities
12 See also
13 References
14 Bibliography
15 External links
History
Lenape and New Netherland
The land comprising what is now Jersey City was inhabited by the Lenape, a collection of tribes (later called Delaware Indian). In 1609, Henry Hudson, seeking an alternate route to East Asia, anchored his small vessel Halve Maen (English: Half Moon) at Sandy Hook, Harsimus Cove and Weehawken Cove, and elsewhere along what was later named the North River. After spending nine days surveying the area and meeting its inhabitants, he sailed as far north as Albany. By 1621, the Dutch West India Company was organized to manage this new territory and in June 1623, New Netherland became a Dutch province, with headquarters in New Amsterdam. Michael Reyniersz Pauw received a land grant as patroon on the condition that he would establish a settlement of not fewer than fifty persons within four years. He chose the west bank of the North River (Hudson River) and purchased the land from the Lenape. This grant is dated November 22, 1630 and is the earliest known conveyance for what are now Hoboken and Jersey City. Pauw, however, was an absentee landlord who neglected to populate the area and was obliged to sell his holdings back to the Company in 1633.[40] That year, a house was built at Communipaw for Jan Evertsen Bout, superintendent of the colony, which had been named Pavonia (the Latinized form of Pauw's name, which means "peacock").[41] Shortly after, another house was built at Harsimus Cove and became the home of Cornelius Van Vorst, who had succeeded Bout as superintendent, and whose family would become influential in the development of the city. Relations with the Lenape deteriorated, in part because of the colonialist's mismanagement and misunderstanding of the indigenous people, and led to series of raids and reprisals and the virtual destruction of the settlement on the west bank. During Kieft's War, approximately eighty Lenapes were killed by the Dutch in a massacre at Pavonia on the night of February 25, 1643.[42]
Scattered communities of farmsteads characterized the Dutch settlements at Pavonia: Communipaw, Harsimus, Paulus Hook, Hoebuck, Awiehaken, and other lands "behind Kill van Kull". The first village (located inside a palisaded garrison) established on what is now Bergen Square in 1660, and is considered to be the oldest town in what would become the state of New Jersey.[43]
19th century

Panorama of Jersey City in 1854
Among the oldest surviving houses in Jersey City are the Newkirk House (1690),[44] the Van Vorst Farmhouse (1740),[45][46][47] and the Van Wagenen House (1742). During the American Revolutionary War, the area was in the hands of the British who controlled New York. In the Battle of Paulus Hook Major Light Horse Harry Lee attacked a British fortification on August 19, 1779. After this war, Alexander Hamilton and other prominent New Yorkers and New Jerseyeans attempted to develop the area that would become historic downtown Jersey City and laid out the city squares and streets that still characterize the neighborhood, giving them names also seen in Lower Manhattan or after war heroes (Grove, Varick, Mercer, Wayne, Monmouth, and Montgomery among them). During the 19th century, former slaves reached Jersey City on one of the four routes of the Underground Railroad that led to the city.[48]

The ferry docks at the Communipaw Terminal in Liberty State Park in 1893
The City of Jersey was incorporated by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on January 28, 1820, from portions of Bergen Township, while the area was still a part of Bergen County. The city was reincorporated on January 23, 1829, and again on February 22, 1838, at which time it became completely independent of North Bergen and was given its present name. On February 22, 1840, it became part of the newly created Hudson County.[49]

Jersey City and Hoboken in 1886
Soon after the Civil War, the idea arose of uniting all of the towns of Hudson County east of the Hackensack River into one municipality. A bill was approved by the state legislature on April 2, 1869, with a special election to be held October 5, 1869. An element of the bill provide that only contiguous towns could be consolidated. While a majority of the voters across the county approved the merger, the only municipalities that had approved the consolidation plan and that adjoined Jersey City were Hudson City and Bergen City.[50] The consolidation began on March 17, 1870, taking effect on May 3, 1870.[51] Three years later the present outline of Jersey City was completed when Greenville agreed to merge into the Greater Jersey City.[49][52]
1853 to 1859; New Jersey Railroad and Transportation Company original Jersey City terminal: Job Male, six year Superintendent of Construction of the NJRR, 1853–1859, built this complete terminal in Jersey City. He was designer and builder of terminal, docks, ferry houses, and piers, and possibly the maintenance facility between Washington and Green streets built during his term as Superintendent. Reclaiming the natural river front, which included all that section of Hudson Street lying between Essex and Wayne Streets. He planned and built for the company the old circular-roofed depot, which was 500 feet (150 m) in length and 100 feet (30 m) wide, and which was situated on Montgomery Street where the 1858 Pennsylvania Railroad depot was built.[53]
In the late 1880s, three passenger railroad terminals opened in Jersey City next to the Hudson River (Pavonia Terminal,[54]Exchange Place[55] and Communipaw[56]). Tens of millions of immigrants passed through these stations as they made their way westward from Ellis Island into the United States.[56] The railroads transformed the geography of the city by building the Erie Cut as well as several large freight rail yards.[57][58] The railroads became and would remain the largest employers in Jersey City into and during the early 20th century.
20th and 21st centuries
Jersey City was a dock and manufacturing town for much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Much like New York City, Jersey City has always been a destination for new immigrants to the United States. In its heyday before World War II, German, Irish, and Italian immigrants found work at Colgate, Chloro or Dixon Ticonderoga. In 1908, the first permanent, drinking water disinfection system in the U.S. was installed on the water supply for the City by John L. Leal.[59] The Hudson Tubes opened in 1911, allowing passengers to take the train to Manhattan as an alternative to the extensive ferry system. The Black Tom explosion occurred on July 30, 1916, as an act of sabotage on American ammunition supplies by German agents to prevent the materials from being used by the Allies in World War I.[60]
From 1917 to 1947, Jersey City was governed by Mayor Frank Hague. Originally elected as a candidate supporting reform in governance, the Jersey City History website says his name is "synonymous with the early twentieth century urban American blend of political favoritism and social welfare known as bossism".[61] Hague ran the city with an iron fist while, at the same time, molding governors, United States senators, and judges to his whims. Boss Hague was known to be loud and vulgar, but dressed in a stylish manner earning him the nickname "King Hanky-Panky".[62] In his later years in office, Hague would often dismiss his enemies as "reds" or "commies". Hague lived like a millionaire, despite having an annual salary that never exceeded $8,500. He was able to maintain a fourteen-room duplex apartment in Jersey City, a suite at the Plaza Hotel in Manhattan, and a palatial summer home in the seaside community of Deal, and travel to Europe yearly in the royal suites of the best ocean liners.[63]
After Hague's retirement from politics, a series of mayors including John V. Kenny, Thomas J. Whelan and Thomas F. X. Smith attempted to take control of Hague's organization, usually under the mantle of political reform. None were able to duplicate the level of power held by Hague,[64] but the city and the county remained notorious for political corruption for years.[65][66][67] By the 1970s, the city experienced a period of urban decline that saw many of its wealthy residents leave for the suburbs, due to rising crime, civil unrest, political corruption, and economic hardship. From 1950 to 1980, Jersey City lost 75,000 residents, and from 1975 to 1982, it lost 5,000 jobs, or 9% of its workforce.[68]
Beginning in the 1980s, development of the waterfront in an area previously occupied by rail yards and factories helped to stir the beginnings of a renaissance for Jersey City. The rapid construction of numerous high-rise buildings increased the population and led to the development of the Exchange Place financial district, also known as "Wall Street West", one of the largest banking centers in the United States. Large financial institutions such as UBS, Goldman Sachs, Chase Bank, Citibank, and Merrill Lynch occupy prominent buildings on the Jersey City waterfront, some of which are among the tallest buildings in New Jersey. Simultaneous to this building boom, the light-rail network was developed.[69] With 18,000,000 square feet (1,700,000 m2) of office space, it has the nation's 12th-largest downtown.[70]
City Ordinance 13.097, passed in October 2013, requires employers with ten or more employees to offer up to five paid sick days a year. The bill impacts all businesses employing workers who work at least 80 hours a calendar year in Jersey City.[71]
In November 2015, Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump made the claim that "thousands and thousands" of Muslims in Jersey City cheered as they watched the Twin Towers burn after their collapse during the September 11 terrorist attacks, and used the unsubstantiated allegation as justification for his proposal that certain mosques in the United States should be monitored by authorities.[72]

Liberty Island and Liberty State Park
Geography

As seen from Manhattan
Jersey City is the seat of Hudson County, New Jersey, and the second-largest city in New Jersey.[29] According to the United States Census Bureau, the city had a total area of 21.080 square miles (54.596 km2), including 14.794 square miles (38.316 km2) of land and 6.286 square miles (16.281 km2) of water (29.82%).[11][12] As of the 1990 Census, it had the smallest land area of the 100 most populous cities in America.[73]
Jersey City is bordered to the east by the Hudson River, to the north by Secaucus, North Bergen, Union City and Hoboken, to the west, across the Hackensack, by Kearny and Newark, and to the south by Bayonne. Jersey City includes most of Ellis Island. Given their proximity and accessibility by rapid transit to Manhattan, Jersey City and Hudson County are sometimes referred to as New York City's Sixth Borough.[74][75][76]
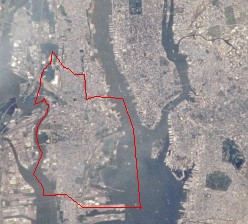
Image of Jersey City taken by NASA (red line demarcates the municipal boundaries of Jersey City)
Neighborhoods

Newport

Journal Square
Jersey City (and most of Hudson County) is located on the peninsula known as Bergen Neck, with a waterfront on the east at the Hudson River and New York Bay and on the west at the Hackensack River and Newark Bay. Its north-south axis corresponds with the ridge of Bergen Hill, the emergence of the Hudson Palisades.[77] The city is the site of some of the earliest European settlements in North America, which grew into each other rather expanding from a central point.[78][79] This growth and the topography greatly influenced the development of the sections of the city[80][81] and its various neighborhoods.[64] The city is divided into six wards.[82]
Downtown Jersey City
Downtown Jersey City is the area from the Hudson River westward to the Newark Bay Extension of the New Jersey Turnpike (Interstate 78) and the New Jersey Palisades; it is also bounded by Hoboken to the north and Liberty State Park to the south.
Historic Downtown is an area of mostly low-rise buildings to the west of the waterfront that is highly desirable due to its proximity to local amenities and Manhattan. It includes the neighborhoods of Van Vorst Park and Hamilton Park, which are both square parks surrounded by brownstones. This historic downtown also includes Paulus Hook, the Village and Harsimus Cove neighborhoods. Newark Avenue & Grove Street, are the main thoroughfares in Downtown Jersey City, both have seen a lot of development and the surrounding neighborhoods have many stores and restaurants.[83] The Grove Street PATH station is in the process of being renovated[84] and a number of new residential buildings are being built around the stop, including a proposed 50-story building at 90 Columbus.[85] Historic Downtown is home to many cultural attractions including the Jersey City Museum, the Hudson and Manhattan Railroad Powerhouse (planned to become a museum and artist housing) and the Harsimus Stem Embankment along Sixth Street, which a citizens' movement is working to turn into public parkland that would be modeled after the High Line in Manhattan.[86]
Newport and Exchange Place are redeveloped waterfront areas consisting mostly of residential towers, hotels and office buildings. Newport is a planned mixed-use community, built on the old Erie Lackawanna Railway yards, made up of residential rental towers, condominiums, office buildings, a marina, schools, restaurants, hotels, Newport Centre Mall, a waterfront walkway, transportation facilities, and on-site parking for more than 15,000 vehicles. Newport had a hand in the renaissance of Jersey City although, before ground was broken, much of the downtown area had already begun a steady climb (much like Hoboken). In recent years, this area of Jersey City has undergone gentrification that has seen the improvement in neighborhoods. This has also caused a rise of the standard of living throughout the city. Downtown also includes the Newport Centre area, which is also home of the Westin Hotel.[87] Prior to the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks Jersey City had three office towers over 100 meters. Since then, three more office towers and 10 residential buildings over 100 meters have been completed.[88] In January 2016, the Federal Aviation Administration gave navigational clearance for construction of a 79-story, 900-foot (270 m) residential and commercial tower planned by the Chinese Overseas America Corporation, which would succeed the Goldman Sachs Tower, also in Downtown Jersey City, as the tallest skyscraper in New Jersey.[89]
Bergen-Lafayette
Bergen-Lafayette, formerly Bergen City, New Jersey, lies between Greenville to the south and McGinley Square to the north, while bordering Liberty State Park and Downtown to the east and the West Side neighborhood to the west. Communipaw Avenue, Bergen Avenue, Martin Luther King Drive, and Ocean Avenue are main thoroughfares. The former Jersey City Medical Center complex, a cluster of Art Deco buildings on a rise in the center of the city, has been converted into residential complexes called The Beacon.[90]Berry Lane Park, which is the largest municipal park in Jersey City, is located along Garfield Avenue in the northern section of Bergen-Lafayette.
The Heights
The Heights or Jersey City Heights is a district in the north end of Jersey City atop the New Jersey Palisades overlooking Hoboken to the east and Croxton in the Meadowlands to the west. Previously the city of Hudson City, The Heights was incorporated into Jersey City in 1869.[50] The southern border of The Heights is generally considered to be north of Bergen Arches and The Divided Highway, while Paterson Plank Road in Washington Park is its main northern boundary. Transfer Station is just over the city line. Its postal area ZIP Code is 07307. The Heights mostly contains two- and three-family houses and low rise apartment buildings, and is similar to North Hudson architectural style and neighborhood character.[91]
Journal Square
McGinley Square
Hamilton Park
Greenville

View of Jersey City from the northwest. Lower Manhattan is in the background.
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Jersey City has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.[92] Jersey City is in USDA hardiness zone 7a on the west side of the city and hardiness zone 7b on the east side.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 3,072 | — | |
| 1850 | 6,856 | 123.2% | |
| 1860 | 29,226 | 326.3% | |
| 1870 | 82,546 | * | 182.4% |
| 1880 | 120,722 | * | 46.2% |
| 1890 | 163,003 | 35.0% | |
| 1900 | 206,433 | 26.6% | |
| 1910 | 267,779 | 29.7% | |
| 1920 | 298,103 | 11.3% | |
| 1930 | 316,715 | 6.2% | |
| 1940 | 301,173 | −4.9% | |
| 1950 | 299,017 | −0.7% | |
| 1960 | 276,101 | −7.7% | |
| 1970 | 260,350 | −5.7% | |
| 1980 | 223,532 | −14.1% | |
| 1990 | 228,537 | 2.2% | |
| 2000 | 240,055 | 5.0% | |
| 2010 | 247,597 | 3.1% | |
| Est. 2017 | 270,753 | [22][93] | 9.4% |
| Population sources: 1840–1920[94] 1840[95] 1850–1870[96] 1850[97] 1870[98] 1880–1890[99] 1890–1910[100] 1840–1930[101] 1930–1990[102] 2000[103][104] 2010[19][20][21] * = Gained territory in previous decade.[49] | |||
| Racial composition | 2010[32] | 1990[105] | 1970[105] | 1940[105] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 32.7% | 48.2% | 77.8% | 95.5% |
| —Non-Hispanic | 21.5% | 36.6% | 69.5%[106] | n/a |
| Black or African American | 25.8% | 29.7% | 21.0% | 4.5% |
Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 27.6% | 24.2% | 9.1%[106] | n/a |
| Asian | 23.7% | 11.4% | 0.5% | − |
2010 Census

India Square, in the Bombay neighborhood of Jersey City, is home to the highest concentration of Asian Indians in the Western Hemisphere.[107]
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 247,597 people, 96,859 households, and 57,631 families residing in the city. The population density was 16,736.6 per square mile (6,462.0/km2). There were 108,720 housing units at an average density of 7,349.1 per square mile (2,837.5/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 32.67% (80,885) White, 25.85% (64,002) Black or African American, 0.51% (1,272) Native American, 23.67% (58,595) Asian, 0.07% (161) Pacific Islander, 12.81% (31,726) from other races, and 4.42% (10,956) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 27.57% (68,256) of the population.[19]
There were 96,859 households out of which 27.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 35.5% were married couples living together, 18.2% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.5% were non-families. 30.2% of all households were made up of individuals, and 7.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.53 and the average family size was 3.20.[19]
In the city, the population was spread out with 21.1% under the age of 18, 10.0% from 18 to 24, 37.6% from 25 to 44, 22.2% from 45 to 64, and 9.0% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 33.2 years. For every 100 females there were 97.6 males. For every 100 females ages 18 and older there were 96.0 males.[19]
The Census Bureau's 2006–2010 American Community Survey showed that (in 2010 inflation-adjusted dollars) median household income was $54,280 (with a margin of error of +/- $1,460) and the median family income was $58,533 (+/- $2,116). Males had a median income of $49,582 (+/- $1,968) versus $43,458 (+/- $1,837) for females. The per capita income for the borough was $30,490 (+/- $668). About 15.1% of families and 17.5% of the population were below the poverty line, including 28.1% of those under age 18 and 15.6% of those age 65 or over.[108]
As of the 2010 Census, Jersey City experienced an increase of 7,542 residents (3.1%) from its 2000 Census population of 240,055.[19][29] Since it was believed the earlier population was under documented, the 2010 census was anticipated with the possibility that Jersey City might become the state's most populated city, surpassing Newark.[109] The city hired an outside firm to contest the results, citing the fact that development in the city between 2000 and 2010 substantially increased the number of housing units and that new populations may have been undercounted by as many as 30,000 residents based on the city's calculations.[110][111] Preliminary findings indicated that 19,000 housing units went uncounted.[112]
2000 Census

Satellite view of Jersey City
As of the 2000 United States Census, the population was 240,055 making Jersey City the 72nd-most-populous city in the U.S.[113] Among cities with a population higher than 100,000 ranked in the 2000 Census, Jersey City was the fourth most densely populated large city in the United States, behind New York City; Paterson, New Jersey; and San Francisco.[114] There were 88,632 households, and 55,660 families residing in the city. The population density was 16,093.7/mi2 (6,212.2/km2). There were 93,648 housing units at an average density of 6,278.3 per square mile (2,423.4/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 34.01% White, 28.32% African American, 0.45% Native American, 16.20% Asian, 0.08% Pacific Islander, 15.11% from other races, and 5.84% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino people of any race were 28.31% of the population.[103][104]
As of the 2000 Census, the most common reported ancestries were Italian (6.6%), Irish (5.6%), Polish (3.0%), Arab (2.8%), and German (2.7%).[115]
Of all 88,632 households, 31.1% had children under the age of 18 living there, 36.4% were married couples living together, 20.2% had a female householder with no husband present, and 37.2% were non-families. 29.2% of all households were made up of individuals and 8.2% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.67 and the average family size was 3.37.[103][104]
In the city, the population was spread out with 24.7% under the age of 18, 10.7% from 18 to 24, 35.1% from 25 to 44, 19.7% from 45 to 64, and 9.8% who are 65 years of age or older. The median age was 32 years. For every 100 females, there were 95.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 92.6 males.[103][104]
The median income of its households was $37,862, and the median income of its families was $41,639. Males had a median income of $35,119 versus $30,494 for females. The per capita income for the city was $19,410. About 16.4% of families and 18.6% of the population were below the poverty line, including 27.0% of those under age 18 and 17.5% of those age 65 or over.[103][104]
Community diversity
Jersey City is one of the most ethnically diverse cities in the world.[116][117] The city is a major port of entry for immigration to the United States and a major employment center at the approximate core of the New York City metropolitan region; and given its proximity to Manhattan, Jersey City has evolved a globally cosmopolitan ambiance of its own, demonstrating a robust and growing demographic and cultural diversity with respect to metrics including nationality, religion, race, and domiciliary partnership.[116]
Latin American
There were an estimated 73,479 Hispanic Americans in Jersey City, 28.1% of the population, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[118] representing a 0.9% increase from 68,256 Hispanic Americans enumerated in the 2010 United States Census.[119] Immigrants from South America, led by Ecuador, are a growing component of Jersey City's population/[116]Puerto Rican Americans constitute the largest Hispanic group in Jersey City.[118] While Cuban Americans are not as highly concentrated in Jersey City as they are in northern Hudson County, Jersey City has hosted the annual Cuban Parade and Festival of New Jersey at Exchange Place on its downtown waterfront since it was established in 2001.[120]
Puerto Rican
There were an estimated 26,529 Puerto Rican residents in Jersey City, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[118] representing a 3.3% increase from the 25,677 Puerto Rican residents enumerated in the 2010 United States Census.[119]
Asian American
There were an estimated 65,450 Asian Americans in Jersey City, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[118] representing an 11.7% increase from 58,595 Asian Americans enumerated in the 2010 United States Census.[119]
Indian American
India Square, also known as "Little India" or "Little Bombay",[121] home to the highest concentration of Asian Indians in the Western Hemisphere,[107] is a rapidly growing Indian American ethnic enclave in Jersey City. Indian Americans constituted 10.9% of the overall population of Jersey City in 2010,[19] the highest proportion of any major U.S. city. India Square has been home to the largest outdoor Navratri festivities in New Jersey as well as several Hindu temples;[122] while an annual, color-filled spring Holi festival has taken place in Jersey City since 1992, centered upon India Square and attracting significant participation and international media attention.[123][124] There were an estimated 30,976 Indian Americans in Jersey City, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[118] representing a 14.3% increase from 27,111 Indian Americans enumerated in the 2010 United States Census.[119]
Filipino American
Filipino people make up 6.4% of Jersey City's population, based on the results of the 2016 American Community Survey.[118][125] The Five Corners district is home to a thriving Filipino community and Jersey City's Little Manila, which is the second-largest Asian American subgroup in the city.[19] A variety of Filipino restaurants, shippers and freighters, doctors' officers, bakeries, stores, and an office of The Filipino Channel have made Newark Avenue their home. The largest Filipino-owned grocery store on the East Coast of the United States, Phil-Am Food, has been there since 1973.[126] An array of Filipino-owned businesses can also be found at the section of West Side of Jersey City, where many of its residents are of Filipino descent. In 2006, a Red Ribbon pastry shop, one of the Philippines' most famous food chains, opened its first branch on the East Coast in the Garden State.[127]Manila Avenue in Downtown Jersey City was named for the Philippine capital city because of the many Filipinos who built their homes on this street during the 1970s. A memorial, dedicated to the Filipino American veterans of the Vietnam War, was built in a small square on Manila Avenue. A park and statue dedicated to Jose P. Rizal, a national hero of the Philippines, is located in downtown Jersey City.[128] Jersey City is the host of the annual Philippine-American Friendship Day Parade, an event that occurs yearly in June, on its last Sunday. The City Hall of Jersey City raises the Philippine flag in correlation to this event and as a tribute to the contributions of the Filipino community. The Santacruzan Procession along Manila Avenue has taken place since 1977.[129] There were an estimated 16,766 Filipino Americans in Jersey City, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[118] representing a 3,4% increase from 16,213 Filipino Americans enumerated in the 2010 United States Census.[119]
Behind English and Spanish, Tagalog is the third-most-common language spoken in Jersey City.[130]
Chinese American
Jersey City, highly accessible to Lower Manhattan in New York City and its Chinatown by rapid transit, was home to an estimated 8,420 Chinese Americans, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[118] representing a notably rapid growth of 49.2% from the 5,643 Chinese Americans enumerated in the 2010 United States Census.[119] Chinese nationals have also been obtaining EB-5 immigrant visas by investing US$500,000 apiece in new Downtown Jersey City residential skyscrapers.[131]
Vietnamese American
New Jersey's largest Vietnamese American population resides in Jersey City. There were an estimated 1,485 Vietnamese Americans in Jersey City, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[118] representing a7.6% decline from 1,607 Vietnamese Americans enumerated in the 2010 United States Census.[119]
European American
There were an estimated 56,101 non-Hispanic whites in Jersey City, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[118] representing a 5.4% increase from 53,236 non-Hispanic whites enumerated in the 2010 United States Census.[119] Many non-Hispanic whites have settled in the newer developments in the Newport and Exchange Place neighborhoods along the Jersey City waterfront.
Ever since the settling of New Netherland in the 1600s, comprising what is now the Gateway Region of northeastern New Jersey as well as portions of Downstate New York in the New York City metropolitan area, the Dutch and British, along with German and Irish Americans, have established an integral role in the subsequent long-term development of Jersey City over the centuries.
African American
There were an estimated 64,998 African Americans in Jersey City, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[118] representing a 1.6% increase from 64,002 African Americans enumerated in the 2010 United States Census.[119] This is in contrast with Hudson County overall, where there were an estimated 85,172 African Americans, according to the 2016 American Community Survey,[132] representing a 1.5% increase from 83,925 African Americans enumerated in the county in the 2010 United States Census.[133] However, modest growth in the African immigrant population, most notably the growing Nigerian American and Kenyan American populations[134][135] in Jersey City, is partially offsetting the decline in the city's American-born black population, which as a whole has been experiencing an exodus from northern New Jersey to the Southern United States.[136]
Arab American
Arab Americans numbered an estimated 18,628 individuals in Hudson County as per the 2010-2014 American Community Survey, representing 2.8% of the county's total population.[137] the second- highest percentage in New Jersey after Passaic County.[138] Arab Americans are most concentrated in Jersey City, led by Egyptian Americans, including the largest population of Coptic Christians in the United States.[116][117] There is a notable Moroccan American population in Jersey City.
Muslim American
Muslims constitute 4.2% of religious adherents in Jersey City.[115] The growing Muslim American population in Jersey City and Hudson County.[139]Pakistani Americans, Bangladeshi Americans, and Arab Americans compose a significant proportion of Jersey City's Muslim population.
Same-sex couples
There were 2,726 same-sex couples in Hudson County in 2010, with Jersey City being the hub,[140] prior to the commencement of same-sex marriages in New Jersey on October 21, 2013.[141]
Artists-in-residence
Based on a 2011 survey of census data on the number of artists as a percentages of the population, The Atlantic magazine called Jersey City the 10th-most-artistic city in the United States.[142][143]
Economy
Jersey City is a regional employment center with over 100,000 private and public sector jobs, which creates a daytime swell in population. Many jobs are in the financial and service sectors, as well as in shipping, logistics, and retail.[144]
Jersey City's tax base grew by $136 million in 2017 giving Jersey City the largest municipal tax base in the State of New Jersey.[145] As part of a 2017 revaluation, the city's property tax base is expected to increase from $6.2 billion to $26 billion.[146]
Wall Street West
Jersey City's Hudson River waterfront, from Exchange Place to Newport, is known as Wall Street West and has over 13 million square feet of Class A office space.[144] One third of the private sector jobs in the city are in the financial services sector: more than 60% are in the securities industry, 20% are in banking and 8% in insurance.[147]
Jersey City is home to the headquarters of Verisk Analytics[148] and Lord Abbett, a privately held money management firm.[149] Companies such as Computershare, NEX Group, ADP, and Fidelity Investments also conduct operations in the city.[150] In 2014, Forbes magazine moved its headquarters to the district, having been awarded a $27 million tax grant in exchange for bringing 350 jobs to the city over a ten-year period.[151]
Retail
Jersey City has several shopping districts, some of which are traditional main streets for their respective neighborhoods, such as Central, Danforth, and West Side Avenues. Journal Square is a major commercial district. Newport Mall is a regional shopping area.[152]
Portions of the city are part of an Urban Enterprise Zone, one of 27 zones in the state. In addition to other benefits to encourage employment in the zone, shoppers can take advantage of a reduced 3.3125% sales tax rate (versus the 6.625% rate charged statewide, effective January 1, 2018) at eligible merchants.[153][154][155]
About one third of Jersey City is included in the state's largest Urban Enterprise Zone, established in 1992 (the zone's status is due to expire in November 2023).[156][157][158]
Port Jersey
Port Jersey is an intermodal freight transport facility that includes a container terminal located on the Upper New York Bay in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The municipal border of the Hudson County cities of Jersey City and Bayonne runs along the long pier extending into the bay.The north end of the facility houses the Greenville Yard, a rail yard located on a manmade peninsula that was built in the early 1900s by the Pennsylvania Railroad,[159][160] in addition to the Claremont Terminal, once part of the Lehigh Valley Terminal Railway operations. The central area of the facility contains GCT Bayonne, a major post-panamax shipping facility operated by Global Container Terminals that underwent a major expansion in June 2014.[161][162] The largest ship ever to call at the Port of New York-New Jersey, the MOL Benefactor, docked at Port Jersey in July 2016 after sailing from China through the newly widened Panama Canal.[163]
Other
Goya Foods, which had been headquartered in adjacent Secaucus, opened a new headquarters including a 600,000-square-foot warehouse and distribution center in Jersey City in April 2015.[164]
In 2014, Paul Fireman proposed a 95-story tower for Jersey City that would include a casino. The project, which endorsed by Mayor Steve Fulop, would cost an estimated $4.6 billion.[165] In February 2014, New Jersey State Senate President Stephen Sweeney argued that Jersey City, among other distressed cities, could benefit from a casino—were construction of one outside of Atlantic City eventually permitted by New Jersey.[166]
Art and culture
Notable landmarks
- See List of Registered Historic Places in Hudson County, New Jersey
Statue of Liberty National Monument, Ellis Island and Liberty Island (Liberty Island and part of Ellis Island are located in New York)- Liberty Science Center
- The Katyń Memorial by well-known Polish-American artist Andrzej Pitynski on Exchange Place is the first memorial of its kind to be raised on American soil to honor the dead of the Katyń Forest Massacre.[167]
- The Colgate Clock, promoted by Colgate-Palmolive as the largest in the world, sits in Jersey City and faces Lower New York Bay and Lower Manhattan (it is clearly visible from Battery Park in lower Manhattan). The clock, which is 50 feet (15 m) in diameter with a minute hand weighing 2,200 pounds, was erected in 1924 to replace a smaller one that was relocated to a plant in Jeffersonville, Indiana.[168]
- The Landmark Loew's Jersey Theatre, one of the five Loew's Wonder Theatres constructed in the 1920s and the only one located outside of New York City, is located in Journal Square. Currently presenting classic films, live performances, and events while the theatre undergoes restoration by volunteers.[169][170]
- The White Eagle Hall is a recently renovated and re-opened historic theater. Constructed in 1910, it had served as the practice gym for the Saint Anthony High School Friars basketball program.[171]
Museums and libraries
The Jersey City Free Public Library has five regional branches, some of which have permanent collections and host exhibitions. At the Main Library, the New Jersey Room contains historical archives and photos. The Greenville Branch is home to the Afro-American Historical and Cultural Society Museum. The Five Corners Branch specializes in works related to music and the fine arts, and is a gallery space. The library system also supports a bookmobile and five neighborhood libraries.[172]
Liberty State Park is home to Central Railroad of New Jersey Terminal, the Interpretive Center, and Liberty Science Center, an interactive science and learning center. The center, which first opened in 1993 as New Jersey's first major state science museum, has science exhibits, the world's largest IMAX Dome theater, numerous educational resources, and the original Hoberman sphere.[173] From the park, ferries travel to both Ellis Island and the Immigration Museum and Liberty Island, site of the Statue of Liberty.[174]
The Jersey City Museum, Mana Contemporary, and the Museum of Russian Art, which specializes in Soviet Nonconformist Art,[175] include permanent collections and special exhibits.
Some stations of the Hudson Bergen Light Rail feature public art exhibitions, including those at Exchange Place, Danforth Avenue[176] and Martin Luther King Drive station.[177][178]
Hudson County Shakespeare Festival
Since 1992, the Hudson Shakespeare Company has been the resident Shakespeare festival of Hudson County performing a free Shakespeare production for each month of the summer throughout various parks in the city. The group regularly performs at Hamilton Park (9th Street & Jersey Avenue), Van Vorst Park (Jersey Avenue & Montgomery Street), and The Historic Jersey City and Harsimus Cemetery (435 Newark Avenue).[179]
In literature
The American poet Wallace Stevens described the city as a place where "the deer and the dachshund are one."[180]
Government

City Hall, on Grove Street
Local government
Jersey City is governed under the Faulkner Act (Mayor-Council) form of municipal government by a mayor and a nine-member city council. The city council consists of six members elected from wards[181] and three elected at large, all elected to four-year terms on a concurrent basis in non-partisan elections.[17][82]
As of 2018[update], the mayor is Steven Fulop, whose term of office ends December 31, 2018.[13] Members of the City Council are Council President Rolando R. Lavarro Jr., Daniel Rivera (at large), Joyce Watterman (at large), Denise Ridley (Ward A – Greenville), Mira Prinz-Arey (Ward B – West Side), Richard Boggiano (Ward C – Journal Square), Michael Yun (Ward D – The Heights), James Solomon (Ward E – Downtown) and Jermaine D. Robinson (Ward F – Bergen/Lafayette), all of whom are serving concurrent terms of office running from January 1, 2018 until December 31, 2021.[182][183][184][185]
The Business Administrator is Robert Kakoleski.[15] The City Clerk is Robert Byrne.[16]
Federal, state and county representation
Jersey City is split between the 8th and 10th Congressional Districts[186] and is part of New Jersey's 31st and 33rd state legislative districts.[20][187][188] Prior to the 2011 reapportionment following the 2010 Census, Jersey City had been in the 31st, 32nd and the 33rd state legislative districts.[189] Prior to the 2010 Census, Jersey City had been split between the 9th Congressional District, 10th Congressional District and the 13th Congressional District, a change made by the New Jersey Redistricting Commission that took effect in January 2013, based on the results of the November 2012 general elections.[189] The split that went into effect in 2013 placed 111,678 residents living in the city's north and east in the 8th District, while 139,519 residents in the southwest portion of the city were placed in the 10th District.[186][190]
New Jersey's Eighth Congressional District is represented by Albio Sires (D, West New York).[191]New Jersey's Tenth Congressional District is represented by Donald Payne Jr. (D, Newark).[192] New Jersey is represented in the United States Senate by Democrats Cory Booker (Newark, term ends 2021)[193] and Bob Menendez (Paramus, 2019).[194][195]
For the 2018–2019 session (Senate, General Assembly), the 31st Legislative District of the New Jersey Legislature is represented in the State Senate by Sandra Bolden Cunningham (D, Jersey City) and in the General Assembly by Nicholas Chiaravalloti (D, Bayonne) and Angela V. McKnight (D, Jersey City).[196][197] For the 2018–2019 session (Senate, General Assembly), the 33rd Legislative District of the New Jersey Legislature is represented in the State Senate by Brian P. Stack (D, Union City) and in the General Assembly by Raj Mukherji (D, Jersey City) and Annette Chaparro (D, Hoboken).[198][199] The Governor of New Jersey is Phil Murphy (D, Middletown Township).[200] The Lieutenant Governor of New Jersey is Sheila Oliver (D, East Orange).[201]
The city encompasses three Hudson County freeholder districts in their entirety, while three others are shared with adjacent municipalities. The Hudson County Executive, elected at-large, is Thomas A. DeGise.[202]Hudson County Board of Chosen Freeholders Districts 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 8 are located partially or entirely in Jersey City. District 1 comprises neighboring Bayonne and a small part of Jersey City, Country Village,[203] and is represented by Doreen McAndrew DiDomenico.[204][205]
District 2 includes the West Side and parts of the Marion Section and Journal Square[206] and is represented by Bill O'Dea.[204][205] District 3, which stretches from Paulus Hook through Bergen Hill to the east side of Greenville[207] is represented by Jeffrey Dublin.[204][205] District 4 includes Harsimus, Hamilton Park, and portions of Journal Square and the Heights [208] and is represented by Eliu Rivera.[204][205] District 5, comprising portions of the Heights and all of neighboring Hoboken,[209] is represented by Anthony Romano.[204][205] District 8 compromises all of North Bergen, the North End of Secaucus and the northern tip of the city near Transfer Station.[210] It is represented by Thomas Liggio.[204]
Politics
As of March 23, 2011, there was a total of 120,229 registered voters in Jersey City, of whom 58,194 (48.4%) were registered as Democrats, 7,655 (6.4%) were registered as Republicans, and 54,293 (45.2%) were registered as Unaffiliated. There were 87 voters registered to other parties.[211]
In the 2012 presidential election, Democrat Barack Obama received 85.5% of the vote (64,052 cast), ahead of Republican Mitt Romney with 13.5% (10,120 votes), and other candidates with 1.0% (751 votes), among the 75,506 ballots cast by the city's 133,197 registered voters (583 ballots were spoiled), for a turnout of 56.7%.[212][213] In the 2008 presidential election, Democrat Barack Obama received 81.8% of the vote (65,780 cast), ahead of Republican John McCain with 16.8% (13,529 votes) and other candidates with 0.7% (584 votes), among the 80,381 ballots cast by the city's 139,158 registered voters, for a turnout of 57.8%.[214] In the 2004 presidential election, Democrat John Kerry received 74.5% of the vote (52,979 ballots cast), out polling Republican George W. Bush with 22.8% (16,216 votes) and other candidates with 0.5% (559 votes), among the 71,130 ballots cast by the city's 119,723 registered voters, for a turnout percentage of 59.4.[215]
In the 2013 gubernatorial election, Democrat Barbara Buono received 66.5% of the vote (20,421 cast), ahead of Republican Chris Christie with 31.8% (9,784 votes), and other candidates with 1.7% (514 votes), among the 32,347 ballots cast by the city's 139,265 registered voters (1,628 ballots were spoiled), for a turnout of 23.2%.[216][217] In the 2009 gubernatorial election, Democrat Jon Corzine received 76.2% of the vote (29,817 ballots cast), ahead of Republican Chris Christie with 18.7% (7,336 votes), Independent Chris Daggett with 3.2% (1,263 votes) and other candidates with 0.9% (371 votes), among the 39,143 ballots cast by the city's 120,269 registered voters, yielding a 32.5% turnout.[218]
Emergency services
Jersey City Fire Department - Due to budget cuts, several companies are placed out of service or "off duty" daily on a rotational basis. (JCFD) has 550 uniformed firefighters operating out of 14 stations[219] Jersey City is a member of the Metro USAR Strike Team, which is composed of nine north Jersey fire departments.[220]
- Jersey City Medical Center Emergency Medical Services
- Jersey City Police Department (JCPD) dates back to the appointment of watchmen in 1829.[221]
- Port Authority of New York and New Jersey Police Department
- Hudson County Sheriff's Office (Patrol, county owned buildings and county parks in Jersey City)
- United States Park Police (Ellis Island, Liberty Island, and the screening facilities for the ferries located in Jersey City)
- National Park Service Emergency Medical Services (Ellis Island)
- New Jersey State Park Police (Liberty State Park located in Jersey City)
- CSX Railroad Police (the CSX and Conrail rail road lines running through Jersey City)
- New Jersey Transit Police (the Hudson-Bergen lightrail line running through Jersey City)
- New Jersey State Police (the turnpike and turnpike extension running through Jersey City)
Education
Colleges and universities

The Yanitelli Center on the campus of Saint Peter's University
Jersey City is home to New Jersey City University[222] and Saint Peter's University,[223] both of which are located in the city's West Side district. The business school of New Jersey City University is at Harborside overlooking Lower Manhattan. The University of Phoenix has a small location at Newport[224] and Rutgers University offers MBA classes at Harborside Center.[225]Hudson County Community College is a junior college located in the Journal Square area offering courses to help students transition into a larger university.[226]
Public schools

Dr. Ronald E. McNair Academic High School
The Jersey City Public Schools serve students in pre-kindergarten through twelfth grade. The district is one of 31 former Abbott districts statewide,[227] which are now referred to as "SDA Districts" based on the requirement that the state cover all costs for school building and renovation projects in these districts under the supervision of the New Jersey Schools Development Authority.[228][229] As of the 2014-15 school year, the district and its 38 schools had an enrollment of 30,845 students and 2,389.0 classroom teachers (on an FTE basis), for a student–teacher ratio of 12.9:1.[230]
High schools in the district (with 2014-15 enrollment data from the National Center for Education Statistics[231]) are
William L. Dickinson High School Academy of the Sciences[232] (2,185; 9-12),
James J. Ferris High School Academy of International Enterprise[233] (1,232; 9-12),
Infinity Institute[234] (261; 6-12),
Innovation High School[235] (9-12),
Liberty High School[236] (197; 9-12),
Lincoln High School Academy of Governance and Social Sciences[237] (830; 9-12),
Dr. Ronald E. McNair Academic High School[238] (716; 9-12),
Renaissance Institute[239] (9-12) and
Henry Snyder High School Academy of the Arts[240] (993; 9-12).[241][242]
Dr. Ronald E. McNair Academic High School was the first-ranked public high school in New Jersey out of 322 schools statewide, in New Jersey Monthly magazine's September 2010 cover story on the state's "Top Public High Schools", after being ranked second in 2008 out of 316 schools.[243] and was selected as 41st best high school in the United States in Newsweek magazine's national 2011 survey.[244] William L. Dickinson High School is the oldest high school in the city and one of the largest schools in Hudson County in terms of student population. Opened in 1906 as the Jersey City High School it is one of the oldest school sites in the city, it is a four-story Beaux-Arts building located on a hilltop facing the Hudson River.[245] Liberty High School is the district's only high school that focuses on all academics.
Among Jersey City's elementary and middle schools is Academy I Middle School and Frank R. Conwell Middle School #4, which is part of the Academic Enrichment Program for Gifted Students. Another school is Alexander D. Sullivan P.S. #30, an ESL magnet school in the Greenville district, which serves nearly 800 Pre-k through 5th grade students.[246]
The Hudson County Schools of Technology (which also has campuses in North Bergen and Secaucus) has a campus in Jersey City, which includes County Prep High School.[247]
Jersey City also has 12 charter schools, which are run under a special charter granted by the Commissioner of the New Jersey Department of Education, including the Mathematics, Engineering, Technology and Science Charter School (for grades 6 – 12) and the Dr. Lena Edwards Charter School (for K-8), which were approved in January 2011.[248] BelovED Community Charter School opened in 2012 and has purchased a half-acre parcel of land on Grand Street to make room for a new 40,000-square-foot (3,700 m2), $12 million middle school building designed to serve 240 students in sixth through ninth grades.[249]
Private schools
Catholic schools
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Newark maintains a network of elementary and secondary Catholic schools serve every area of Jersey City. High schools administered by the Archdiocese are Hudson Catholic Regional High School, St. Anthony High School, Saint Dominic Academy and St. Peter's Preparatory School.[250]St. Mary High School closed in June 2011 due to declining enrollment.[251]
Catholic K-8 elementary schools include Our Lady of Czestochowa School,[252]Sacred Heart School,[253] Saint Aloysius Elementary Academy,[254] St. Joseph School[255] and St. Nicholas School.[256][257] In 2015, Our Lady of Czestochowa School was one of 15 schools in New Jersey, and one of six private schools, recognized as a National Blue Ribbon School in the exemplary high performing category by the United States Department of Education.[258][259]
In the face of declining enrollment and rising expenses, the Newark Archdiocese closed Our Lady of Mercy Academy (founded in 1964) and Resurrection School at the end of the 2012-13 school year.[260] St. Anne School closed at the end of the 2011-12 school year after 112 years, as enrollment declined from 700 students in 1976 to 240 in 2010-11 and 188 in the school's final year of operation.[261]
Other private schools

French American Academy on 3rd Street
Other private high schools in Jersey City include First Christian Pentecostal Academy[262] and Stevens Cooperative School.[263]Kenmare High School is operated through the York Street Project as part of an effort to reduce rates of poverty in households headed by women, through a program that offers small class sizes, individualized learning and development of life skills.[264]
The French American Academy, at the former St. Mary's High School, is a private bilingual school PK-2 to 5.[265] is located in a 3-story building, built a century ago which offers 23 classrooms and gymnasium for physical education or indoor recess. It will open its middle school in September 2018.
A number of other private schools are also available. Genesis Educational Center[266] is a private Christian school located in downtown Jersey City for ages newborn through 8th grade. The Jersey City Art School is a private art school located in downtown Jersey City for all ages.[267]

Central Railroad of New Jersey Terminal
Media
Jersey City is located in the New York media market, and most of its daily papers are available for sale or delivery. The daily newspaper The Jersey Journal, located at its namesake Journal Square, covers Hudson County, its morning daily, Hudson Dispatch now defunct.[268] The Jersey City Reporter is part of The Hudson Reporter group of local weeklies. The Jersey City Independent is a web-only news outlet that covers politics and culture in the city.[269] The River View Observer is another weekly published in the city and distributed throughout the county. Another countywide weekly, El Especialito, also serves the city.[270] The Jersey City Independent is an online newspaper covering Jersey City and surrounding municipalities. It also publishes JCI Magazine, a print quarterly magazine.[271] The Daily News maintains extensive publishing and distribution facilities at Liberty Industrial Park.[115]
WFMU 91.1FM (WMFU 90.1 FM in the Hudson Valley), the longest-running freeform radio station in the United States, moved to Jersey City in 1998.[272]WSNR-620 AM is also licensed in the city.
Jersey City is the filming location for the 2012 reality television series Snooki & JWoww, a spinoff of Jersey Shore that stars Nicole "Snooki" Polizzi and Jennifer "JWoww" Farley living at a former firehouse at 38 Mercer Street at Grove Street in Downtown Jersey City.[273]
Transportation
Of all Jersey City commuters, 8.17% walk to work, and 46.62% take public transit.[274] This is the second highest percentage of public transit riders of any city with a population of 100,000+ in the United States, behind only New York City and ahead of Washington, D.C. 40.67% of Jersey City households do not own an automobile, the second-highest of all cities in the United States with 50,000 to 250,000 residents.[274]
Air
Newark Liberty International Airport (EWR), the closest of the metropolitan area's three major airports
LaGuardia Airport (LGA), in northern Queens
John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK), on Jamaica Bay in southern Queens
Teterboro Airport, in the Hackensack Meadowlands, serves private and corporate planes- Newport Helistop Heliport, at Hudson River at Newport[275]
Mass transit
Rail

Hudson-Bergen Light Rail
Hudson-Bergen Light Rail: One of the most popular forms of transportation in the city. Of the 24 HBLR stations that connect its three terminus points, 13 are located in Jersey City.[276]
PATH: 24-hour rapid transit system with four stations in Jersey City: Exchange Place, Newport, Grove Street, and Journal Square to Hoboken Terminal (HOB), midtown Manhattan (33rd) (along 6th Ave to Herald Square/Pennsylvania Station), World Trade Center (WTC), and Newark Penn Station (NWK).[277]
Hoboken Terminal-NJ Transit Hoboken Division: Main Line (to Suffern, and in partnership with MTA/Metro-North, express service to Port Jervis), Bergen County Line, and Pascack Valley Line, all via Secaucus Junction (where transfer is possible to Northeast Corridor Line); Montclair-Boonton Line and Morris and Essex Lines (both via Newark Broad Street Station); North Jersey Coast Line (limited service as Waterfront Connection via Newark Penn Station to Long Branch and Bay Head); Raritan Valley Line (limited service via Newark Penn Station).[278]
Water
NY Waterway ferries operate between Paulus Hook Ferry Terminal, Liberty Harbor, Port Liberté to Manhattan at Battery Park City Ferry Terminal, Pier 11/Wall Street, and West Midtown Ferry Terminal, where free transfer is available to a variety of "loop" buses.[279]
Statue Cruises provides service to and between Ellis Island and Liberty Island[280][281]
Liberty Water Taxi operates ferries between Liberty Landing Marina, Warren Street and the World Financial Center.[282]
Bus
The Journal Square Transportation Center, Exchange Place and Hoboken Terminal (just over the city line's northeast corner) are major origination/destination points for buses. Service is available to numerous points in Jersey City, Hudson County, and some suburban areas as well as to Newark on the 1, 2, 6, 10, 22, 64, 67, 68, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 123, 125, 305, 319 lines.[283] Also serving Jersey City are various lines operated by Academy Bus and A&C Bus. Increased use of jitneys, locally known as dollar vans, have greatly affected travel patterns in Hudson County, leading to decreased bus ridership on traditional bus lines. After studies examining existing systems and changes in public transportation usage patterns it was determined that a Journal Square-Bayonne bus rapid transit system should be investigated. In 2012, the Board of Chosen Freeholders authorized the identification of possible BRT corridors.[284][285][286][287][288]
As of 2016[update] two Taiwanese airlines, China Airlines and EVA Air, provide private bus services to and from John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York City for customers based in New Jersey. These bus services stop in Jersey City.[289][290]
Road

Entrance to the Holland Tunnel, which carries high amounts of vehicular traffic from New Jersey to Lower Manhattan
As of May 2010[update], the city had a total of 218.57 miles (351.75 km) of roadways, of which 189.88 miles (305.58 km) were maintained by the municipality, 10.34 miles (16.64 km) by Hudson County and 12.23 miles (19.68 km) by the New Jersey Department of Transportation and 6.12 miles (9.85 km) by the New Jersey Turnpike Authority.[291]
Holland Tunnel: From Boyle Plaza in downtown Jersey City to its eastern terminus at Canal Street, Manhattan (carries Interstate 78 and Route 139)
Highways include the New Jersey Turnpike Extension (Interstate 78); the Pulaski Skyway (U.S. Route 1/9), Route 139 and Route 440.
Bike

East Coast Greenway dedication ceremony
A part of the East Coast Greenway, a planned unbroken bike route from Maine to the Florida Keys, will travel through the city. In June 2012, part of the route was officially designated in Lincoln Park and over the Lincoln Highway Hackensack River Bridge.[292][293] Both the Hudson River Waterfront Walkway and Hackensack RiverWalk are bicycle friendly.[294] In April 2012, the city initiated the Morris Canal Greenway Plan to investigate the establishment of a greenway, including a bicycle path, that would follow the route of the Morris Canal to the greatest extent possible.[295][296][297] in the same month, the city established bikes lanes along the length Grove Street, originally meant to temporary. In December 2012, the city announced that Grove Street lanes would become permanent and that it would add an additional 54 miles (87 km) of both dedicated and shared bike lanes.[298]The Harbor Ring is an initiative to create a 50-mile bike route along the Lower Hudson River, Upper New York Bay, and Kill van Kull that would incorporate bike paths in the city.[299][300][301] In 2013, the city simplified the application and reduced the cost for business and residences to install bike racks as well as making them obligatory for certain new construction projects.[302] Hudson County has initiated exploration of a bike-share program.[303] Jersey City, Hoboken and Weehawken intended to operate the program starting 2014[304] but delayed the launch due to lack of sponsorship. The revamped program officially launched on September 21, 2015 as Citi Bike with membership working in New York City.[305]
Modal characteristics
Jersey City has a high percentage of residents who commute without a car. In 2015, 40.1 percent of city Jersey City households were without a car, which decreased to 37.1 percent in 2016. The national average was 8.7 percent in 2016. Jersey City averaged 0.85 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8 per household.[306]
Notable people
Sister cities
Jersey City has participated in the sister city program since establishing a relationship with Cusco, Peru in 1988. Currently they have relationships with 12 international cities, showing a spirit of economic and cultural exchange and mutual friendship.[307]
|
|
See also
- Bergen Township, Bergen County, New Jersey (Historical 1893)
- Demographics of New Jersey
- Filipinos in the New York City metropolitan region
- Gateway Region
- Gold Coast, New Jersey
- St. Mark Coptic Orthodox Church (Jersey City, New Jersey)
- Timeline of Jersey City area railroads
References
^ Speiser, Matthew. "NJCU business school plans to turn 'Wall Street West' into learning environment', The Jersey Journal, February 10, 2015. Accessed June 1, 2015. "Downtown Jersey City, also known as "Wall Street West," will now serve as more than just a financial hub for New Jersey."
^ Kaulessar, Ricardo. "Why do people call Jersey City 'Chilltown'?", The Hudson Reporter, April 19, 2005. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Hortillosa, Summer Dawn. "Is Jersey City New York City's 'Sixth Borough'?", The Jersey Journal, May 6, 2014. Accessed July 18, 2017. "Is Jersey City really the 'Sixth Borough?' The city picked up the nickname for its proximity to New York City and its close relationship with its sister city."
^ "Jersey City: America's Golden Door". JC Online. 2007. Retrieved July 29, 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "The Golden Door..." Random Number. Archived from the original on November 12, 2012. Retrieved July 29, 2017.
^ "Jersey City America's Golden Door". Legal Force Trademarks. Retrieved July 29, 2017.
^ "Jersey City: "Wall Street West"". Business Weekly. October 28, 2001. Retrieved July 29, 2017.
^ "Hudson Shakespeare Company". Hudson Shakespeare Company. Retrieved July 29, 2017.
^ Staff. "Topics of the Week", The New York Times, August 7, 1909. Accessed December 21, 2011. "The seal of the city with the popular motto, 'Let Jersey Prosper,' appears on the cover."
^ "A New Effort From a 'New' Jersey City Urges, 'Make It Yours'". New York Times. October 6, 2014. Retrieved October 2, 2018.
^ abcdef 2010 Census Gazetteer Files: New Jersey County Subdivisions, United States Census Bureau. Accessed May 21, 2015.
^ ab US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
^ ab Mayor's Office, City of Jersey City. Accessed January 27, 2018.
^ 2017 New Jersey Mayors Directory, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs. Accessed May 30, 2017.
^ ab [1], Hudson County View. Accessed April 14, 2018.
^ ab City Clerk, City of Jersey City. Accessed January 27, 2018.
^ ab 2012 New Jersey Legislative District Data Book, Rutgers University Edward J. Bloustein School of Planning and Public Policy, March 2013, p. 139.
^ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: City of Jersey City, Geographic Names Information System. Accessed March 6, 2013.
^ abcdefgh DP-1 – Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Jersey City city, Hudson County, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 21, 2011.
^ abc Municipalities Grouped by 2011–2020 Legislative Districts, New Jersey Department of State, p. 13,14. Accessed January 6, 2013.
^ abc Table DP-1. Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2010 for Jersey City Archived January 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine., New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed December 21, 2011.
^ abc PEPANNRES - Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2017 - 2017 Population Estimates for New Jersey municipalities, United States Census Bureau. Accessed October 23, 2018.
^ Cite error: The named referencePEPANNRSIPwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
^ Look Up a ZIP Code for Jersey City, NJ, United States Postal Service. Accessed September 5, 2011.
^ Area Code Lookup – NPA NXX for Jersey City, NJ, Area-Codes.com. Accessed April 1, 2015.
^ American FactFinder, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
^ A Cure for the Common Codes: New Jersey, Missouri Census Data Center. Accessed August 14, 2012.
^ US Board on Geographic Names, United States Geological Survey. Accessed September 4, 2014.
^ abc The Counties and Most Populous Cities and Townships in 2010 in New Jersey: 2000 and 2010 Archived February 21, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., United States Census Bureau. Accessed November 7, 2011.
^ New Jersey County Map, New Jersey Department of State. Accessed July 10, 2017.
^ Stirling, Stephen. "What are N.J.'s fastest growing and shrinking towns?", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, May 21, 2015. Accessed June 1, 2015. "Jersey City has gained nearly 15,000 residents since 2010, making it the fastest growing municipality in the state and a symbol of the Garden State's reinvigorated urban core."
^ ab State & County QuickFacts – Jersey City (city), New Jersey Archived May 8, 2012, at the Wayback Machine., United States Census Bureau. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ PEPANNRSIP - Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places of 50,000 or More, Ranked by July 1, 2017 Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2017 - United States -- Places of 50,000+ Population from the 2017 Population Estimates, United States Census Bureau. Accessed October 23, 2018.
^ Greenfield, Douglas J.; and Hsu, Naomi. Sandy Recovery Strategic Planning Report; A Strategic Plan for Resilience Archived December 16, 2016, at the Wayback Machine., City of Jersey City, August 2014. Accessed November 14, 2016. "Jersey City was inundated by Hurricane Sandy all along its 30.7 miles of waterfront of rivers and bays. Flood waters came in from the Hackensack River and Newark Bay to the west and from the Hudson River and Upper New York Bay to the east."
^ Kaysen, Ronda. "Moving to Jersey City? Join the Club",The New York Times, February 12, 2016. Accessed August 22, 2018.
^ [2] Accessed July 8, 2017.
^ A Vision for Smart Transit in Jersey City, United States Department of Transportation, February 4, 2016. Accessed July 18, 2017. "Development along the Hudson River waterfront led to the development of the 'Wall Street West' financial district, one of the largest centers of banking and finance in the nation."
^ Staff. Population and Housing Archived June 2, 2013, at the Wayback Machine., Jersey City Economic Development Corporation. Accessed November 12, 2012. "Although the 5% population growth in Jersey City during the 1990s was below growth in the rest of Hudson County, the state and the nation, it was a reversal of five decades of population decline. Between 1930 and 1980, the number of Jersey City residents had dropped by almost 30% from a peak of 316,715 persons in 1930 to 223,532 persons in 1980."
^ Table 7. Population for the Counties and Municipalities in New Jersey: 1990, 2000 and 2010 Archived May 20, 2013, at the Wayback Machine., New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development, February 2011. Accessed November 12, 2012.
^ Jersey City Past and Present: Pavonia, New Jersey City University. Accessed May 10, 2006.
^ A Virtual Tour of New Netherland, New Netherland Institute. Accessed May 10, 2006.
^ Ellis, Edward Robb. The Epic of New York City, p. 38. Old Town Books, 1966.
ISBN 9780786714360.
^ Jersey City's Oldest House, Jersey City History. Accessed September 11, 2007.
^ Karnoutsos, Carmela. Summit House/Newkirk House Archived October 3, 2015, at the Wayback Machine., Jersey City Past and Present, New Jersey City University. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Karnoutsos, Carmela. Van Vorst House 531 Palisade Avenue, Jersey City Past and Present, New Jersey City University. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Jersey City Heights/Van Vorst House, Forgotten New York, February 28, 2008. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ Olszewski, Anthony. From Before the Revolutionary War! Jersey City's Oldest House, Jersey City History, 2002. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ Zinsli, Christopher. "Jersey City's Underground Railroad history: Thousands of former slaves sought freedom by passing through Jersey City", The Hudson Reporter, March 23, 2007. Accessed April 1, 2015. "New Jersey alone had as many as four main routes, all of which converged in Jersey City.... As the last stop in New Jersey before fugitive slaves reached New York, Jersey City played an integral role – by some estimates, more than 60,000 escaped slaves traveled through Jersey City."
^ abc Snyder, John P. The Story of New Jersey's Civil Boundaries: 1606–1968, Bureau of Geology and Topography; Trenton, New Jersey; 1969. pp. 146–147. Accessed July 27, 2013.
^ ab Winfield, Charles Hardenburg. "History of the County of Hudson, New Jersey, from Its Earliest Settlement to the Present Time", p. 289. Kennard & Hay Stationery M'fg and Print. Co., 1874. Accessed December 21, 2011.
^ Staff. "The New Government of Jersey City – The Subordinate Offices", The New York Times, April 25, 1870. Accessed December 21, 2011. "The new City Government of Jersey City goes into operation on the first Tuesday in May."
^ "Municipal Incorporations of the State of New Jersey (according to Counties)" prepared by the Division of Local Government, Department of the Treasury (New Jersey); December 1, 1958, p. 78 – Extinct List.
^ from epitaph of Job Mail, in Plainfield Daily Press, January 30, 1891.
^ "A Handsome Building: The Erie Railway's New Station at Jersey City.", The New York Times, December 4, 1887. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ Condit, Carl (1980). The Port of New York. A History of the Rail and Terminal System from the Beginnings to Pennsylvania Station (Volume 1). University of Chicago Press. pp. 46–52, 152–168. ISBN 978-0-226-11460-6.
^ ab Liberty State Park: CRRNJ, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ "Finish Erie Tunnel in Jersey Heights", The New York Times, June 13, 1910. Accessed July 18, 2017.
^ The Bergen Arches of the Erie Railroad Archived December 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine., Jersey City Landmarks Conservancy. Accessed April 1, 2015.
^ Leal, John L. (1909). "The Sterilization Plant of the Jersey City Water Supply Company at Boonton, N.J." Proceedings American Water Works Association. pp. 100–9.
^ "A Byte Out of FBI History; 1916 'Black Tom' Bombing Propels Bureau Into National Security Arena", Federal Bureau of Investigation, July 30, 2004. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Jersey City History website
^ Alexander, Jack. "Boss Hague:King Hanky-Panky of Jersey", copy of article from The Saturday Evening Post, October 26, 1940, available at the City of Jersey City website. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Staff. "Hague's End", Time (magazine), May 23, 1949. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ ab Grundy, J. Owen (1975). The History of Jersey City (1609–1976). Jersey City: Walter E. Knight, Progress Printing Company. p. 5.
^ "Hudson County's Degradation. Where Official Corruption Runs Riot is Not Concealed." The New York Times, October 22, 1893
^ Strum, Charles. "Another Milepost on the Long Trail of Corruption in Hudson County", The New York Times, December 19, 1991. Accessed April 1, 2015.
^ Strunsky, Steve. "Why Can't Hudson County Get Any Respect?; Despite Soaring Towers, Rising Property Values and Even a Light Rail, the Region Struggles to Polish Its Image", The New York Times, January 14, 2001. Accessed April 1, 2015.
^ Jacobs, Andrew. "A City Whose Time Has Come Again; After Years of Deprivation, Jersey City, an Old Industrial Powerhouse, Is Remaking Itself", The New York Times, April 30, 2000. Accessed April 1, 2015.
^ Hudson-Bergen Light Rail schedule (PDF)
^ Healy, Jerramiah. "Renaissance on the Waterfront and Beyond: Jersey City's Reach for the Stars" Archived July 26, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.. New Jersey State League of Municipalities.
^ Murphy, Meredith R. "Jersey City Passes Paid Sick Leave Law", The National Law Review, October 16, 2013. Accessed April 1, 2015.
^ Johnson, Brent. "Trump: 'Thousands' in Jersey City cheered on 9/11", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, November 22, 2015. Accessed March 16, 2015. "Republican presidential front-runner Donald Trump on Saturday continued his call for surveillance of 'certain' U.S. mosques — and at one point supported his case by claiming he witnessed 'thousands and thousands of people' cheering in Jersey City as the Twin Towers fell on Sept. 11, 2001."
^ Population of the 100 Largest Urban Places: 1990, United States Census Bureau, June 15, 1998. Accessed November 27, 2011.
^ Strunsky, Steve. "CITIES; Bright Lights, Big Retail", The New York Times, December 9, 2001. Accessed April 1, 2015. "Macy's has arrived on this former industrial shoreline. And with it, at least in retail terms, so has Jersey City.... While hardly Saks Fifth Avenue or even Neiman Marcus, Macy's is certainly the most upscale department store in this city, whose status as virtually a sixth borough of New York has become increasingly obvious as jobs jump across the Hudson, rents rise like skyscrapers and trendier residents look around for places to lighten their wallets."
^ Holusha, John. "Commercial Property / The Jersey Riverfront; On the Hudson's West Bank, Optimistic Developers", The New York Times, October 11, 1998. Accessed August 22, 2018. "'That simply is out of the question in midtown,' he said, adding that some formerly fringe areas in Midtown South that had previously been available were filled up as well. Given that the buildings on the New Jersey waterfront are new and equipped with the latest technology and just a few stops on the PATH trains from Manhattan, they become an attractive alternative. 'It's the sixth borough', he said."
^ Belson, Ken. "In Stamford, a Plan to Rebuild an Area and Build an Advantage", The New York Times, May 21, 2007. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Hudson County New Jersey Street Map. Hagstrom Map Company, Inc. 2008. ISBN 0-88097-763-9.
^ Lynch, Kevin. Images of the City, p. 26. MIT Press, 1960.
ISBN 978-0-262-62001-7.
^ Gabrielan, Randall (1999). Jersey City in Vintage Postcards. Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7385-4954-5
^ Lagorio, Christine. "Close-Up on the Jersey City Waterfront", The Village Voice, January 11, 2005. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ Staff. "The New Jersey Suburbs How New York is Extending on the West Side of the Hudson", The New York Times, April 22, 1872. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ ab "JC Ward map". Jerseycityindependent.com. January 6, 2009. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
^ http://abclocal.go.com/wabc/firstatfour/story?section=firstatfour&id=8452406[permanent dead link]
^ McDonald, Terrence T. "Construction to begin on $4M Grove Street PATH station elevator", The Jersey Journal, April 21, 2015. Accessed March 16, 2016. "Jersey City — Construction is set to begin on a $4.04 million project to add a handicapped-accessible entrance to the Grove Street PATH station."
^ McDonald, Terrence T. "Jersey City development boom reaching new heights", The Jersey Journal, March 13, 2015. Accessed March 16, 2016. "Later in the year, 70 Columbus -- which features 545 rental units, 20,000 square feet of commercial space adjacent to the Grove Street PATH station -- is expected to be completed, while construction on its sister tower, 90 Columbus, which will have 630 units in 50 stories, should begin by December."
^ Haddon, Heather. "Embankment Deal Stalls", The Wall Street Journal, September 11, 2012. Accessed March 16, 2016. "A deal to turn an abandoned elevated railway in Jersey City into a park in the spirit of Manhattan's High Line has hit a roadblock, with one of the parties involved balking on a settlement proposed to resolve the decadelong dispute."
^ Goldberger, Paul. "Shanghai on the Hudson; Jersey City wants to be like lower Manhattan, only neat and clean.", The New Yorker, August 2, 2004. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ Jersey City Facts, The Skyscraper Center. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ McDonald, Terrence T. "Plans for N.J.'s new tallest tower get federal OK", The Jersey Journal, January 12, 2016. Accessed January 14, 2016. "China Oversea America is behind the project, which is set to include 781 condo units. Originally planned to rise 950 feet and include 95 stories, the newest plans have it topping out at 900 feet and 79 stories."
^ Hampson, Rick. "Model of urban future: Jersey City?", USA Today, April 16, 2007. Accessed December 21, 2011. "This was the former Jersey City Medical Center, a cluster of Art Deco buildings on a rise in the center of the city, far from the booming waterfront. Now the medical center was becoming The Beacon condominium complex, one of the nation's largest historic renovation projects."
^ The Heights, Jersey City Redevelopment Agency. Accessed December 21, 2011.
^ Jersey City, New Jersey Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase), Weatherbase. Accessed March 16, 2016.
^ Census Estimates for New Jersey April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2017, United States Census Bureau. Accessed October 23, 2018.
^ Compendium of censuses 1726–1905: together with the tabulated returns of 1905, New Jersey Department of State, 1906. Accessed July 27, 2013.
^ Bowen, Francis. American Almanac and Repository of Useful Knowledge for the Year 1843, p. 231, David H. Williams, 1842. Accessed July 27, 2013. Population on 1840 of 3,033 is listed, 39 less than shown in other sources.
^ Raum, John O. The History of New Jersey: From Its Earliest Settlement to the Present Time, Volume 1, p. 278, J. E. Potter and company, 1877. Accessed July 27, 2013. "Jersey City is divided into sixteen wards and contained in 1850 a population of 6,856; in 1860, 29,226; and in 1870, 82,546. The population of this city has increased with wonderful rapidity having more than trebled within the last decade."
^ Debow, James Dunwoody Brownson. The Seventh Census of the United States: 1850, p. 139. R. Armstrong, 1853. Accessed July 27, 2013.
^ Staff. A compendium of the ninth census, 1870, p. 259. United States Census Bureau, 1872. Accessed July 27, 2013.
^ Porter, Robert Percival. Preliminary Results as Contained in the Eleventh Census Bulletins: Volume III – 51 to 75, p. 98. United States Census Bureau, 1890. Accessed July 27, 2013.
^ Thirteenth Census of the United States, 1910: Population by Counties and Minor Civil Divisions, 1910, 1900, 1890, United States Census Bureau, p. 337. Accessed July 27, 2013.
^ Fifteenth Census of the United States : 1930 – Population Volume I, United States Census Bureau, p. 714. Accessed December 21, 2011.
^ Table 6. New Jersey Resident Population by Municipality: 1930 – 1990 Archived May 10, 2015, at the Wayback Machine., New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed June 28, 2015.
^ abcde Census 2000 Profiles of Demographic / Social / Economic / Housing Characteristics for Jersey City city, New Jersey Archived June 1, 2012, at the Wayback Machine., United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 27, 2013.
^ abcde DP-1: Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2000 – Census 2000 Summary File 1 (SF 1) 100-Percent Data for Jersey City city, Hudson County, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 27, 2013.
^ abc Gibson, Campbell; and Jung, Kay. "Historical Census Statistics On Population Totals By Race, 1790 to 1990, and By Hispanic Origin, 1970 to 1990, For Large Cities And Other Urban Places In The United States" Archived August 6, 2012, at WebCite, United States Census Bureau, February 2005. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ ab From 15% sample
^ ab Wirstiuk, Laryssa. "Neighborhood Spotlight: Journal Square", Jersey City Independent, April 21, 2014. Accessed July 3, 2018. "India Square, for example, is situated between John F. Kennedy Boulevard and Tonnelle Avenue on Newark Ave., and is home to the highest concentration of Asian Indians in the Western Hemisphere."
^ DP03: Selected Economic Characteristics from the 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates for Jersey City city, Hudson County, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 27, 2013.
^ Hayes, Melissa. "2010 Census road tour stops in Jersey City", The Jersey Journal, January 5, 2010. Accessed July 8, 2015.
^ Hunger, Matt. "Jersey City Hires Outside Firm to Help Challenge 2010 Census Count", Jersey City Independent, June 16, 2011. Accessed July 8, 2015.
^ McDonald, Terrence T. "Jersey City paying consultant $25,000 to challenge Census count", The Jersey Journal, June 16, 2011. Accessed July 8, 2015. "Jersey City is spending $25,000 to hire an outside consultant to help it challenge recent U.S. Census figures that city officials believe underestimate the city's total population.... The city feels it has been undercounted by as many as 30,000 residents, said city spokeswoman Jennifer Morrill."
^ Hunger, Matt. "Firm's Preliminary Findings Say 2010 Census Count Missed 19,000 Housing Units in Jersey City", Jersey City Independent, September 1, 2011. Accessed July 8, 2015.
^ Cities with 100,000 or More Population in 2000 ranked by Population, 2000 in Rank Order, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 5, 2011.
^ Cities with 100,000 or More Population in 2000 ranked by Population per Square Mile, 2000 in Rank Order Archived June 29, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 5, 2011.
^ abc Jersey City, New Jersey, City-Data. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ abcd Hortillosa, Summer Dawn. "Jersey City named most diverse city in America: report", The Jersey Journal, February 17, 2015. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ ab McKee, Spencer. "53 Things You Probably Didn't Know About Jersey City", Movoto. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ abcdefghijk DP05: ACS Demographic And Housing Estimates 2012–2016 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates – Jersey City city, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed October 3, 2018.
^ abcdefghi DP-1: Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 – Demographic Profile Data – Jersey City city, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed March 16, 2016.
^ Speiser, Matthew. "Cuban festival takes over Exchange Place on Jersey City waterfront", The Jersey Journal, May 31, 2015. Accessed March 16, 2016. "The salsa music was so loud they probably could have heard it across the river in Manhattan. Such was the atmosphere at the 15th annual Cuban festival at Exchange Place this afternoon on the Jersey City waterfront."
^ Kiniry, Laura. Moon Handbooks New Jersey, Avalon Travel Publishing, 2006. pg. 34
ISBN 1-56691-949-5
^ "India Square" Archived October 15, 2013, at the Wayback Machine., accessed July 26, 2006
^ Rogoza, Rafal. "Thousands of colorful revelers partake in 21st Annual Phagwah Parade in Jersey City", The Jersey Journal, March 30, 2013, updated March 31, 2013. Accessed July 6, 2015. "The 29-year-old Princeton Avenue resident was one of the thousands of people who descended on Lincoln Park in Jersey City this afternoon for the 21st Annual Phagwah Parade and Holi Hai Day festivities, a colorful Hindu spring harvest tradition that is celebrated by revelers who playfully shower each other with various colors of organic powder."
^ Speiser, Matthew. "Colorful Holi Hai festival in Jersey City celebrates rites of spring", The Jersey Journal, March 29, 2015. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ Timeline, Filipino-Americans in Jersey City. Accessed June 28, 2017.
^ Silvestre, Edmund M. "Phil-Am Food's future is now", Filipino Reporter, March 2, 2014. Accessed November 14, 2016. "For four decades now, Phil-Am Food, the largest Filipino-owned grocery store on the U.S. East Coast, has served as a bastion of vibrant Filipino community here as it consistently provides patrons a sense of being 'back home' with its extensive array of Philippine food products no other Pinoy store in this coast can match."
^ "The Standard – Latest News in the Philippines". manilastandardtoday.com. Retrieved September 23, 2015.
^ Nash, Margo. "Jersey Footlights", The New York Times, May 1, 2005. Accessed August 22, 2018. "The Knights made an agreement five years ago with Bret Schundler, who was mayor then, allowing them to lease a street corner at Columbus Drive and Brunswick Street for 20 years at $1 a year to build tiny Rizal Park with a statue of Rizal (1861-1896). The city paid for the upkeep, the Knights paid for the monument and insurance. Each year since then the Knights have held ceremonies at the park on June 19 to mark Rizal's birth."
^ Kowsh, Kate. "Amid Delays, 33rd Annual Santacruzan procession circles downtown neighborhood", The Jersey Journal, May 29, 2011. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ Stirling, Stephen. ""The 44 N.J. towns where English is not the dominant language", NJ Adavance Media for NJ.com, November 14, 2016. Accessed November 14, 2016. "When divided up by language, rather than region, a clearer picture emerges of the patchwork of immigrant communities represented in Jersey City. While English and Spanish are the two main languages spoken here, Tagalog, a Filipino dialect, is third.
^ Bradsher, Keith; Tang, Ailin; and Drucker, Jesse. "Trump Looms as Kushner Companies Courts Investors in China", The New York Times, May 7, 2017. Accessed June 28, 2017. "At the event in Beijing, Mr. Kushner's sister, Nicole Meyer, cited her brother's service to the company, which he led as chief executive until January. She said the project in Jersey City 'means a lot to me and my entire family.'"
^ ACS Demographic And Housing Estimates 2012–2016 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates for Hudson County, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed October 3, 2018.
^ DP-1 – Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 from 2010 Demographic Profile Data, United States Census Bureau. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ Schmidt, Margaret. "Kenyan immigrants in Jersey City celebrate Obama", The Jersey Journal, February 15, 2009. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ Duffy, Peter. "Kenyan Unrest, Jersey Style", The Village Voice, February 5, 2008. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ Sheingold, Dave. "North Jersey black families leaving for lure of new South", The Record (Bergen County), February 20, 2011. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ Hudson County Population and Races, USA.com. Accessed June 28, 2017.
^ New Jersey Arab as First Ancestry Population Percentage County Rank, USA.com. Accessed June 28, 2017.
^ Cusido, Carmen. "Embracing IslamWhy Latinos are drawn to Muslim beliefs, culture.", New Jersey Monthly, February 8, 2010. Accessed June 28, 2017.
^ Staff. "Where do gay couples live in New Jersey?", Out in Jersey, March 16, 2014. Accessed July 18, 2017. "Essex County leads with the most same-sex couples households at 2,819 with Hudson County close behind at 2,726."
^ MELISSA HAYES, KIBRET MARKOS, CHRIS HARRIS AND SCOTT FALLON (October 21, 2013). "Christie drops appeal of ruling allowing gay marriage in NJ". North Jersey Media Group. Archived from the original on February 9, 2014. Retrieved May 14, 2015.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Carroll, Brendan. "Artists React to Jersey City’s Designation as 10th Most Artistic US City", Jersey City Independent, December 21, 2011. Accessed July 18, 2017. "Jersey City is the tenth most artistic city in the United States, according to a recent ranking by The Atlantic magazine.... Richard Florida, the senior editor of The Atlantic, used data from the U.S. Census Bureau’s American Community Survey to rank cities based on the number of artists who live there compared to the overall population."
^ Florida, Richard. "The Most Artistic Cities in America", CityLab (web magazine), November 30, 2011. Accessed July 18, 2017.
^ ab Sandy Recovery Strategic Planning Report A Strategic Plan for Resilience, City of Jersey City, August 2014. Accessed July 18, 2017. "Jersey City is home to a waterfront regional employment center known as 'Wall Street West,' with 13.3 million square feet of Class A office space located in flood zones. It also has a major shipping port, and sizable manufacturing, wholesale, retail and service sectors. It is an economic engine for the state, and its daytime population swells with visitors and jobs. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, there were 108,914 public and private sector jobs in Jersey City at the beginning of the second quarter in 2011."
^ "Mayor Fulop to Introduce 2017 Budget With No Tax Increase; Fourth Consecutive Year With No Municipal Tax Increase as Fulop Administration Brings Long-Term Fiscal Stability to Jersey City" Archived June 28, 2017, at the Wayback Machine., City of Jersey City, March 22, 2017. Accessed July 18, 2017. "In 2017, the tax base, or ratable base, grew in Jersey City by $136 million due to Fulop Administration policies encouraging economic investment throughout the city. In four years, the tax base has grown by $415 million, with Jersey City having the largest municipal tax base in the state."
^ McDonald, Terrence T. "Jersey City homeowners uneasy as long-delayed revaluation begins", The Jersey Journal, April 21, 2017. Accessed July 18, 2017. "When the reval is complete, city officials expect the city's taxable property base to rise in value to about $26 billion from its current $6.2 billion."
^ "Your Gateway to Opportunity, Enterprise Zone Five Year Strategic Plan 2010" (PDF). Jersey City Economic Development Corporation. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 28, 2013. Retrieved May 23, 2013.
^ Todd, Susan. "Verisk Analytics of Jersey City raises $1.9B in stock offering", The Star-Ledger, October 8, 2009. Accessed October 8, 2009.
^ Lord Abbett: Contact Us, accessed April 2, 2011.
^ Major Employer's List Archived July 18, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., Hudson County Economic Development Corporation, accessed March 18, 2011.
^ Staff. 'Forbes moving into Jersey City offices on Monday, report says", The Jersey Journal, December 12, 2014. Accessed June 1, 2015. "Forbes has committed to spending 10 years in Jersey City, for which it will receive a $27 million Grow New Jersey tax grant because of its pledge to bring at least 350 jobs to the state."
^ "JC Shopping Districts". Jerseycityonline.com. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
^ Urban Enterprise Zone Program, State of New Jersey. Accessed January 8, 2018.
^ New Jersey Urban Enterprise Zone Locations, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs, locations as of January 1, 2017. Accessed January 8, 2018.
^ "NJ Division of Taxation Reminds Consumers & Business Owners That Sales Tax Rate Will Change to 6.625% in the New Year", New Jersey Department of Treasury, press release dated December 27, 2017. Accessed January 8, 2018. "The New Jersey Division of Taxation is reminding business owners that the State Sales and Use Tax rate will be reduced to 6.625% on Jan. 1, 2018.... Rates for State Sales Tax in Urban Enterprise Zones also will change on Jan. 1, 2018. The rate in a designated UEZ will be 50 percent of the Sales Tax rate, or 3.3125 percent. The previous UEZ rate was 3.4375 percent."
^ Urban Enterprise Zones Effective and Expiration Dates, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs. Accessed January 8, 2018.
^ Urban Enterprise Zone Archived October 24, 2017, at the Wayback Machine., Jersey City Economic Development Corporation. Accessed January 9, 2018. "One-third of Jersey City is designated as Urban Enterprise Zone. The Jersey City Urban Enterprise Zone is the largest and most productive UEZ in New Jersey."
^ Jersey City, New Jersey Urban Enterprise Zone Boundary Changes for 2011 Archived October 4, 2015, at the Wayback Machine., Jersey City Economic Development Corporation, May 2011. Accessed January 9, 2018.
^ New York Cross Harbor Railraid website with description of Greenville Yard
^ US Army Corp of Engineers
^ Conte, Michaelangelo (June 19, 2014). "Global Container Terminals in Jersey City unveils $325M expansion project". The Jersey Journal. Retrieved June 25, 2014.
^ Sullivan, Al (June 22, 2014). "JC hosts high tech container port Global unveils most modern facility in the nation". Hudson Reporter. Retrieved June 28, 2014.
^ http://www.northjersey.com/news/mega-ship-s-arrival-in-bayonne-a-sign-of-the-future-1.1628020
^ Hugh R. Morley (April 29, 2015). "Goya Foods opens new HQ-warehouse in Jersey City". North Jersey Media Group. Retrieved May 16, 2015.
^ Bagli, Charles V. "Reebok Founder Proposes 95-Story Tower With Casino for Jersey City", The New York Times, July 10, 2014. Accessed June 1, 2015. "Mr. Fireman, the founder and former chairman of Reebok International, is proposing a $4.6 billion project, including a 95-story skyscraper, adjoining his 160-acre golf course on the Hudson River, at the south end of Jersey City."
^ Associated Press (February 7, 2014). "Sweeney Floats Idea of Casinos in Newark, Camden or Jersey City". NJ.com (powered by Independent Press).
^ Stoltzfus, Duane (June 6, 1991). "Statue Erected as Memorial to Victims of Katyn Massacre". The Record.
^ Lyons, Richard (July 9, 1989). "Jersey City Landmark; Now It's Time to Move the Colgate Clock". The New York Times. Retrieved January 30, 2010.
^ Staff. "Grant to restore Loew's balcony", The Jersey Journal, July 6, 2009. Accessed February 11, 2012. "The Landmark Loew's Jersey Theatre in Jersey City is taking another step toward returning to its former glory, thanks to a grant from The Provident Bank Foundation.... The historic theater is only one of five 'Wonder Theatres' built by movie baron Marcus Lewis outside New York City."
^ Staff, Village Voice (October 20, 2010). "BEST OF NYC®: Landmark Loews Jersey Theater, Best Movie Theater". Village Voice. Retrieved February 12, 2012.
^ Testa, Jim. "Historic White Eagle Hall to officially re-open with first concert", The Jersey Journal, May 3, 2017. Accessed January 27, 2018. "The renovated White Eagle Hall in Downtown Jersey City opens on Friday, May 5, with a ribbon-cutting ceremony by Mayor Steven Fulop, followed by a performance by Jersey City favorite musician sons Rye Coalition.... The historic structure was built by Polish immigrants in 1910 and for much of the 20th century hosted events and programs under the aegis of St. Anthony's Church and High School. For years, the famous St. Anthony's High School basketball team under Hall of Fame coach Bob Hurley practiced at White Eagle Hall, and the wooden boards from that gym floor have been repurposed in modernizing the facility."
^ Net Ops. "JC Free Public Library". Jclibrary.org. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
^ Liberty State Park, New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection. Accessed August 1, 2013.
^ Home Page, Statue Cruises. Accessed August 1, 2013.
^ Staff. "Unofficial Soviet Art On View in Jersey City", The New York Times, October 27, 1981. Accessed April 1, 2015. "The 25th anniversary of nonconformist art in the Soviet Union is being observed by the Museum of Soviet Unofficial Art in Jersey City with an exhibition of 200 works by 70 artists."
^ "Hudson Bergen Light Rail (HBLR)" Archived April 29, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.. Station Reporter. Accessed January 3, 2012.
^ "MLK Station". Subwaynut.com. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
^ Hudson-Bergen Light Rail. world.nycsubway.org. Accessed January 3, 2012.
^ Ciccarelli, Jon. "Hudson Shakespeare Company venues".
^ "Ellen Cantor and Joseph Grigley". Frieze magazine. Jan–Feb 2004. Archived from the original on October 30, 2007.
^ Ward Map, City of Jersey City. Accessed January 27, 2018.
^ City Council, City of Jersey City. Accessed January 27, 2018.
^ 2017 Municipal Data Sheet, City of Jersey City. Accessed January 27, 2018.
^ Municipal Officials, Hudson County, New Jersey Clerk. Accessed January 27, 2018.
^ Hudson County General Election 2017 Statement of Vote November 7, 2017, Hudson County, New Jersey Clerk, updated November 17, 2017. Accessed January 1, 2018.
^ ab Plan Components Report, New Jersey Redistricting Commission, December 23, 2011. Accessed January 6, 2013.
^ 2017 New Jersey Citizen's Guide to Government Archived April 7, 2017, at the Wayback Machine., p. 59, New Jersey League of Women Voters. Accessed May 30, 2017.
^ Districts by Number for 2011–2020, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 6, 2013.
^ ab 2011 New Jersey Citizen's Guide to Government, p. 59, New Jersey League of Women Voters. Accessed May 22, 2015.
^ New Jersey Congressional Districts 2012–2021: Jersey City Map, New Jersey Department of State. Accessed January 6, 2013.
^ Directory of Representatives: New Jersey, United States House of Representatives. Accessed January 5, 2012.
^ Directory of Representatives: New Jersey, United States House of Representatives. Accessed January 5, 2012.
^ About Cory Booker, United States Senate. Accessed January 26, 2015. "He now owns a home and lives in Newark's Central Ward community."
^ Biography of Bob Menendez, United States Senate, January 26, 2015. "He currently lives in Paramus and has two children, Alicia and Robert."
^ Senators of the 114th Congress from New Jersey. United States Senate. Accessed January 26, 2015. "Booker, Cory A. - (D - NJ) Class II; Menendez, Robert - (D - NJ) Class I"
^ Legislative Roster 2018-2019 Session, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 22, 2018.
^ District 31 Legislators, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 22, 2018.
^ Legislative Roster 2018-2019 Session, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 22, 2018.
^ District 33 Legislators, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 22, 2018.
^ Governor Phil Murphy, State of New Jersey. Accessed January 16, 2018.
^ Lieutenant Governor Oliver, State of New Jersey. Accessed January 16, 2018. "Assemblywoman Oliver has resided in the City of East Orange for over 40 years."
^ Thomas A. Degise, Hudson County Executive, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 5, 2011.
^ Freeholder District 1, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 15, 2011.
^ abcdef Bichao, Sergio (June 3, 2008). "Hudson County results". nj.com. Retrieved 2011-01-15.
^ abcde Freeholder Biographies, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 15, 2011.
^ Freeholder District 2, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 15, 2011.
^ Freeholder District 3, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 15, 2011.
^ Freeholder District 4, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 15, 2011.
^ Freeholder District 5, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 15, 2011.
^ Freeholder District 8, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 15, 2011.
^ Voter Registration Summary – Hudson, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, March 23, 2011. Accessed November 13, 2012.
^ "Presidential General Election Results – November 6, 2012 – Hudson County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. March 15, 2013. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
^ "Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast – November 6, 2012 – General Election Results – Hudson County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. March 15, 2013. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
^ 2008 Presidential General Election Results: Hudson County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 23, 2008. Accessed November 13, 2012.
^ 2004 Presidential Election: Hudson County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 13, 2004. Accessed November 13, 2012.
^ "Governor – Hudson County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 29, 2014. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
^ "Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast – November 5, 2013 – General Election Results – Hudson County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 29, 2014. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
^ 2009 Governor: Hudson County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 31, 2009. Accessed November 13, 2012.
^ Fire Department Archived April 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine., City of Jersey City. Accessed June 16, 2016.
^ Steadman, Andrew. "Bayonne firefighters participate in mock disaster drills in Newark", The Jersey Journal, May 1, 2012. Accessed August 22, 2018. "According to the press release, the Metro USAR Strike Team is made up of nine fire departments from Bayonne, Elizabeth, Hackensack, Hoboken, Jersey City, Newark, Paterson, Morristown as well as the five-municipality North Hudson Regional Fire and Rescue Agency."
^ History of the JCPD, Jersey City Police Department. Accessed June 16, 2016.
^ About, New Jersey City University. Accessed June 28, 2017. "New Jersey City University provides students the best of many worlds: small classes led by world-class faculty mentors, a broad array of high-quality undergraduate and graduate degree programs, and the lowest tuition offered by a four-year public university in the state of New Jersey—all on a thriving campus in bustling, cosmopolitan Jersey City."
^ Campus Map, Saint Peter's University. Accessed June 28, 2017.
^ Jersey City Campus, University of Phoenix. Accessed June 28, 2017. "The University of Phoenix Jersey City Campus is conveniently located on Town Square Place in Jersey City, New Jersey."
^ Jersey City Directions, Rutgers University. Accessed June 28, 2017. "The Rutgers Part-Time MBA satellite location at Harborside in Jersey City brings the Rutgers MBA experience to your doorstep."
^ College Directions & Map Archived January 19, 2012, at the Wayback Machine., Hudson County Community College. Accessed December 21, 2011.
^ Abbott School Districts, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed June 15, 2016.
^ About SDA Archived August 16, 2016, at the Wayback Machine., New Jersey Schools Development Authority. Accessed January 8, 2017.
^ SDA Capital Program Archived November 9, 2016, at the Wayback Machine., New Jersey Schools Development Authority. Accessed January 8, 2017.
^ District information for Jersey City Public Schools, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed December 7, 2016.
^ School Data for the Jersey City Public Schools, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed December 7, 2016.
^ Academy of the Sciences at William L. Dickinson High School, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Academy of International Enterprise at James J. Ferris High School, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Infinity Institute, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Innovation High School, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Liberty High School, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Academy of Governance and Social Sciences at Lincoln High School, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Dr. Ronald E. McNair Academic High School, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Renaissance Institute, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Academy of the Arts at Henry Snyder High School, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Schools, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ New Jersey School Directory for the Jersey City Public Schools, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed May 8, 2017.
^ Staff. "2010 Top High Schools", New Jersey Monthly, August 16, 2010. Accessed December 21, 2011.
^ Staff. "36 N.J. high schools named among Newsweek's top 1000 in America", The Star-Ledger, June 21, 2011. Accessed December 21, 2011.
^ Goodnough, Abby. "Once Upon a Time, When High Schools Were Palaces", The New York Times, October 6, 1996. Accessed December 21, 2011. "NINETY years ago, an enormous Beaux Arts building went up on a hill overlooking the Hudson River. It had Corinthian columns, terrazzo floors and a vestibule lined with English marble. It could have passed for a palace, or at least a palatial estate. But it was neither. It was, in fact, William L. Dickinson High School, the first public secondary school in Jersey City.... When it opened in 1906, Dickinson had a 2,000-seat auditorium used not just for school functions but for political debates, plays and concerts."
^ Alexander D. Sullivan School - PS 30, Jersey City Public Schools. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ High Schools Archived November 5, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., Hudson County Schools of Technology. Accessed November 16, 2011.
^ Staff. "State approves 2 New Jersey City charter schools", The Jersey Journal, January 19, 2011. Accessed November 16, 2011.
^ Ojutiku, Max. "Jersey City charter school to build $12M middle school", The Jersey Journal, April 21, 2016. Accessed November 14, 2016. "A Jersey City charter school has purchased a half-acre parcel of land on Grand Street to make room for its new $12 million middle school. The BelovED Community Charter School's new school building at 535 Grand St. will be 40,000 square feet and serve 240 students in sixth through ninth grades, according to Bret Schundler, a former Jersey City mayor and the Commissioner of Education for New Jersey who serves as chairman of the BelovED Community Charter School Foundation."
^ Hudson County Catholic High Schools, Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Newark. Accessed July 20, 2016.
^ Persaud, Vishal. "Announcement St. Mary High School in Jersey City will close in June has some parents, students and staff stunned", The Jersey Journal, February 9, 2011. Accessed September 2, 2011. "Parents, students and staff at St. Mary High School in Jersey City remained stunned yesterday by Monday's news that the school is closing at the end of June.... St. Mary will graduate 72 seniors in June, which would have put the school's enrollment at 93 among the remaining classes. Ten years ago, St. Mary had 381 students, Lalicato said. At its peak in the mid-1980s, the school had more than 450 students."
^ About Us Archived November 15, 2016, at the Wayback Machine., Our Lady of Czestochowa School. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ Thorbourne, Ken. "Amid economic challenges, Jersey City's Sacred Heart School continues mission", The Jersey Journal, June 26, 2014. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ About Us, Saint Aloysius Elementary Academy. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ History, St. Joseph Catholic School. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ About Us, Saint Nicholas School. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ Hudson County Catholic Elementary Schools, Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Newark. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ 2015 National Blue Ribbon Schools All Public and Private, National Blue Ribbon Schools Program. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ Mueller, Mark. "Which N.J. schools were named National Blue Ribbon schools?", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, September 29, 2015. Accessed November 14, 2016. "Fifteen New Jersey schools have been recognized by the federal government as National Blue Ribbon Schools, a designation that celebrates excellence in academics or progress in closing the achievement gap among groups of students.... Each of the 15 New Jersey schools was chosen for the 'exemplary high performing' category, which weighs state or national tests, high school graduation rates and the performance of subgroups of students, such as those who are economically disadvantaged."
^ Conte, Michaelangelo. "Jersey City losing another Catholic elementary school in June: Our Lady of Mercy Academy", The Jersey Journal, April 13, 2013. Accessed November 14, 2016. "Our Lady of Mercy Academy in Jersey City will close at the end of the 2012-2013 school year. The pre-K through eighth grade school on Bartholdi Avenue opened its doors in 1964. The closures of OLM and Resurrection School at the end of the school year will leave Jersey City with just five Catholic grammar schools."
^ Scrivner, Michael. "St. Anne's School in Jersey City Heights graduates its last class, will close on Thursday", The Jersey Journal, June 12, 2012. Accessed November 14, 2016. "The 112-year-old school at Kennedy Boulevard and Congress Street will close its doors for good on Thursday due to rising debt and declining enrollment, school officials said. At its peak in 1976, the school had more than 700 students. This school year, there were 188 students, down from 240 last year."
^ Our History Archived April 26, 2012, at the Wayback Machine., First Pentecostal Church of God. Accessed January 3, 2012. "First Christian Pentecostal Academy spans from grades K4 through 8th. It is a ministry that God has used and continues to use to serve children and their families."
^ About Us Archived December 21, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., Stevens Cooperative School. Accessed January 3, 2012. Welcome to Stevens Cooperative School, a school for children age two through 8th grade that has since 1949 been a beacon of progressive education in Hudson County.
^ Who We Are: Kenmare High School Archived August 29, 2009, at the Wayback Machine., The York Street Project. Accessed September 2, 2011.
^ http://www.faacademy.org
^ "Genesis Educational Center". Riversidecares.org. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
^ About, Jersey City Art School. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ Staff. "Owners Warn That Hudson County Newspaper Could Be Closed", The New York Times, January 3, 2002. Accessed September 5, 2011.
^ "Jersey City Independent".
^ "El Especial". El Especial. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
^ Germano, Sara (May 18, 2011). "Jersey City Independent". Columbia Journalism Review. Retrieved August 31, 2014.
^ About, WFMU. Accessed November 14, 2016. "WFMU-FM is a listener-supported, non-commercial radio station broadcasting at 91.1 Mhz FM in Jersey City, NJ, right across the Hudson from lower Manhattan. It is currently the longest running freeform radio station in the United States.The station also broadcasts to the Hudson Valley and Lower Catskills in New York, Western New Jersey and Eastern Pennsylvania via its 90.1 signal at WMFU in Mount Hope, NY."
^ "PHOTOS: Snooki, JWoww move into old Jersey City firehouse for 'Jersey Shore' spinoff", The Jersey Journal, February 26, 2012. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ ab Most Public Transit Commuters in Cities with 50,000 to 250,000 Residents, Cars At Work, backed up by the Internet Archive as of October 13, 2007. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Newport Helistop Heliport , SkyVector. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Hudson-Bergen Light Rail System Map, NJ Transit. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Maps & Schedule, Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Hoboken, NJ Transit. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Fares, Routes & Schedules, NY Waterway. Accessed June 1, 2015.
^ Ferry System Map, National Park Service. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ About, Statue Cruises. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ Route, Liberty Landing Ferry. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ Hudson County Bus / Rail Connections. NJ Transit, backed up by the Internet Archive as of May 25, 2009. Accessed September 5, 2011.
^ "Hudson County Jitney Study". North Jersey Transportation Planning Authority. July 2011. Archived from the original on May 18, 2015. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
^ Urbitran Associates (November 2007). "Final Report" (PDF). Hudson County Bus Circulation and Infrastructure Study. NJTPA. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 15, 2013. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
^ NJ Transit; et al. (November 2009). "Executive Summary" (PDF). Final Report Jersey City Local Bus Study. NJT. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 15, 2011. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
^ "Jersey City/Journal Square/Bayonne Bus Rapid Transit Study" (PDF). NJTPA FY 2012–2013 Subregional Studies Program Proposal. NJTPA. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
[permanent dead link]
^ Hack, Charles. "Hudson freeholders to study express bus service between Jersey City and Bayonne", The Jersey Journal, January 25, 2012. Accessed November 14, 2016.
^ "Service to Connect PA & NJ." EVA Air. Accessed February 29, 2016.
^ "Free Shuttle Service To/From JFK Airport Archived March 6, 2016, at the Wayback Machine.." China Airlines. September 15, 2015. Accessed February 29, 2016.
^ Hudson County Mileage by Municipality and Jurisdiction, New Jersey Department of Transportation, May 2010. Accessed July 18, 2014.
^ Haddon, Heather (May 12, 2012). "Greenway Clears Gritty Hurdle". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved December 8, 2012.
^ Reyes, Daniel (June 25, 2012). "New Bike Path Connects Jersey City and Newark". The Jersey Journal. Retrieved November 28, 2012.
^ "Easy Riders JC". Easy Riders JC. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
^ Wright, E. Assata (May 28, 2013). "Advancing the Morris Canal Greenway". Hudson Reporter. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ "Morris Canal Greenway Plan". Archived from the original on April 21, 2013. Retrieved December 7, 2012.
^ "Technical Memorandum 1: Data Findings, Opportunities & Constraints Mapping" (PDF). City of Jersey City Morris Canal Greenway Plan. RBA Group. July 16, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2013.
^ Nathan, Sarah (December 7, 2012). "Move over, drivers: Jersey City plans to add 54 miles of bike lanes". The Jersey Journal. Retrieved December 7, 2012.
^ Cruz, Vera (February 24, 2013). "New York Harbor and New Jersey meet Bike and pedestrian route planned to encourage recreation and transportation". Hudson Reporter. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
^ "The Harbor Ring". Transportation Alternatives. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
^ Goodyear, Sarah (October 12, 2012). "Could You One Day Ride Your Bike All the Way Around New York Harbor?". Atlantic Cities. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
^ Copeland, Dennis (March 18, 2013). "Two major new bike initiatives to enhance Jersey City's bike infrastructure". The Jersey Journal. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
^ "Exploration of Public Bike Share Program in Hudson County". Together North Jersey. Retrieved May 10, 2012.
[permanent dead link]
^ Benazil, Kathryn (December 17, 2013). "Ready to roll: Hoboken, Jersey City and Weehawken plan regional bike-sharing program". The Jersey Journal. Retrieved December 16, 2013.
^ Tangel, Andrew. "North Jersey Bike-Sharing Program Faces Delays; Program Won't Roll Out for at Least Several Months in Jersey City, Hoboken and Weehawken", The Wall Street Journal, June 20, 2014. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ "Car Ownership in U.S. Cities Data and Map". Governing. Retrieved May 4, 2018.
^ Sister Cities, Destination Jersey City. Accessed August 30, 2015.
^ "Position Paper on Sister State and Sister City Relations Between Australia and China", Australia-China Chamber of Commerce and Industry of New South Wales, dated November 14, 2001. Accessed August 30, 2015.
Bibliography
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Jersey City, New Jersey. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Jersey City. |
- Official website
- Destination Jersey City
- Jersey City List
- Jersey City Guide
 "Jersey City". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
"Jersey City". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.





